
Test the cause of many miscarriages, a deeply personal and often painful journey for many. This exploration delves into the multifaceted factors that contribute to pregnancy loss, examining everything from genetic predispositions to environmental influences and lifestyle choices. We’ll navigate the complexities of understanding miscarriage, providing a comprehensive overview and a look at the research currently available.
From common causes like chromosomal abnormalities to less frequently considered factors like uterine issues and infectious diseases, this in-depth look aims to shed light on the diverse range of potential triggers for miscarriage. We’ll also explore the role of maternal health conditions, lifestyle factors, and even medical procedures in the context of pregnancy loss. It’s important to remember that each case is unique and requires a nuanced understanding.
Understanding the Scope of Miscarriage
Miscarriage, the spontaneous loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week, is a deeply personal and often distressing experience. It’s a significant public health concern, affecting countless individuals and families worldwide. This exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of miscarriage, examining its different types, potential causes, and the diverse perspectives surrounding this sensitive topic.The experience of miscarriage varies greatly, and understanding its scope requires a multifaceted approach, considering the range of potential causes and the impact on individuals and society.
This exploration aims to provide a comprehensive overview, highlighting common and less common factors while acknowledging the importance of empathy and support.
Types and Stages of Miscarriage
Miscarriage can occur at various stages of pregnancy, with different symptoms and implications. Understanding these stages is crucial for appropriate medical management and emotional support. Early miscarriages typically happen before the 12th week, often without noticeable symptoms. Later miscarriages, while still emotionally challenging, often present with more discernible symptoms. The range of miscarriage experiences highlights the complex interplay of physical and emotional factors.
Frequencies and Prevalence of Miscarriage
Miscarriage is unfortunately more common than generally perceived. Estimates suggest that between 10-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. This statistic underscores the importance of understanding the factors contributing to these losses and the need for supportive care. Factors like maternal age, underlying health conditions, and environmental exposures can all influence the likelihood of miscarriage.
Potential Causes of Miscarriage
A wide range of factors can contribute to miscarriage, with some having established links and others still under investigation. Common causes include chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, hormonal imbalances in the mother, and certain infections. Less frequent but potentially significant causes include uterine abnormalities, autoimmune disorders, and exposure to certain medications or environmental toxins. This complexity underscores the need for a thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals to determine the specific cause in each case.
Medical and Non-Medical Perspectives
The experience of miscarriage is viewed differently from medical and non-medical perspectives. Medical professionals focus on diagnosing the cause and providing appropriate management. Non-medical perspectives emphasize the emotional and psychological toll on individuals and families. Both perspectives are crucial in understanding the full impact of miscarriage.
Comparison of Miscarriage Causes by Population Groups
| Population Group | Common Causes | Less Frequent but Significant Causes | Prevalence (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Women under 35 | Chromosomal abnormalities, hormonal imbalances | Uterine abnormalities, infections | 10-15% |
| Women 35-40 | Chromosomal abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, age-related factors | Autoimmune disorders, certain medications | 15-20% |
| Women over 40 | Chromosomal abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, age-related factors | Uterine abnormalities, underlying health conditions | 20-25% |
| Low socioeconomic status | Malnutrition, infections, exposure to toxins | Limited access to healthcare, stress | Potentially higher, due to increased risk factors |
The table above provides a general comparison. Exact prevalence figures vary significantly based on specific factors and access to healthcare.
Genetic Factors in Miscarriage
A significant portion of pregnancy losses are attributed to genetic abnormalities. Understanding these factors can offer valuable insights into the causes of miscarriage and potentially lead to better preventative measures or support for affected individuals. This exploration will delve into the most common genetic anomalies associated with pregnancy loss, their impact on fetal development, and the crucial role of chromosomal abnormalities in early pregnancy loss.Genetic material plays a critical role in fetal development.
Errors in this material, often occurring during the early stages of conception, can lead to abnormalities that are incompatible with a healthy pregnancy. These abnormalities can range from subtle changes to significant structural issues. The consequences of these errors can manifest in various ways, often resulting in spontaneous abortion or miscarriage.
Common Genetic Abnormalities Linked to Miscarriage
Genetic abnormalities are a leading cause of early pregnancy loss. These abnormalities frequently involve the number or structure of chromosomes, the thread-like structures carrying genetic information. Errors in chromosome number or structure can disrupt the normal process of cell division and development, leading to fetal abnormalities and ultimately, miscarriage.
Chromosomal Abnormalities in Early Pregnancy Loss
Chromosomal abnormalities are a frequent cause of early pregnancy loss. These abnormalities can arise from errors during the formation of sperm or eggs (meiosis) or during the early stages of embryo development. Errors in the number of chromosomes (aneuploidy) are among the most common.
Frequency of Specific Chromosomal Abnormalities
The frequency of specific chromosomal abnormalities varies. A comprehensive understanding of these frequencies can provide valuable insights into the causes of pregnancy loss.
| Chromosomal Abnormality | Frequency (Approximate) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) | 1 in 700 live births; higher frequency in pregnancies of women older than 35 | An extra copy of chromosome 21. Results in developmental delays and various physical and intellectual disabilities. Often leads to miscarriage in early pregnancy. |
| Trisomy 18 (Edwards Syndrome) | 1 in 6,000 live births; higher frequency in pregnancies of women older than 35 | An extra copy of chromosome 18. Associated with severe physical abnormalities and intellectual disability. Often leads to miscarriage in early pregnancy. |
| Trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome) | 1 in 10,000 live births; higher frequency in pregnancies of women older than 35 | An extra copy of chromosome 13. Associated with severe physical abnormalities and intellectual disability. Often leads to miscarriage in early pregnancy. |
| Monosomy X (Turner Syndrome) | 1 in 2,500 female births; often results in miscarriage | A missing X chromosome. Characterized by short stature, underdeveloped sexual characteristics, and other medical issues. Often leads to pregnancy loss in early pregnancy. |
| Other Structural Abnormalities | Variable | These include translocations, inversions, and deletions that affect the structure of chromosomes. These structural anomalies can interfere with normal development and increase the risk of miscarriage. |
The table above provides a general overview of the approximate frequencies of some common chromosomal abnormalities. It is important to note that these frequencies are estimates, and actual frequencies may vary based on factors such as maternal age, ethnicity, and other medical conditions.
Environmental Factors and Miscarriage: Test The Cause Of Many Miscarriages
Beyond genetic predispositions and lifestyle choices, environmental factors can play a significant role in miscarriage risk. Exposure to certain toxins and chemicals during pregnancy can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance and physiological processes essential for a healthy pregnancy. Understanding these environmental influences is crucial for proactive measures to protect reproductive health.
Potential Environmental Toxins and Their Effects
Environmental toxins can negatively impact pregnancy outcomes by interfering with the development and growth of the fetus. These toxins can disrupt cellular processes, leading to various abnormalities and potentially causing miscarriage. Exposure during different stages of pregnancy can have varying degrees of impact.
Environmental Factors Linked to Miscarriage Risk
Several environmental exposures have been linked to an increased risk of miscarriage. These exposures can vary in their potential impact depending on the duration and level of exposure. Factors like geographic location, occupation, and lifestyle choices can influence exposure levels.
- Air Pollution: Exposure to particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants in the air can potentially contribute to increased miscarriage risk. Studies have shown a correlation between high air pollution levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes. For instance, women living in areas with high traffic density or industrial activity might experience a higher incidence of miscarriages compared to those in cleaner environments.
- Heavy Metals: Exposure to heavy metals like lead, mercury, and cadmium can have detrimental effects on fetal development. These metals can disrupt various metabolic processes, potentially leading to chromosomal damage and increased miscarriage risk. Workers in certain industries or individuals residing near industrial facilities might be at higher risk.
- Pesticides and Herbicides: Exposure to pesticides and herbicides, frequently encountered in agricultural areas or through food consumption, can potentially affect pregnancy outcomes. These chemicals can disrupt hormone production and interfere with cell division, increasing the risk of miscarriage. For example, farmers or individuals with frequent exposure to pesticide-treated crops may be more susceptible.
- Industrial Chemicals: Exposure to certain industrial chemicals, including solvents and plasticizers, can be detrimental to pregnancy. These chemicals can have endocrine-disrupting effects, potentially impacting hormonal balance and increasing miscarriage risk. Individuals working in industries involving these chemicals may be at higher risk.
- Radiation: Exposure to ionizing radiation, such as from medical procedures or environmental sources, can potentially harm the developing fetus. This can lead to genetic mutations and an increased risk of miscarriage. Medical professionals and individuals exposed to high levels of radiation should be particularly cautious during pregnancy.
Comparing Effects of Different Environmental Exposures
The impact of different environmental exposures on miscarriage risk can vary. The severity of the effects depends on the type of toxin, the duration and level of exposure, and the specific stage of pregnancy during which exposure occurred.
- Heavy Metals vs. Pesticides: While both heavy metals and pesticides can have negative impacts on fetal development, the specific mechanisms and the severity of effects might differ. Heavy metals can directly damage cells, while pesticides might primarily disrupt hormonal pathways. The level of exposure is also crucial. A short-term, high-level exposure to pesticides may be more damaging than a long-term, low-level exposure to heavy metals.
- Air Pollution vs. Industrial Chemicals: Air pollution, encompassing various pollutants, may have a broader impact on pregnancy outcomes. Industrial chemicals, on the other hand, are often more concentrated in specific environments, potentially leading to more targeted effects on the developing fetus. The types of pollutants and the concentrations involved will differ in their impact on pregnancy outcomes.
Maternal Health Conditions and Miscarriage Risk
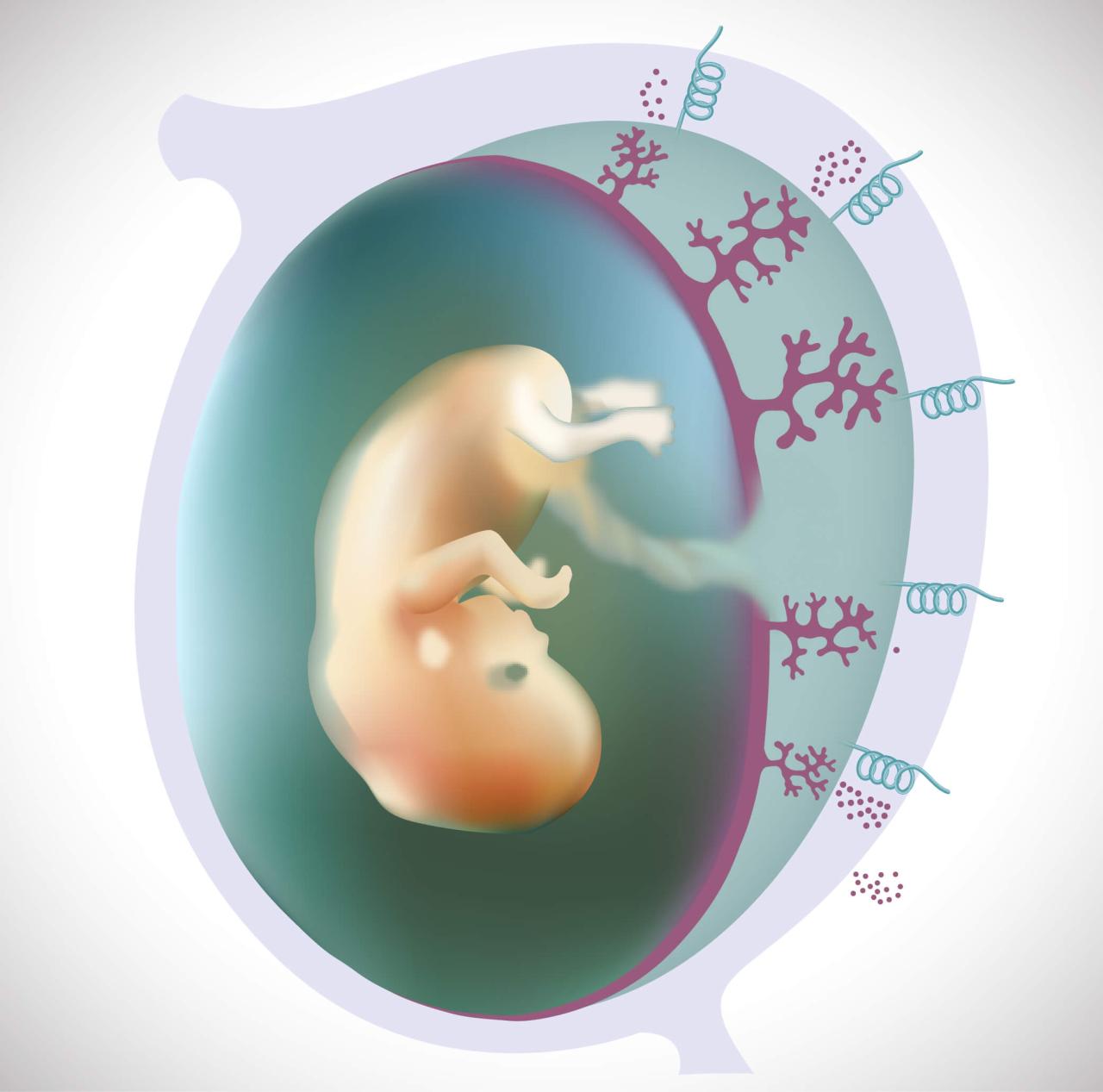
A significant contributor to miscarriage risk is the presence of underlying maternal health conditions. These conditions can impact the delicate balance required for a healthy pregnancy, potentially hindering the development of the fetus and increasing the likelihood of loss. Understanding these connections is crucial for both prevention and management of pregnancy complications.Chronic diseases, especially those affecting the cardiovascular, endocrine, or immune systems, can substantially increase the risk of miscarriage.
Factors such as uncontrolled blood sugar levels, autoimmune disorders, and certain infections can disrupt the intricate physiological processes necessary for successful fetal implantation and growth. This disruption can lead to various pregnancy complications, highlighting the importance of proactive management of pre-existing conditions.
Specific Maternal Health Conditions and Miscarriage Risk
Various maternal health conditions are associated with an increased risk of miscarriage. These conditions encompass a wide range of diseases and can have different levels of impact. Understanding these connections helps healthcare professionals tailor preventative measures and support strategies to individual patients.
Chronic Diseases and Pregnancy Success
Chronic diseases, when poorly managed, can significantly affect pregnancy success. Uncontrolled blood pressure, for instance, can restrict blood flow to the uterus, impacting fetal development and potentially leading to miscarriage. Similarly, uncontrolled diabetes can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance essential for a healthy pregnancy, increasing the likelihood of complications and loss.
Examples of Maternal Health Issues Affecting Pregnancy
Examples of maternal health issues that can affect pregnancy include thyroid disorders, where hormonal imbalances can disrupt fetal development. Kidney diseases can pose challenges by affecting the mother’s overall health and potentially impacting the pregnancy. Certain infections, like rubella, can be detrimental to the developing fetus. Furthermore, autoimmune disorders, such as lupus, can create an environment that is less supportive of a healthy pregnancy.
Trying to pinpoint the cause of so many miscarriages is a tough journey. One aspect that sometimes gets overlooked is the subtle differences between certain types of berries, like black raspberry and regular raspberry. Understanding the potential nuances in these seemingly similar fruits could provide valuable insights in future research on this complex issue. For example, exploring the specific properties of black raspberry vs raspberry might offer a new angle to the investigation into the causes of miscarriages, leading to more targeted and effective solutions.
This further highlights the importance of continuing research into this heartbreaking issue.
Table: Association Between Maternal Health Conditions and Increased Miscarriage Risk
| Maternal Health Condition | Potential Impact on Pregnancy | Increased Miscarriage Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Uncontrolled Hypertension | Restricted blood flow to the uterus, impacting fetal development. | High |
| Uncontrolled Diabetes | Disrupts hormonal balance, increasing risk of complications. | High |
| Autoimmune Diseases (e.g., Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis) | Creates an environment less supportive of a healthy pregnancy, potentially affecting placental function. | High |
| Thyroid Disorders | Hormonal imbalances can disrupt fetal development. | Moderate |
| Kidney Diseases | Affects overall health and can potentially impact pregnancy. | Moderate |
| Infections (e.g., Rubella) | Directly affects the developing fetus. | High |
| Blood Clotting Disorders | Increased risk of complications like preeclampsia. | Moderate to High |
Lifestyle Factors and Miscarriage

Lifestyle choices can significantly impact a woman’s chances of a successful pregnancy. While many factors contribute to miscarriage, understanding how daily habits affect the delicate process of fetal development is crucial for informed decision-making. This section explores the potential links between lifestyle factors and miscarriage risk.Lifestyle choices, including diet, exercise, stress levels, smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use, can all influence the health of both the mother and the developing fetus.
Factors like nutrition, physical activity, and emotional well-being play vital roles in maintaining a healthy pregnancy environment. Understanding the influence of these factors allows for proactive measures to mitigate potential risks.
Diet and Miscarriage Risk
Proper nutrition is essential for a healthy pregnancy. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients provides the building blocks for fetal growth and development. Inadequate intake of crucial vitamins and minerals, such as folic acid, iron, and calcium, can increase the risk of complications, including miscarriage. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods, unhealthy fats, and excessive sugar can negatively impact both maternal and fetal health.
Studies have shown a correlation between a balanced diet and improved pregnancy outcomes, highlighting the importance of mindful dietary choices.
Exercise and Pregnancy
Regular exercise is generally beneficial for overall health and can support a healthy pregnancy. However, extreme or strenuous exercise during pregnancy may pose risks. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate level of physical activity for individual circumstances. Maintaining a moderate exercise routine, tailored to the pregnant woman’s condition, can contribute to overall well-being. Excessive or poorly managed exercise could potentially lead to stress on the body, which might have negative consequences on the pregnancy.
Stress and Miscarriage
Stressful situations can have a negative impact on both physical and emotional well-being. Prolonged or intense stress during pregnancy can potentially affect hormone levels and increase the risk of complications. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as relaxation techniques, support systems, and adequate rest, is crucial for a healthy pregnancy. Chronic stress can negatively impact the immune system, potentially increasing the risk of miscarriage.
Smoking, Alcohol, and Drug Use
Smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use are strongly linked to increased miscarriage risk. The harmful effects of these substances on the developing fetus are well-documented. Nicotine, alcohol, and certain drugs can disrupt normal fetal development and increase the likelihood of complications. Stopping these habits significantly improves the chances of a healthy pregnancy. Avoiding these substances entirely is crucial for maintaining a healthy pregnancy environment.
Potential Lifestyle Factors and Miscarriage Risk
| Lifestyle Factor | Association with Miscarriage Risk |
|---|---|
| Poor Diet (lack of essential nutrients) | Increased risk |
| Extreme Exercise | Increased risk |
| Prolonged/Intense Stress | Increased risk |
| Smoking | Increased risk |
| Alcohol Consumption | Increased risk |
| Drug Use | Increased risk |
| Maintaining a Healthy Weight | Reduced risk |
| Balanced Diet | Reduced risk |
| Moderate Exercise | Reduced risk |
| Stress Management Techniques | Reduced risk |
Infectious Diseases and Miscarriage
Pregnancy is a delicate time, and the developing fetus is particularly vulnerable to infections. Many infections, while manageable for adults, can have devastating consequences for a developing embryo or fetus. Understanding the link between infectious diseases and miscarriage risk is crucial for both expectant parents and healthcare providers. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve pregnancy outcomes.Infectious agents can disrupt the delicate balance of the maternal-fetal environment.
This disruption can lead to a range of adverse effects, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune system activation. These processes can negatively impact the developing embryo or fetus, potentially leading to miscarriage.
The Impact of Infections on Pregnancy
Infections can interfere with various aspects of embryonic and fetal development. They can affect placental function, disrupt blood flow, and potentially cause structural abnormalities. Early-stage infections can have a significant impact, often leading to a complete loss of the pregnancy. Later-stage infections can cause significant growth retardation or developmental issues.
Specific Infectious Agents and Their Effects
Various infectious agents can pose a risk to pregnancy. A thorough understanding of these agents and their potential impact is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Viral Infections: Rubella, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and influenza are known to cause severe congenital anomalies and miscarriages. Rubella, in particular, is extremely dangerous during the first trimester. A woman who contracts rubella during this time has a high risk of miscarriage or birth defects. A significant percentage of pregnancies exposed to rubella in the first trimester end in miscarriage.
- Bacterial Infections: Certain bacterial infections, such as Listeria monocytogenes, can invade the placenta and directly affect the developing fetus. Listeria is a significant threat during pregnancy, with potential effects ranging from miscarriage to serious complications in the newborn.
- Parasitic Infections: Toxoplasmosis, a parasitic infection, can cross the placenta and cause severe damage to the developing fetus. Infections during early pregnancy can be particularly detrimental. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to mitigate the risk of fetal damage or loss.
Different Infections and Pregnancy Outcomes
The severity of the impact of an infection on pregnancy outcome can vary significantly. Factors like the type of infection, the stage of pregnancy, and the individual’s immune response all play a role. For example, a woman who contracts a mild infection in the third trimester may experience a healthy pregnancy outcome. Conversely, a woman who contracts a severe infection, like rubella, in the first trimester, has a higher chance of experiencing a miscarriage.
Maternal Immune Response
A mother’s immune response plays a crucial role in how her body reacts to infection during pregnancy. A strong immune response can help clear the infection but can also potentially cause harm to the developing fetus. Understanding the complexities of the maternal immune response during pregnancy is vital in developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Medical Procedures and Miscarriage Risk
Pregnancy is a delicate journey, and while many medical procedures are essential for overall health, some carry potential risks for pregnancy loss. Understanding these risks allows expectant parents to make informed decisions with their healthcare providers. This section explores the connection between medical procedures and miscarriage risk, examining potential influences on pregnancy outcomes and the risks associated with specific treatments during pregnancy.Medical procedures, even those deemed necessary, can sometimes introduce complications for a developing pregnancy.
Researchers are hard at work trying to pinpoint the root causes of many miscarriages. It’s a complex issue, and while physical factors are often investigated, mental health plays a surprising role. For example, the emotional toll of a heart attack can sometimes lead to depression, which in turn could potentially impact future reproductive health. Understanding the interplay between physical and mental well-being is crucial when trying to test the cause of many miscarriages.
Depression after heart attack can be a significant factor in the overall health picture, and this is something that needs to be considered as part of the research.
Factors like the timing of the procedure, the specific intervention, and the overall health of the mother and fetus all play a role in determining the potential impact on pregnancy outcomes. It is crucial to discuss any existing health conditions or concerns with your healthcare provider before undergoing any medical procedure, especially during pregnancy.
Potential Influence of Medical Interventions on Pregnancy Outcomes
Various medical interventions can potentially affect pregnancy outcomes. These interventions may involve medications, surgeries, or other procedures that could disrupt the delicate balance of the pregnancy environment. The impact depends on numerous factors, including the specific procedure, the gestational age of the pregnancy, and the overall health of the mother.
Risks Associated with Specific Medical Treatments During Pregnancy, Test the cause of many miscarriages
Certain medical treatments, even those deemed necessary, can pose risks to a developing pregnancy. These risks may range from increased likelihood of miscarriage to complications in the mother or fetus. Understanding these potential risks is crucial for informed decision-making and open communication with healthcare providers. For instance, some medications, especially those used to treat pre-existing conditions, might carry a higher risk of miscarriage if not carefully managed.
It’s important to remember that individual responses to medical treatments can vary greatly.
Comparison of Miscarriage Risk Associated with Various Medical Procedures
A definitive comparison of miscarriage risk associated with specific medical procedures is challenging due to the complexities of individual cases. Factors such as the mother’s pre-existing conditions, the specific procedure, and the timing of the procedure all contribute to the outcome. A definitive table quantifying these risks would not be accurate or reliable.Instead of a specific table, it’s essential to discuss each procedure with a healthcare professional to evaluate the risks and benefits, especially during pregnancy.
Open communication between patients and their doctors is paramount in making informed decisions about medical procedures during pregnancy. The focus should always be on the overall well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus.
Uterine and Cervical Factors in Miscarriage
Understanding the intricacies of miscarriage requires exploring various contributing factors. Uterine and cervical abnormalities frequently play a significant role in pregnancy loss. These issues can stem from pre-existing conditions or develop during pregnancy. A deeper dive into these factors provides critical insight into potential causes of miscarriage.Uterine abnormalities can disrupt the delicate balance necessary for a healthy pregnancy.
These issues can range from structural problems to hormonal imbalances that influence the uterine environment. These issues can manifest in various ways, affecting implantation, fetal development, and overall pregnancy success. Cervical insufficiency, on the other hand, is a condition where the cervix is unable to support the growing pregnancy. This weakness often leads to premature dilation and subsequent loss of the pregnancy.
Uterine Abnormalities
Uterine abnormalities encompass a range of structural and functional issues that can negatively impact pregnancy. These issues can be congenital (present from birth) or acquired (develop later in life). For instance, a bicornuate uterus, where the uterus has two horns instead of one, can hinder proper implantation and support of the developing fetus. Other structural problems, such as uterine septa (partitions within the uterus), can create uneven environments that hinder optimal pregnancy progression.
These issues may lead to repeated miscarriages. Sometimes, uterine polyps or fibroids can obstruct the uterine cavity or disrupt blood flow, making it difficult for the embryo to implant or for the pregnancy to sustain itself. Furthermore, certain uterine conditions can result in a distorted uterine shape, making it less receptive to implantation or unsuitable for the development of the fetus.
Researchers are diligently testing the cause of many miscarriages, a deeply concerning issue for expectant parents. This intricate investigation often involves examining a wide range of potential factors. Interestingly, recent breakthroughs in neurological treatments, like the deep brain stimulation that helped this man with parkinsons experienced improvement after trying deep brain stimulation , might offer some surprising parallels and insights into the complex mechanisms involved in reproductive health.
Further research in this area could potentially uncover new avenues for understanding and preventing miscarriages.
Cervical Insufficiency
Cervical insufficiency is a condition where the cervix is unable to remain closed throughout pregnancy. This often leads to premature dilation of the cervix, resulting in the expulsion of the pregnancy before it can fully develop. It is important to understand that cervical insufficiency is often associated with structural weaknesses of the cervix or an inability to maintain adequate tone.
A history of previous cervical trauma or surgeries may also contribute. The cervix’s inability to support the weight of the growing fetus, leading to early labor and miscarriage, is a key consequence. Cervical insufficiency is a significant concern, as it can be addressed through various preventative measures, including cerclage procedures, to protect the pregnancy. The condition is often diagnosed during routine prenatal check-ups or after a miscarriage.
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that can develop in the uterine wall. While they may not always cause miscarriage directly, their presence can create an environment that hinders pregnancy. For instance, fibroids can obstruct the uterine cavity, potentially affecting implantation or fetal development. In some cases, they can distort the uterine shape, compromising the pregnancy’s ability to sustain itself.
Furthermore, fibroids can influence blood flow, impacting the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the growing fetus. They may also increase the risk of preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes. The severity of the impact of uterine fibroids on pregnancy depends on the size, location, and number of fibroids present. The presence of fibroids and its impact on pregnancy requires careful consideration by medical professionals.
Multifactorial Causes of Miscarriage
Miscarriage, the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks, is a complex issue with various potential causes. While some miscarriages stem from a single, identifiable factor, many are the result of a combination of interwoven elements. Understanding these multifactorial causes is crucial for developing effective support and prevention strategies. The interaction of these factors can significantly impact the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.The interplay of different risk factors can dramatically increase the risk of miscarriage.
It’s not always a straightforward cause-and-effect relationship. For instance, a woman with a history of recurrent miscarriages might have a genetic predisposition, coupled with an unhealthy lifestyle, further compounded by a pre-existing medical condition. This combination of risk factors significantly elevates her risk of losing subsequent pregnancies. This complex interplay is not unique; it highlights the necessity for a holistic approach to understanding miscarriage.
Identifying and Understanding Combined Risk Factors
The complexity of miscarriage causes lies in the intricate interplay of multiple risk factors. It’s not simply about identifying one cause; often, a combination of factors contributes to the loss. This requires a comprehensive assessment, considering genetic predispositions, environmental influences, lifestyle choices, maternal health, and potentially even infectious diseases.
Examples of Multifactorial Miscarriage Cases
Consider a young woman with a family history of recurrent miscarriages (genetic predisposition). She smokes, experiences chronic stress (lifestyle factor), and has a mild thyroid condition (maternal health condition). The combination of these factors creates a significantly elevated risk compared to someone without any of these individual factors. This synergistic effect highlights how seemingly minor factors can accumulate and increase the risk.Another example could be a woman with a known uterine anomaly (structural uterine factor) who also experiences frequent infections (infectious disease).
These two factors, combined, could substantially increase the likelihood of pregnancy loss. This highlights the importance of considering all possible risk factors, not just isolated events. A detailed evaluation is necessary to understand the individual contributions and their combined impact.
The Complexity of Miscarriage Causation
Pinpointing the precise cause of a miscarriage can be challenging. The interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors is frequently involved. This complexity underscores the need for thorough investigation and a nuanced understanding of the specific circumstances surrounding each case. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution, and each case must be examined individually to identify the contributing factors.
The Combined Effect of Risk Factors
A simplified table can illustrate the cumulative effect of various risk factors:
| Risk Factor | Description | Potential Combined Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic predisposition | Inherited traits increasing miscarriage risk | Increases susceptibility to other risk factors |
| Environmental toxins | Exposure to harmful substances | Potentially interacts with genetic predisposition or lifestyle factors |
| Lifestyle choices | Smoking, alcohol, poor diet | Exacerbates other risk factors, potentially affecting fetal development |
| Maternal health conditions | Underlying medical issues | Compounds the risk of adverse outcomes |
The table above illustrates how the combined effect of multiple risk factors can increase the risk of miscarriage, highlighting the need for a holistic approach to understanding and addressing this complex issue. This table emphasizes the interconnected nature of the contributing factors, making it crucial to consider the overall picture rather than isolated elements.
Research and Current Understanding of Miscarriage
Navigating the complexities of pregnancy loss can be incredibly challenging, and understanding the reasons behind miscarriage is a critical aspect of this journey. While significant progress has been made in identifying potential causes, research continues to unravel the intricate interplay of factors contributing to this heartbreaking experience. This ongoing exploration aims to not only provide answers but also foster a deeper understanding of pregnancy itself.Current research endeavors are focused on identifying the root causes of miscarriage and developing strategies for prevention and treatment.
The intricate nature of the process requires multifaceted approaches, involving genetic testing, environmental analyses, and meticulous examination of maternal health. Researchers are diligently exploring the biological pathways that lead to pregnancy loss, with a focus on improving outcomes for future pregnancies.
Summary of Current Research Efforts
Research into miscarriage encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including genetics, reproductive endocrinology, and maternal-fetal medicine. Researchers are meticulously analyzing the intricate biological processes involved in successful implantation and early embryonic development, seeking to identify markers or factors that predict or cause pregnancy loss. This often involves comparing the biological profiles of pregnancies that progress to term versus those that result in miscarriage.
Progress in Understanding Causes of Miscarriage
Significant progress has been made in understanding the genetic factors contributing to miscarriage. Chromosomal abnormalities in the developing embryo are a well-recognized cause, and advancements in genetic testing are enabling the identification of these abnormalities earlier in pregnancy. Research also increasingly investigates the role of environmental exposures, maternal health conditions, and lifestyle choices in the risk of miscarriage.
Evolving Understanding of Pregnancy Loss
The understanding of pregnancy loss is continually evolving. Early research often focused on isolated factors, but modern research recognizes the interplay of various factors. A woman’s overall health, including her lifestyle, stress levels, and exposure to toxins, is increasingly recognized as contributing to miscarriage risk. This holistic approach acknowledges that the complex processes of pregnancy are not solely determined by one single cause.
Current Research Methodologies in Investigating Miscarriage Causes
Researchers employ a variety of methodologies to investigate miscarriage causes. Advanced genetic testing techniques, including karyotyping and chromosomal microarray analysis, are crucial in identifying chromosomal abnormalities. Epidemiological studies, analyzing large datasets of pregnancies, are used to identify potential environmental risk factors. Observational studies tracking maternal health conditions and lifestyle factors throughout pregnancy are essential in understanding their potential contribution.
Animal models and in vitro studies are also used to investigate the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in early pregnancy development.
For instance, a recent study using a large cohort of pregnant women found a correlation between exposure to certain environmental pollutants and an increased risk of miscarriage. This suggests a crucial role for environmental factors in the complex tapestry of pregnancy loss.
End of Discussion
Ultimately, understanding the causes of miscarriage is crucial for both providing support to those affected and advancing research. While many factors contribute to pregnancy loss, this examination highlights the intricate interplay of genetic, environmental, and personal elements. The research continues, and ongoing studies promise to uncover even more about this complex issue, offering hope for improved outcomes in the future.
