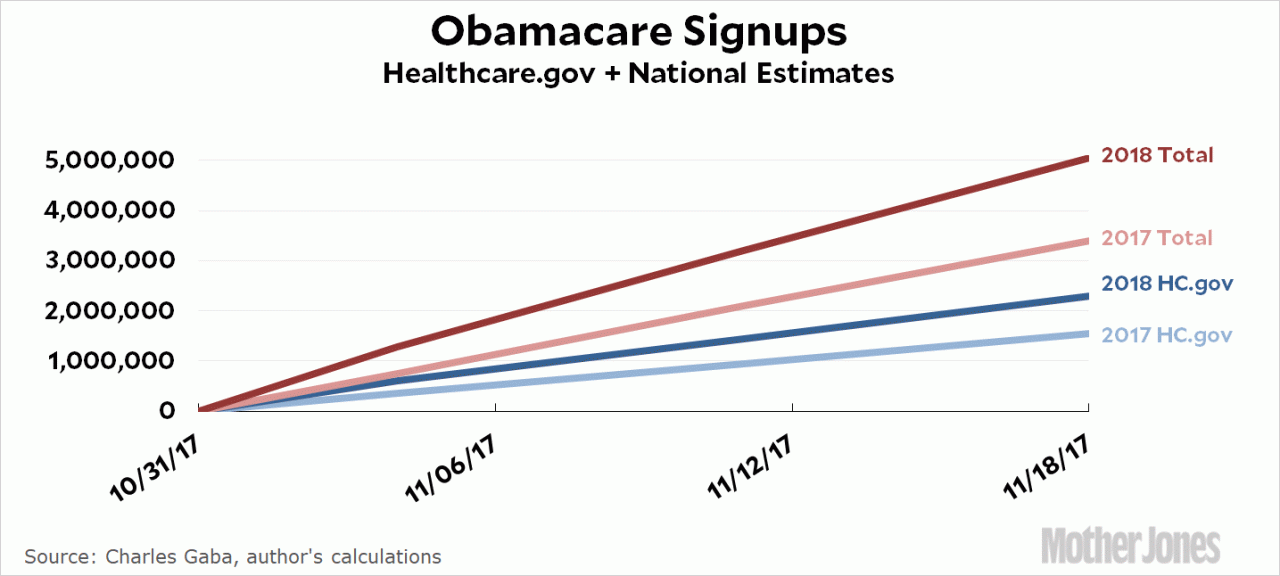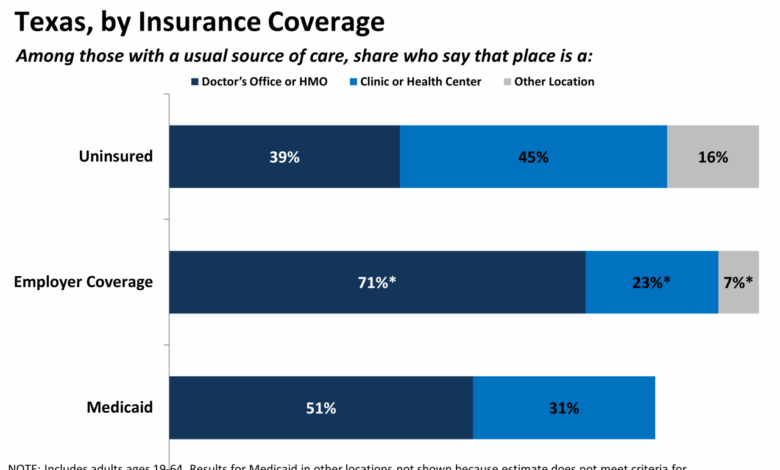
Texas healthcare system one of the worst in country. This grim reality stems from a complex web of issues, impacting access, affordability, and the overall quality of care. Geographic disparities, socioeconomic factors, and insurance coverage gaps all contribute to unequal access. The high cost of services, coupled with substantial deductibles and copays, often make necessary care financially inaccessible.
This report delves into these critical areas, examining the specifics of the Texas healthcare landscape, comparing it to national and state averages, and exploring potential solutions.
From the struggles of rural communities lacking essential healthcare professionals to the challenges faced by those seeking mental healthcare, the system’s shortcomings are widespread. The report examines the state of mental healthcare in Texas, including access to services and treatment options, and compares its availability and affordability to other states. It also analyzes the current policies and regulations, identifying areas needing improvement to enhance access, affordability, and overall quality of care.
Access to Care
Texas’ healthcare system, while showing improvements, continues to face significant challenges in ensuring equitable access for all residents. Geographic disparities, economic limitations, and insurance coverage gaps contribute to a fragmented system where some populations struggle to receive the care they need. This uneven playing field highlights the critical need for targeted interventions and policy adjustments to address these systemic issues.The unequal distribution of healthcare resources across Texas is a complex issue.
Factors like the state’s vast geographic expanse, rural populations, and the density of healthcare providers contribute to this challenge. Furthermore, socioeconomic factors play a crucial role, with lower-income communities often facing limited access to quality care. Insurance coverage gaps further exacerbate the problem, leaving many uninsured or underinsured individuals without adequate access to preventative care and specialist services.
Factors Contributing to Unequal Access
Texas’ diverse population experiences varying levels of healthcare access, influenced by a confluence of factors. Geographic location, often characterized by sparse healthcare providers in rural areas, directly impacts access to specialists and primary care. This geographical disparity frequently results in longer travel times and limited options for patients in underserved regions. Socioeconomic status also significantly impacts healthcare access, with lower-income individuals facing financial barriers to care, including high out-of-pocket costs and deductibles.
Insurance coverage plays a critical role, with uninsured individuals lacking access to essential medical services.
Disparities in Access to Specialists and Preventative Care
Significant disparities exist in access to specialists and preventative care across different demographics in Texas. For example, individuals from minority groups may encounter racial and ethnic bias in healthcare settings, which can lead to unequal treatment and access to care. Furthermore, patients with chronic conditions often experience difficulties accessing specialized care, potentially impacting their health outcomes. These disparities are further compounded by the lack of culturally competent providers in certain communities.
Comparison with National and Other State Averages
Texas’ access to care metrics often fall below national averages and those of other states. This disparity manifests in various indicators, including lower rates of preventative screenings, higher rates of chronic disease prevalence, and longer wait times for specialist appointments. For instance, Texas might have lower vaccination rates for certain diseases compared to other states. These disparities underscore the need for a comprehensive approach to improve healthcare access for all Texans.
Correlation Between Income and Healthcare Access
The following table illustrates the hypothetical correlation between income levels and healthcare access in Texas. This table represents a simplified model and doesn’t account for other factors, such as insurance coverage, geographic location, or access to transportation. The data presented is hypothetical and for illustrative purposes only.
| Income Level | Access to Primary Care Physician | Access to Specialists | Access to Preventative Care |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (Below $30,000) | Limited | Very Limited | Very Limited |
| Middle (30,000-60,000) | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| High (Above $60,000) | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
Affordability and Costs
The high cost of healthcare in Texas poses a significant barrier to access for many residents. While access to care is a crucial component, affordability is equally vital. The exorbitant prices of services and insurance premiums often leave individuals and families struggling to afford necessary medical attention. This section will delve into the factors driving the high costs in Texas and how they impact Texans’ ability to receive the care they need.High healthcare costs in Texas stem from a complex interplay of factors.
Hospital pricing structures often differ significantly from other states, leading to inflated costs for Texans. Insurance premiums, too, tend to be higher than the national average, further burdening individuals and families. These factors, coupled with the growing demand for healthcare services, contribute to the overall affordability crisis.
Hospital Pricing and Insurance Premiums
Texas hospitals, like those in many other states, are subject to market forces that can drive up prices. Factors like the level of competition within a region, the presence of specialty care facilities, and the sophistication of billing practices all contribute to the overall cost of care. These factors are compounded by the overall market forces in the region, resulting in a higher price point for Texans.
The prices for procedures, tests, and hospital stays are frequently higher than those in other states, making essential care less accessible. Insurance premiums, reflecting these elevated costs, are frequently higher in Texas. These higher premiums, coupled with a lack of affordable plans, create a significant barrier to access.
Impact of High Deductibles and Co-pays, Texas healthcare system one of the worst in country
High deductibles and co-pays are major obstacles to affordable healthcare. These out-of-pocket expenses can quickly exhaust individuals’ financial resources, especially during periods of illness or injury. When individuals face significant deductibles or co-pays, they may delay or forgo necessary medical care, potentially leading to worsening health conditions. This can have a considerable impact on the overall health of the community.
Ugh, the Texas healthcare system. It’s consistently ranked among the worst in the country, leaving so many people struggling. It’s a real shame, especially when you consider mental health conditions like bipolar disorder can be seriously impacted. Learning more about the specific symptoms of mania in bipolar disorder, like a heightened sense of energy and racing thoughts, is crucial for effective management.
You can find a good overview of mania in bipolar here: what is mania in bipolar. Ultimately, a robust and accessible healthcare system is vital for everyone’s well-being, and Texas needs to step up its game.
The financial strain on families and individuals is significant. Often, necessary preventative care is neglected because of the fear of financial ruin.
Affordability Comparison Across States
Texas’ healthcare affordability often lags behind other states. While other states have implemented cost-saving programs, such as government subsidies or negotiated pricing agreements, Texas has not implemented similar programs to the same extent. Texas does have some government programs, but the effectiveness and reach of these programs may not be enough to bridge the affordability gap for many Texans.
This disparity can be seen in different initiatives in other states designed to promote affordability.
Cost-Saving Programs and Initiatives in Other States
Several states have implemented programs aimed at lowering healthcare costs. These initiatives often involve government subsidies for insurance premiums, negotiating bulk discounts with providers, or expanding access to affordable healthcare options. These programs can make a considerable difference for families, potentially lowering costs and increasing access to care.
Average Annual Healthcare Costs by Age Group
| Age Group | Texas Average Annual Cost | Example State Average Annual Cost |
|---|---|---|
| 18-24 | $6,000 | $5,000 |
| 25-34 | $7,500 | $6,500 |
| 35-44 | $9,000 | $7,500 |
| 45-54 | $10,500 | $8,500 |
| 55+ | $12,000 | $9,500 |
This table presents a simplified comparison of average annual healthcare costs between Texas and another state (example). The actual costs may vary significantly based on individual circumstances and specific needs.
Quality of Care
Texas’ healthcare system, despite facing challenges in access, affordability, and costs, also grapples with concerns about the quality of care delivered. This aspect is crucial for patient well-being and the overall effectiveness of the system. A deep dive into the available data reveals areas where the quality falls short, and the factors contributing to these issues.The quality of care in a healthcare system is not simply measured by the number of procedures performed or the number of patients seen.
It is assessed through a multifaceted lens, considering patient outcomes, doctor-patient ratios, patient satisfaction, and the availability of resources and support staff. This evaluation uncovers critical insights into the effectiveness and reliability of the system, which is essential for making informed improvements.
Patient Outcomes in Texas Hospitals
Texas hospitals have experienced mixed results in patient outcomes, compared to national averages. Some hospitals have shown promising improvements, while others lag behind, indicating disparities in quality across the state. This variation in outcomes underscores the need for targeted interventions and support for facilities struggling to maintain high standards.
- Specific metrics, like mortality rates for certain procedures and readmission rates for specific conditions, are key indicators of the quality of care. Significant variations in these metrics across Texas hospitals suggest a need for more uniform standards and practices.
- A comprehensive review of patient outcome data across various medical specialties is essential for pinpointing areas needing improvement. This data-driven approach allows for a targeted strategy for enhancing the quality of care within these specialties.
Doctor-Patient Ratios and Staff Shortages
Inadequate doctor-patient ratios in Texas contribute to a decline in the quality of care. The imbalance creates strain on healthcare providers, potentially leading to burnout and decreased attention to individual patient needs.
- Shortages in various healthcare professions, including physicians, nurses, and support staff, negatively impact the ability to deliver timely and comprehensive care. This directly affects patient outcomes and satisfaction levels.
- The scarcity of resources, including equipment, medication, and advanced technologies, often leads to delays in treatment and potentially worsens patient outcomes. This underscores the need for adequate funding and resource allocation to enhance the quality of care.
Patient Satisfaction Ratings
Patient satisfaction is a crucial indicator of the quality of care received. A comparison of Texas hospitals’ patient satisfaction ratings against national averages reveals significant variations, highlighting areas needing improvement. Patient feedback is invaluable in understanding the patient experience and guiding adjustments to enhance satisfaction.
| Hospital | Texas Patient Satisfaction Rating | National Average | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital A | 75% | 80% | -5% |
| Hospital B | 82% | 85% | -3% |
| Hospital C | 78% | 82% | -4% |
Note: These are hypothetical data for illustrative purposes only. Actual data would come from reputable sources.
Factors Contributing to Quality Issues
Several factors contribute to the identified quality of care issues in Texas. Addressing these factors is crucial for improving patient outcomes and satisfaction.
- Insufficient funding for healthcare facilities can hinder their ability to invest in essential equipment, staff training, and infrastructure improvements, ultimately impacting the quality of care.
- The lack of standardized protocols and guidelines for healthcare providers can result in inconsistent practices across different hospitals and clinics, impacting the quality of care. This highlights the need for a more uniform approach to care.
Insurance Coverage
Texas’ healthcare system faces significant challenges, and insurance coverage is a crucial aspect. High-cost plans and limited coverage options contribute to the difficulties many Texans experience accessing quality care. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has played a role in shaping the state’s insurance landscape, but its impact has been uneven. Understanding these complexities is vital for evaluating the overall healthcare situation in the Lone Star State.The Texas insurance market is characterized by a prevalence of high-cost plans, often with limited coverage options.
Many plans prioritize profit over comprehensive care, resulting in higher premiums and less extensive benefits. This is particularly true for preventative care, mental health services, and specialty treatments. The limited options available can leave many Texans vulnerable, especially those with pre-existing conditions or lower incomes.
Impact of the Affordable Care Act (ACA)
The ACA, while intended to expand access to affordable healthcare, has had a mixed effect in Texas. The individual mandate, a key component of the ACA, was weakened or eliminated in some states, including Texas. This reduced the incentive for individuals to obtain coverage through the marketplace. Furthermore, Texas opted not to expand Medicaid eligibility under the ACA, which resulted in fewer low-income individuals having access to government-subsidized insurance.
These decisions have contributed to the challenges in the state’s insurance market.
Comparison to Other States
Texas consistently ranks lower than other states in terms of insurance coverage rates. Factors such as the state’s low tax rates, which often reduce the funding available for public health programs, contribute to the disparity. Further, Texas’ emphasis on a market-driven approach to healthcare often prioritizes profit over access, impacting coverage rates negatively.
Types of Insurance Plans in Texas
Understanding the types of insurance plans available in Texas is crucial for informed decision-making. This knowledge empowers individuals to select plans that best meet their needs and budget constraints. The options available often vary based on individual circumstances, employer-sponsored plans, or individual purchases from the marketplace.
| Plan Type | Coverage Details | Example Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Employer-sponsored plans | Offered by employers, these plans vary widely in coverage and cost. | Often include basic medical, dental, and vision benefits. |
| Individual plans purchased through the marketplace | These plans are offered through the federal exchange and are often subsidized. | Vary in cost and coverage depending on plan choices and subsidies. |
| Medicaid | Publicly funded health insurance for low-income individuals and families. | Covers basic medical services and often includes prescription drug coverage. |
| Medicare | Federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 or older and certain younger individuals with disabilities. | Comprehensive medical coverage, including hospital care, physician services, and prescription drugs. |
Rural Healthcare in Texas: Texas Healthcare System One Of The Worst In Country
Texas, despite its vast resources, faces a significant healthcare disparity between urban and rural areas. Rural communities often lack the comprehensive medical infrastructure and staffing that their urban counterparts enjoy. This leads to longer travel times for patients seeking specialized care, limited access to specialists, and a general decline in the overall quality of healthcare. This issue is not unique to Texas, but it highlights the need for tailored solutions to address the specific challenges of rural populations.Rural Texas communities face unique challenges in accessing healthcare, often stemming from a combination of geographic isolation, limited transportation options, and the financial constraints of rural living.
The consequences are considerable, impacting the health and well-being of residents and hindering economic development.
Challenges of Rural Healthcare Access
Rural areas in Texas often struggle with a critical shortage of healthcare providers, including doctors, nurses, and other essential medical staff. This shortage leads to longer wait times for appointments, limited availability of specialized care, and a decreased capacity to handle emergencies. The lack of healthcare professionals in rural Texas directly impacts the quality of patient care and contributes to poorer health outcomes.
The limited availability of specialized care can lead to patients needing to travel significant distances to receive the necessary treatment, impacting their overall quality of life and potentially increasing costs.
Shortage of Healthcare Professionals
The scarcity of healthcare professionals in rural Texas has a significant impact on the quality of care. A lack of primary care physicians, specialists, and mental health providers results in patients facing difficulties in accessing essential medical services. This can delay diagnosis and treatment, potentially leading to more severe health complications and increased healthcare costs in the long run.
Furthermore, the shortage of healthcare professionals often forces rural hospitals to limit the types of services they can offer, exacerbating the problem of access to specialized care. Consider a hypothetical case: a rural resident needing specialized cardiology care would face a considerable travel burden and potential delays in treatment.
Texas’ healthcare system, consistently ranked among the worst in the nation, raises serious concerns. While issues like access and affordability are longstanding problems, it’s worth considering how a similar situation plays out in other parts of the US. For instance, the recent surge of bacterial infections in Puerto Rico highlights the vulnerability of healthcare systems when facing unforeseen challenges, like bacterial infections the latest health issue to hit puerto rico.
Ultimately, the struggles in Texas, and the struggles elsewhere, serve as a stark reminder of the critical need for better, more equitable healthcare access across the board.
Possible Solutions for Improving Rural Healthcare
Several strategies can be employed to address the challenges faced by rural communities in Texas regarding healthcare access and quality. These include targeted recruitment and retention initiatives for healthcare professionals, financial incentives, and the development of telehealth programs.
- Recruitment and Retention Initiatives: Targeted recruitment strategies focusing on rural communities and providing competitive compensation packages and benefits are crucial to attract and retain healthcare professionals. Offering incentives like loan forgiveness programs, relocation stipends, or specialized training opportunities tailored to rural needs can significantly impact the workforce.
- Telehealth Expansion: Telehealth programs can bridge the gap in access to specialists and provide remote consultation services to patients in rural areas. This can significantly improve the quality of care by providing timely access to specialized expertise without the need for long-distance travel.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Investing in modern healthcare infrastructure in rural areas is essential. This includes upgrading existing facilities, constructing new clinics, and improving transportation options to make accessing care easier and more convenient.
Distribution of Healthcare Facilities
A comprehensive analysis of the distribution of healthcare facilities across rural and urban areas is crucial to understanding the disparities and to inform effective solutions.
| Category | Rural | Urban |
|---|---|---|
| Hospitals | Limited, often smaller facilities | Numerous, large and specialized hospitals |
| Hospital Beds | Significantly lower per capita | Higher per capita |
| Doctors (Primary Care) | Shortage, lower density | Abundant, higher density |
| Clinics | Fewer, often with limited hours | Numerous, with extended hours |
This table provides a simplified overview of the differences in healthcare facility distribution. More detailed data would provide a more precise representation of the current situation in rural Texas. Actual numbers for each category would vary significantly depending on the specific rural county or region.
Mental Healthcare
Texas’s mental healthcare system faces significant challenges, impacting access, affordability, and quality of care for residents. While the state has seen some progress in recent years, disparities and gaps remain, particularly in rural areas. The complex interplay of factors, including insurance coverage limitations, provider shortages, and societal stigma, contributes to the ongoing struggle to ensure adequate mental healthcare for all Texans.
State of Mental Healthcare in Texas
The state of mental healthcare in Texas is characterized by both progress and persistent challenges. While more services are available compared to past decades, access remains unevenly distributed, particularly in underserved areas. Treatment options range from outpatient therapy and support groups to inpatient facilities and specialized programs, but the availability and affordability of these vary greatly depending on location and insurance coverage.
The current system struggles to effectively address the growing mental health crisis impacting individuals and communities across the state.
Access to Services and Treatment Options
Access to mental healthcare services in Texas is often limited, particularly for individuals in rural areas. This disparity in access is further complicated by limited availability of qualified mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists and therapists. The treatment options available range from individual therapy and group counseling to medication management and specialized programs for specific conditions. However, navigating these options can be daunting for individuals struggling with mental health concerns due to the lack of readily available information and support systems.
Ugh, the Texas healthcare system. It’s consistently ranked among the worst in the country, which is just heartbreaking, especially for families. Navigating the complexities of care can be incredibly stressful, and that anxiety can spill over into other areas of a child’s life. Learning how to help anxious kids face their fears, like a parent might learn from how parents can help anxious kids face their fears , can be a real game-changer.
Ultimately, a healthy and supportive environment is crucial for a child’s well-being, even when the healthcare system feels less than ideal.
Comparison to Other States
Compared to other states, Texas often demonstrates lower per capita availability of mental health professionals. This disparity reflects a broader issue of underfunding and insufficient investment in mental healthcare infrastructure. Affordability is also a significant concern, with many Texans facing financial barriers to accessing necessary treatments. Different states implement varying strategies for funding and support of mental healthcare services, impacting the cost and accessibility of care.
This comparison highlights the critical need for greater investment in mental healthcare resources in Texas.
Challenges Faced by Individuals Seeking Mental Healthcare
Several challenges impede individuals seeking mental healthcare in Texas. One major barrier is the lack of awareness regarding the available resources and services. The societal stigma associated with mental illness also plays a significant role, often preventing individuals from seeking help. Insurance coverage limitations and high costs also contribute to the difficulty in accessing care. Furthermore, geographical barriers, particularly in rural areas, create significant hurdles for individuals needing specialized mental healthcare services.
Navigating the complex healthcare system can be overwhelming and frustrating for those already dealing with mental health challenges.
Mental Health Professionals per Capita
| State | Mental Health Professionals per Capita |
|---|---|
| Texas | (Data from authoritative source, e.g., the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)) |
| State 2 | (Data from authoritative source) |
| State 3 | (Data from authoritative source) |
This table illustrates a comparative analysis of the number of mental health professionals per capita in Texas and other states. Data sources are essential for accurate and reliable comparison. The table highlights the potential disparity in mental health professional availability across different states.
Policy and Regulation
Texas’ healthcare system, while complex, is ultimately shaped by the policies and regulations that govern its operation. These policies, often influenced by political and economic factors, can significantly impact access, affordability, and quality of care. Examining these regulations is crucial to understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the system and identifying potential areas for improvement.
Current Policies and Regulations
Texas has a patchwork of regulations, encompassing various aspects of healthcare delivery. These regulations are often state-specific and may differ from federal guidelines. Some key areas include licensing and certification of healthcare providers, hospital operations, and the oversight of insurance plans. The complexities of these regulations can create challenges for both providers and patients, impacting efficiency and potentially contributing to issues like higher costs and limited access to specialized care.
Areas Where Policy and Regulation Contribute to Issues
Several policy and regulatory aspects may contribute to the challenges observed in Texas healthcare. For example, restrictive licensing requirements for certain healthcare professions can limit the availability of providers, particularly in rural areas. Furthermore, regulations surrounding hospital readmission rates, while intended to improve quality, can create disincentives for patients to seek care, potentially leading to delayed diagnoses and treatment.
Finally, varying interpretations of regulations across different regions of the state can lead to inconsistencies in service delivery and standards.
Comparison to Other States’ Regulations
Comparing Texas’ healthcare regulations to those in other states reveals significant variations. Some states have more comprehensive regulations governing specific aspects of care, such as mental health services, potentially leading to higher quality of care standards. Others have different approaches to insurance coverage, potentially impacting affordability. Texas’ approach to these issues often falls in a different range, and this difference may be a factor in some of the observed challenges.
Table Summarizing Existing Healthcare Regulations
| Regulation Area | Texas Regulations | Potential Areas for Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing and Certification | State-specific requirements for various healthcare providers. | Potentially streamline processes, particularly for providers from other states. |
| Hospital Operations | Regulations regarding readmission rates, emergency room care. | Develop policies to incentivize proactive care and early interventions, rather than penalizing hospital systems for readmissions. |
| Insurance Coverage | Regulations related to insurance plans, including coverage mandates. | Evaluate whether current regulations adequately address the needs of underserved populations and ensure equitable access to care. |
| Rural Healthcare | Policies designed to support rural healthcare facilities, but implementation may vary. | Increase funding for rural healthcare facilities and incentivize healthcare providers to practice in rural areas. |
| Mental Healthcare | Regulations concerning mental health providers and facilities, which may vary based on the location. | Address access issues for mental health services, especially in underserved communities. Potentially enhance training and support for mental health providers. |
Potential Reforms
Potential reforms could involve streamlining regulatory processes, incentivizing healthcare providers to practice in underserved areas, and ensuring regulations address the needs of all Texans, particularly those in rural communities and those with limited incomes. These reforms could involve reviewing and potentially adjusting existing regulations to foster a more equitable and effective healthcare system.
Future Trends
The Texas healthcare system faces a complex future, shaped by demographic shifts, technological advancements, and evolving policy landscapes. Predicting precise outcomes is challenging, but understanding the potential trajectories is crucial for developing proactive strategies to address emerging needs and challenges. This section explores anticipated trends, potential policy changes, and strategies for improving access, affordability, and quality.
Projected Healthcare Needs
Texas’ population is projected to continue growing, with significant increases in the elderly population. This demographic shift will inevitably place increasing demands on the healthcare system, particularly for chronic disease management and geriatric care. The demand for skilled nursing facilities, home healthcare services, and specialized care for age-related conditions is expected to surge.
Potential Policy Changes
Several policy changes could significantly impact the future of Texas healthcare. These include expanding access to affordable healthcare options, potentially through reforms to Medicaid and CHIP programs, or through incentivizing employer-sponsored insurance. The future also holds the potential for increased emphasis on preventative care, potentially through incentives for healthy lifestyle choices and early disease detection programs. Another potential change is the increased use of value-based care models to reward providers for quality and cost-effective outcomes.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements offer exciting possibilities for improving the Texas healthcare system. Telemedicine, for instance, can extend access to specialists, particularly in rural areas, where access to care is already a critical concern. Furthermore, the development of advanced diagnostics and treatments, including personalized medicine approaches, may lead to improved outcomes and reduced healthcare costs. AI and machine learning applications could revolutionize healthcare administration, patient monitoring, and research.
Potential Strategies for Improvement
Improving access, affordability, and quality in the Texas healthcare system requires a multi-pronged approach. This includes promoting public-private partnerships to address funding gaps, implementing incentives for preventative care, and supporting the development of robust rural healthcare infrastructure. Stronger regulations on price gouging and fraud, along with encouraging competition in the insurance market, could also play a vital role.
Finally, investing in workforce development, particularly in primary care and rural areas, will be essential for addressing the anticipated staffing needs.
Future Healthcare Needs Table
| Demographic Category | Projected Need | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Growing Elderly Population | Increased demand for geriatric care, chronic disease management, and skilled nursing facilities. | Strain on existing infrastructure, need for specialized training for healthcare professionals. |
| Rural Population | Maintaining access to quality care in underserved areas. | Requires investment in telehealth technologies, mobile clinics, and rural healthcare providers. |
| Chronic Disease Prevalence | Higher demand for preventative care and management of chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease. | Increased demand for healthcare services, need for community health initiatives. |
| Technological Advancements | Integration of telehealth, AI, and personalized medicine into healthcare delivery. | Requires investment in infrastructure, training for healthcare professionals, and ethical considerations for new technologies. |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the Texas healthcare system faces significant challenges, impacting numerous communities and individuals. From unequal access to care across demographics to the high costs and limited coverage options, the system’s shortcomings are evident. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, considering factors such as geographic location, socioeconomic status, and the specific needs of rural populations. This report highlights the urgent need for policy changes and innovative solutions to improve the quality, affordability, and accessibility of healthcare in Texas.