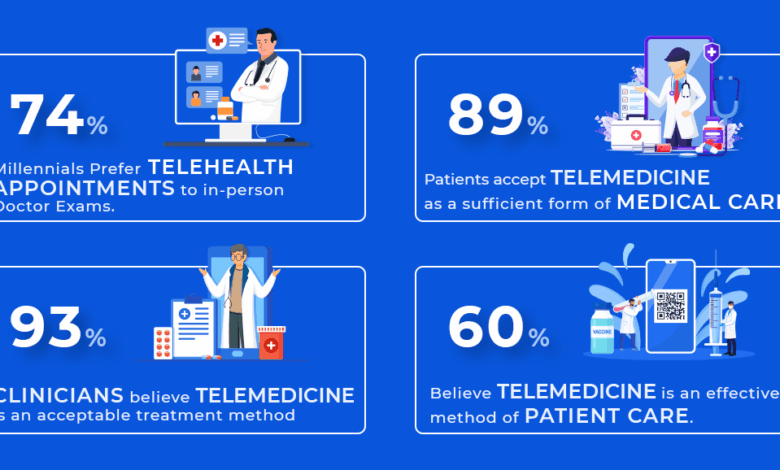
The pros and cons of telemental health services are a complex issue with far-reaching implications. This exploration dives deep into the various advantages and disadvantages, examining everything from accessibility and convenience to the ethical considerations and future trends. From video conferencing to messaging, we’ll uncover the different modalities, historical context, and key differences between in-person and virtual therapy.
This in-depth look at telemental health services will cover various facets, including its impact on diverse populations, cost-effectiveness, and the technological infrastructure needed for success. We’ll also explore patient experience and satisfaction, delving into the potential challenges and offering solutions to enhance the overall quality of virtual care.
Introduction to Telemental Health Services
Telemental health services are rapidly evolving as a crucial component of mental healthcare delivery. These services leverage technology to provide mental health support and counseling remotely, bridging geographical barriers and expanding access to care. This approach offers significant benefits for individuals who may face challenges accessing traditional in-person services, particularly those in rural areas or with mobility limitations.Telemental health encompasses a wide range of modalities, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
It’s important to understand the various ways these services are delivered to fully appreciate their impact on the mental health landscape.
Defining Telemental Health Services
Telemental health services are defined as the delivery of mental health services using technology. This can include a wide array of communication methods, from video conferencing and phone calls to secure messaging platforms. The core principle is to use technology to connect with individuals in a way that facilitates therapeutic interaction and addresses their mental health needs.
Modalities of Telemental Health
Different modalities of telemental health services cater to diverse needs and preferences.
- Video conferencing
- Video conferencing platforms, such as Zoom or Skype, allow for real-time visual interaction between the therapist and client. This modality enables the therapist to observe nonverbal cues, which can enhance understanding and rapport-building.
- Phone calls
- Phone calls provide an accessible alternative for individuals who may not have access to video conferencing or prefer a more private setting. They remain a valuable tool for crisis intervention and brief support.
- Secure messaging
- Secure messaging platforms can facilitate communication between the therapist and client for scheduling, sending reminders, or exchanging brief messages between sessions. They are often used as an adjunct to other modalities.
Historical Context of Telemental Health Development
The evolution of telemental health reflects advancements in technology and growing recognition of the need for accessible mental healthcare. Early applications focused primarily on providing brief counseling or crisis intervention, using simple phone calls. As technology progressed, video conferencing and secure messaging platforms became increasingly sophisticated, enabling more comprehensive and nuanced therapeutic interactions.
Key Differences Between In-Person and Telemental Health Sessions
The following table Artikels some of the key distinctions between in-person and telemental health sessions.
| Characteristic | In-Person Session | Telemental Health Session |
|---|---|---|
| Location | In a physical office or clinic | Remote location, often client’s home |
| Visual Cues | Therapist can observe non-verbal cues, such as body language and facial expressions | Limited non-verbal cues, depending on the modality |
| Accessibility | Limited by geographical location | Increased accessibility, especially for those in rural areas or with mobility issues |
| Environmental Factors | Client’s immediate surroundings can influence the session | Client’s home environment can influence the session |
| Technology Requirements | No specific technology needed | Requires a stable internet connection and appropriate device |
| Insurance Coverage | Often covered by insurance | Insurance coverage varies; some insurance plans may cover telemental health services, while others may not |
Accessibility and Convenience
Teletherapy, or telemental health, is rapidly changing the landscape of mental healthcare, offering significant advantages in terms of accessibility and convenience for both patients and providers. It’s no longer a futuristic concept, but a practical reality that is improving the lives of many. This section will delve into the ways in which telemental health breaks down barriers and makes mental health support more readily available.Teletherapy offers a unique opportunity to overcome geographical limitations and cater to diverse populations.
This is particularly important for those in rural areas, who often face long commutes and limited options for in-person services. Additionally, it caters to individuals with physical disabilities, who may find traditional appointments challenging or impossible to attend.
Accessibility for Diverse Populations
Teletherapy has the potential to greatly expand access to mental health services for various populations. Rural communities, often underserved by traditional mental health providers, can now benefit from remote sessions, connecting them with therapists who might otherwise be geographically distant. Similarly, individuals with mobility impairments or chronic illnesses can access care from the comfort of their homes, eliminating the stress and logistical hurdles of travel.
The potential to connect people in remote or marginalized communities to therapists, previously inaccessible, is a substantial benefit.
Convenience Factors for Patients and Providers
Teletherapy offers a multitude of convenience factors for both patients and providers. For patients, it eliminates the need for travel, parking, and waiting times, allowing them to schedule appointments around their existing commitments. This flexibility can significantly improve adherence to treatment plans, as patients are more likely to engage in therapy when it fits seamlessly into their daily lives.
Teletherapy has its upsides, like convenience and accessibility, but also drawbacks, such as potential technical issues. Finding the right balance between convenience and quality care is key. If you’re looking for great paleo brands and products to support your health journey, check out this list of the best paleo brands and products. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not telemental health is right for you depends on your individual needs and preferences.
For providers, teletherapy can increase their reach and allow them to serve a wider client base, potentially reducing their overhead costs and improving their work-life balance.
Comparison with Traditional In-Person Therapy
While telemental health offers significant advantages, it’s important to acknowledge the differences between it and traditional in-person therapy. Teletherapy sessions may lack the non-verbal cues and in-person connection that some find valuable in traditional therapy. However, modern video conferencing technology can mitigate some of these limitations, and skilled therapists can adapt their techniques to successfully navigate the nuances of remote sessions.
Potential Barriers to Access
Despite the numerous benefits, certain barriers to access remain. Technological limitations, such as unreliable internet connections, technical glitches, or a lack of appropriate devices, can disrupt or impede sessions. Furthermore, ensuring patient privacy and confidentiality in a remote setting requires careful consideration and adherence to strict protocols. In addition, the digital divide and unequal access to technology create significant barriers for some populations, potentially exacerbating existing disparities in mental health care.
| Potential Barrier | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Technology Issues | Problems with internet connectivity, malfunctioning devices, or software glitches can disrupt sessions and hinder effective communication. |
| Internet Availability | Limited or unreliable internet access in certain areas can make it difficult or impossible for individuals to participate in telemental health services. |
| Lack of Privacy | Concerns about confidentiality and security of sensitive information shared during remote sessions must be addressed through secure platforms and appropriate protocols. |
Effectiveness and Outcomes
Telemedicine has revolutionized mental healthcare, offering a potentially powerful tool for reaching individuals in need. However, the effectiveness of telemental health for various mental health conditions is a complex area requiring careful consideration of factors like patient engagement, therapist training, and technological infrastructure. This exploration delves into the evidence surrounding telemental health’s efficacy and identifies both promising avenues and potential limitations.
Evidence-Based Research on Effectiveness
Numerous studies have investigated the effectiveness of telemental health for diverse mental health conditions. Research consistently shows that telemental health can be a viable alternative to in-person therapy for certain populations. For example, studies have demonstrated comparable outcomes in treating depression and anxiety via telehealth platforms compared to traditional face-to-face methods. These findings highlight the potential of telemental health to expand access to care and improve mental well-being.
Examples of Successful Telemental Health Programs
Several successful telemental health programs have emerged, showcasing the practical application of this technology. One example is a program targeting veterans experiencing PTSD, utilizing telehealth to provide access to therapy and support groups in remote areas. This initiative successfully reduced isolation and improved access to specialized care, demonstrating the potential of telemental health to address specific needs. Another example is a program designed to help adolescents with eating disorders.
By offering online therapy sessions and support groups, the program improved communication and encouraged adherence to treatment plans, leading to positive outcomes.
Potential Limitations in Therapeutic Effectiveness
While telemental health holds promise, certain limitations exist. A key consideration is the potential for reduced therapeutic rapport compared to in-person sessions. Building trust and rapport can be challenging through a screen, and nonverbal cues might be missed, potentially impacting the therapeutic process. Furthermore, the technological infrastructure itself can present hurdles. Issues like internet connectivity problems or technical malfunctions can disrupt sessions, leading to frustration and hindering the therapeutic relationship.
Finally, the digital divide can exacerbate existing disparities in access to care. Individuals with limited access to technology or reliable internet connections may face challenges in participating in telemental health programs.
Integration into Existing Mental Health Care Systems
Integrating telemental health into existing mental health care systems requires careful planning and collaboration. Systems should consider training clinicians on the use of telehealth platforms and ensuring patients have access to necessary technological resources. Furthermore, protocols should be established to address potential technical difficulties and ensure continuity of care between in-person and telehealth modalities. This integration should strive to enhance access to care while maintaining the quality and effectiveness of mental health services.
Summary Table: Promising Mental Health Conditions for Telemental Health
| Mental Health Condition | Promising Results |
|---|---|
| Depression | Studies show comparable outcomes to in-person therapy |
| Anxiety | Telehealth can effectively manage anxiety symptoms and improve coping strategies |
| PTSD | Can reduce isolation and improve access to specialized care in remote areas |
| Eating Disorders | Online therapy and support groups can improve communication and adherence to treatment plans |
| Grief and Loss | Can provide support and resources, particularly for individuals in remote areas |
Cost-Effectiveness and Financial Implications

Telemedicine, including telemental health, is poised to reshape the healthcare landscape. A key driver of this shift is the potential for cost-effectiveness, both for patients and the broader healthcare system. Understanding these financial implications is crucial for evaluating the long-term viability and impact of telemental health.Teletherapy can significantly reduce costs in various ways. Reduced travel time and associated expenses for patients translate to financial savings, allowing them to access care more readily and affordably.
For healthcare systems, streamlined operations and potentially lower overhead associated with physical clinic space can lead to substantial long-term cost reductions.
Potential Cost Savings for Patients
The financial burden of traditional in-person therapy can be substantial. Travel expenses, childcare costs, and lost wages due to time off from work are all factors that impact patient affordability. Teletherapy removes these barriers, allowing patients to receive care from the comfort of their own homes, reducing or eliminating these significant financial burdens. Insurance coverage for telemental health services is increasingly common, further mitigating the financial strain for many patients.
Financial Implications for Providers
Implementing telemental health requires upfront investment in technology, including reliable internet access, secure video conferencing platforms, and potentially specialized telehealth software. Ongoing maintenance and training for staff on utilizing these platforms are also considerations. However, the potential for increased patient volume and streamlined administrative processes can offset these initial costs over time. Additionally, some providers are able to leverage telemental health to expand their reach and service more patients in underserved areas.
Teletherapy has its ups and downs, like everything else. It’s convenient, and you can access mental health support from anywhere, but sometimes the lack of in-person connection can be a drawback. Learning how to prepare eggs with lower cholesterol is another important health consideration, and luckily, you can find plenty of delicious options for cooking low cholesterol egg preparation online.
Ultimately, whether telemental health works for you depends on your individual needs and preferences.
Reduced Transportation Costs
Transportation costs associated with in-person therapy can be a significant barrier for many patients. Driving to and from appointments, parking fees, and potential public transportation expenses all add to the overall cost of treatment. Teletherapy significantly reduces or eliminates these transportation-related expenditures, making care more accessible and affordable. This can be especially impactful for patients with mobility limitations or those living in rural areas with limited transportation options.
Teletherapy has its upsides, like convenience and accessibility, but also downsides, like potential technical glitches or the lack of in-person connection. However, some individuals, seeking rapid results, might be tempted by crash diet diabetes remission strategies, like those explored in this article. crash diet diabetes remission Ultimately, while telemental health offers flexibility, a balanced approach considering both the pros and cons is key to successful mental well-being.
Comparison of Costs: Teletherapy vs. In-Person Therapy
| Category | Teletherapy | In-Person Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup Costs | Software, equipment, and training | Lease, maintenance, and staffing of physical space |
| Patient Travel Costs | Eliminated or significantly reduced | Parking, gas, public transportation |
| Administrative Costs | Potentially lower due to reduced office overhead | Higher administrative costs due to managing physical space and scheduling |
| Patient Time Costs | Potentially lower due to reduced travel time | Travel time, potential loss of productivity |
| Overall Cost to Patient | Lower, potentially significantly | Higher, including transportation and time costs |
“A study by [insert reputable source here] found that telemental health resulted in a 25% reduction in patient transportation costs.”
The table above provides a general comparison. Actual costs will vary based on individual circumstances, insurance coverage, and the specific provider. Further research and data collection are crucial to fully understand the long-term cost-effectiveness of telemental health.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Telemental health, while offering significant advantages, also presents a unique set of ethical and legal challenges. Navigating these considerations is crucial for ensuring the safety, well-being, and trust of patients while upholding professional standards. These considerations are paramount to the responsible and effective implementation of telemental health services.
Confidentiality and Informed Consent
Protecting patient confidentiality is paramount in any mental health practice, and telemental health is no exception. Robust measures must be in place to safeguard sensitive information exchanged during virtual sessions. This includes using secure platforms and encryption technologies to protect data transmitted between the patient and provider. Informed consent is also critical. Patients must fully understand the implications of participating in telemental health, including potential limitations on confidentiality (e.g., if the provider is in a shared workspace).
They need to be aware of how their data will be stored, accessed, and protected. Clear and concise information regarding these procedures should be included in the informed consent document.
Legal Frameworks Governing Telemental Health
The legal landscape surrounding telemental health varies considerably across jurisdictions. Different states and countries have established specific regulations and guidelines regarding telehealth practices, including licensure requirements for providers, data security protocols, and the permissible scope of practice. These regulations often reflect the unique needs and concerns of each jurisdiction, impacting the types of services offered, the types of clients seen, and the required measures for data security.
Potential Risks and Safety Concerns, The pros and cons of telemental health services
Telemental health introduces specific risks that must be addressed proactively. Technical glitches, such as internet outages or audio/video malfunctions, can disrupt sessions and compromise confidentiality. Issues with patient access to technology or a lack of reliable internet access in certain locations can limit accessibility and create inequities. Cultural considerations and linguistic barriers also need to be carefully considered, as the virtual environment can present additional challenges for individuals with limited technological experience or those from diverse cultural backgrounds.
Maintaining Patient Confidentiality During Telemental Health Sessions
To ensure confidentiality during telemental health sessions, providers should:
- Employ secure video conferencing platforms with end-to-end encryption.
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to protect accounts.
- Establish clear policies regarding the use of shared workspaces or office environments, where others may overhear.
- Adhere to HIPAA guidelines and other relevant regulations to ensure data security.
- Provide patients with detailed information about confidentiality protocols and data security measures before the first session.
These measures are essential for building trust and maintaining the integrity of the therapeutic relationship.
Ethical Guidelines for Telemental Health Providers
| Ethical Principle | Specific Considerations for Telemental Health |
|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Implement strong encryption and secure platforms; inform patients about limitations of confidentiality; adhere to HIPAA or relevant regulations. |
| Informed Consent | Provide comprehensive information about the use of technology, potential risks, and limitations of confidentiality. |
| Competence | Ensure providers are trained and competent in the use of technology and in delivering services via telehealth. |
| Cultural Sensitivity | Acknowledge and address potential cultural differences and access disparities. |
| Professional Boundaries | Maintain appropriate professional boundaries, even in a virtual setting, to avoid exploitation or harm. |
Technology and Infrastructure
Telemental health relies heavily on robust technology. A seamless and effective telehealth experience hinges on the availability of reliable and user-friendly tools. This encompasses not only the software platforms themselves but also the essential hardware and internet connectivity needed for smooth communication and data transfer. The technology underpinning telehealth needs to be secure, accessible, and adaptable to various user needs.The digital landscape of telemental health demands a comprehensive approach to technology.
The crucial elements of infrastructure, hardware, software, and training all play pivotal roles in shaping the overall success and accessibility of telemental health services. These components work in tandem to deliver high-quality care, regardless of geographical location.
Essential Technologies for Telemental Health
The successful implementation of telemental health necessitates a diverse array of technologies. These range from video conferencing platforms to secure messaging systems and patient portals. These tools facilitate virtual consultations, therapy sessions, medication management, and remote monitoring.
- Video Conferencing Platforms: These platforms form the core of many telemental health interactions. High-quality video and audio are crucial for clear communication and a professional experience. Features such as screen sharing, real-time transcription, and secure file sharing enhance the session’s efficiency and effectiveness.
- Secure Messaging Systems: These systems allow for secure communication between providers and patients outside of scheduled sessions. They facilitate quick exchanges of information, medication reminders, and general support, enhancing the continuity of care.
- Patient Portals: These portals empower patients to manage their health information, schedule appointments, access educational resources, and communicate with their providers conveniently and securely.
- Remote Monitoring Tools: These technologies allow for continuous tracking of patients’ vital signs and other health data, facilitating proactive care and early intervention.
Importance of Reliable Internet Access and Appropriate Devices
Reliable internet access is paramount for a smooth telemental health experience. Patients must have sufficient bandwidth to support video conferencing and other online activities without interruption. Appropriate devices, such as computers, tablets, or smartphones, are also crucial for accessing and using telemental health platforms.
- Internet Connectivity: Adequate internet bandwidth is essential for uninterrupted video calls, secure data transfer, and smooth online interactions. This often translates to a minimum download and upload speed to support the functionalities of telehealth applications. Dial-up connections are generally inadequate for the requirements of telemental health.
- Devices: The devices used for accessing telemental health services should be compatible with the platform’s requirements. This ensures the quality of video and audio, as well as the overall user experience. Mobile devices, while convenient, might face challenges with display size or functionality, compared to dedicated computers.
Training for Providers and Patients
Thorough training is essential for both providers and patients to effectively utilize telemental health platforms. This training should cover the technical aspects of using the platform, including navigating features and addressing common technical issues.
- Provider Training: Providers need training to adapt to the nuances of online communication, such as building rapport and maintaining therapeutic boundaries in a virtual setting. Training must cover navigating the platform, handling technical issues, and utilizing its features effectively for documentation and record-keeping.
- Patient Training: Patients require training to understand how to use the platform, access their medical records, and communicate with their providers efficiently. Training should address any technical issues and provide a comprehensive overview of how to utilize the platform to its full potential.
Challenges of Maintaining Technical Infrastructure
Maintaining the technical infrastructure for telemental health services presents various challenges. These range from ensuring platform security and data privacy to addressing technical glitches and potential disruptions.
- Security Concerns: Protecting patient data is paramount in telemental health. Robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, are necessary to safeguard sensitive information.
- Technical Glitches: Addressing technical issues and ensuring platform stability is essential to maintain patient trust and provide uninterrupted service. Constant monitoring and quick resolution of technical problems are critical.
- Maintaining Equipment: Regular maintenance of equipment and ensuring its compatibility with the latest updates are important aspects of maintaining the technology’s reliability.
Comparison of Telemental Health Platforms
Different platforms offer varying functionalities and features. The optimal choice depends on the specific needs and requirements of the practice.
| Platform | Key Features | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zoom | Video conferencing, screen sharing, chat | Widely used, user-friendly interface | Limited HIPAA compliance features |
| Doxy.me | Video conferencing, secure messaging, patient portal | HIPAA compliant, robust features | Potential learning curve for some users |
| Teladoc | Remote consultations, virtual check-ups, secure messaging | Wide range of services, established platform | May be more expensive for smaller practices |
Patient Experience and Satisfaction

The patient experience in telemental health is a critical factor in determining the success and sustainability of these services. Positive experiences lead to higher satisfaction, adherence to treatment, and ultimately, better mental health outcomes. Conversely, negative experiences can deter patients from utilizing telemental health, potentially limiting access to vital care. Understanding and addressing patient concerns is paramount to improving the overall satisfaction and effectiveness of telemental health.A significant aspect of patient satisfaction is the perception of the technology used.
Ease of use, reliability of the platform, and the clarity of communication are key factors influencing patients’ comfort and confidence in the virtual setting. Furthermore, the perceived level of empathy and professionalism displayed by the provider plays a significant role in the overall patient experience.
Patient Feedback on Telemental Health
Patient feedback provides valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of telemental health services. Positive feedback often highlights the convenience and accessibility of remote sessions, especially for individuals facing geographical limitations or scheduling challenges. For example, a patient might express appreciation for the flexibility of scheduling sessions around work or family commitments. Conversely, negative feedback often points to technical difficulties, poor audio or video quality, or a perceived lack of connection with the provider.
For instance, a patient might mention experiencing audio issues during the session, making it difficult to fully participate. These varying perspectives underscore the importance of addressing specific issues related to patient experience.
Strategies for Addressing Patient Concerns
Effective strategies for addressing patient concerns are crucial to enhancing the patient experience. Proactive communication regarding the technology used, including troubleshooting guides and clear instructions, can alleviate anxieties. Offering multiple communication channels, such as phone support, email, or chat, can enhance accessibility and provide alternative options for assistance. Implementing a comprehensive system for addressing technical issues promptly and efficiently is also vital.
Improving the Patient Experience in Telemental Health Sessions
Improving the patient experience involves several key aspects. First, ensuring reliable and high-quality technology is fundamental. Second, providing thorough pre-session instructions and technical support minimizes the risk of technical disruptions during the session. Third, fostering a sense of connection and rapport with the provider is critical. This can be achieved through active listening, empathetic responses, and clear communication.
Fourth, incorporating interactive elements, such as video demonstrations or interactive exercises, can enhance engagement and promote a more personalized experience.
Common Patient Concerns and Suggested Solutions
| Common Patient Concerns | Suggested Solutions |
|---|---|
| Technical difficulties (e.g., poor audio/video quality, connection issues) | Provide clear pre-session instructions, troubleshoot issues promptly, offer alternative communication channels (phone, email), and ensure reliable internet access. |
| Feeling disconnected from the provider | Encourage active listening, empathetic responses, clear communication, and potentially incorporate interactive elements to enhance engagement. |
| Lack of privacy concerns | Emphasize confidentiality protocols and security measures. Ensure the patient understands the privacy policies and procedures. Provide clear and comprehensive information about data protection and security measures in place. |
| Scheduling difficulties | Offer flexible scheduling options, provide a variety of appointment times, and consider using online scheduling tools to enhance patient convenience. |
| Accessibility and inclusivity | Ensure the platform is accessible to individuals with disabilities (e.g., provide closed captioning, alternative formats). Consider language accessibility and offer multilingual support. |
Future Trends and Developments: The Pros And Cons Of Telemental Health Services
The future of telemental health is brimming with potential, poised to revolutionize mental healthcare access and delivery. Advancements in technology, coupled with a growing understanding of its efficacy, are driving this transformation. This evolution promises to reshape the landscape of mental health services, making them more accessible, affordable, and ultimately, more effective.
Projected Growth and Trends
Telemental health is experiencing exponential growth, driven by factors such as increasing demand for remote services, technological advancements, and evolving reimbursement policies. This expansion is projected to continue, with a significant increase in the adoption of virtual platforms for mental health care. Several trends are emerging, impacting the future of telemental health.
- Increased integration with primary care: Telemental health is increasingly being integrated into primary care settings, allowing for earlier identification and intervention of mental health concerns. This collaboration will facilitate seamless access to mental health support for patients, potentially improving overall health outcomes.
- Expansion of service types: The range of telemental health services is broadening. This includes offering specialized services such as group therapy, couples therapy, and support groups, expanding access to a broader range of mental health needs.
- Focus on culturally sensitive approaches: As telemental health expands globally, there is a growing emphasis on incorporating culturally sensitive practices into telehealth services. This ensures the services are effective and culturally appropriate for diverse populations.
- Integration of AI and machine learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize telemental health by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment recommendations, and providing continuous support and monitoring.
Emerging Technologies
New technologies are rapidly transforming telemental health, offering innovative solutions and enhanced user experiences. These advancements are not only improving the quality of care but also increasing its accessibility and affordability.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR): VR and AR technologies are showing promise in providing immersive therapeutic experiences. Imagine a patient using VR to confront anxieties in a safe, controlled environment, or using AR to visualize and manage stress-inducing situations. These technologies have the potential to significantly enhance the effectiveness of therapy.
- Wearable technology: Wearable devices can monitor vital signs, track activity levels, and collect other physiological data, potentially providing valuable insights into a patient’s well-being. This data can be used to inform treatment strategies and enhance the effectiveness of care.
- Chatbots and AI-powered tools: AI-powered chatbots can provide initial assessments, answer frequently asked questions, and offer basic support. This can reduce the burden on mental health professionals, allowing them to focus on more complex cases.
Impact on Mental Health Access and Affordability
Telemental health is expected to play a critical role in increasing access to mental healthcare, particularly in underserved areas or for individuals facing geographical limitations.
“Telehealth has the potential to significantly reduce the barriers to accessing mental healthcare, making it more accessible and affordable for many.”
Remote services can decrease travel time and costs, and make mental healthcare more affordable by reducing overhead expenses for clinics and providers.
Potential Advancements in Telehealth Technologies
Continued advancements in telehealth technology will lead to more intuitive, user-friendly platforms and improved communication tools.
- Enhanced video conferencing: High-definition video conferencing with features like real-time translation and captioning will improve communication and accessibility for diverse populations.
- Improved data security and privacy: As technology advances, security measures will become more sophisticated, ensuring the protection of patient data and maintaining patient privacy.
- Development of personalized mental health apps: These apps will provide tailored interventions, personalized support, and ongoing monitoring, fostering a more proactive and supportive approach to mental health.
Projected Growth and Trends Table
| Year | Projected Growth Rate (%) | Key Trends |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 25 | Increased adoption of AI-powered tools, focus on integration with primary care. |
| 2025 | 30 | Expansion of specialized services, growing use of VR/AR. |
| 2026 | 35 | Enhanced data security, increased accessibility for diverse populations. |
Last Point
In conclusion, telemental health offers a compelling solution for expanding mental health access, but it’s crucial to understand the potential drawbacks alongside the benefits. From improved accessibility to potential limitations in therapeutic effectiveness, this comprehensive analysis reveals the nuanced landscape of virtual mental health care. The future of telemental health hinges on careful consideration of the ethical, legal, and practical challenges while maximizing its potential for positive change in the mental health field.





