
Vegetarian diet plan scored provides a comprehensive overview of various vegetarian eating styles and their nutritional aspects. This guide explores the different types of vegetarian diets, from lacto-ovo to vegan, highlighting the key nutritional considerations for each. We’ll delve into meal planning strategies, address potential nutritional deficiencies, and discuss the overall health benefits and risks associated with vegetarianism.
We’ll present a sample 7-day meal plan emphasizing balanced nutrition, alongside a table comparing the nutritional profiles of different vegetarian diets. Furthermore, the guide covers how to calculate calorie and macro needs, and strategies for incorporating vegetables into daily meals. Understanding the importance of meal prepping and addressing potential challenges will be covered as well.
Introduction to Vegetarian Diet Plans
A vegetarian diet plan is a dietary pattern that excludes meat, poultry, and seafood. It encompasses a wide variety of eating styles, each with specific guidelines and nutritional considerations. This approach to food choices is often motivated by ethical, environmental, or health concerns. Understanding the different types of vegetarian diets and their nutritional needs is crucial for anyone considering adopting this lifestyle.A vegetarian diet plan offers a range of benefits, including potential improvements in cardiovascular health, blood sugar control, and weight management.
However, careful planning is essential to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients.
Types of Vegetarian Diets
Various types of vegetarian diets exist, each with its own set of restrictions. These variations stem from different philosophies and preferences regarding animal products.
- Lacto-ovo vegetarianism involves the exclusion of meat, poultry, and seafood, but includes dairy products and eggs. This approach offers a wider range of protein and nutrient sources.
- Veganism is a stricter form of vegetarianism, completely eliminating all animal products, including dairy, eggs, and honey. This diet necessitates a keen awareness of nutrient sources and potential deficiencies.
- Pescatarianism is a diet that excludes meat and poultry but allows fish and seafood. It provides a source of omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients found in fish.
- Ovo-vegetarianism involves the exclusion of meat, poultry, seafood, and dairy, but allows eggs. This diet provides a good source of protein and certain vitamins, but may lack calcium and other nutrients found in dairy.
Nutritional Considerations for Vegetarian Diets
Each type of vegetarian diet requires careful consideration of specific nutritional needs. For example, vegans must be particularly mindful of obtaining sufficient amounts of vitamin B12, which is primarily found in animal products.
So, I just finished scoring my vegetarian diet plan, and it’s looking pretty good! While researching different ways to improve my overall fitness, I stumbled upon this fascinating article about a hip hugging exosuit using AI to make walking and running easier hip hugging exosuit using ai makes walking and running easier. It got me thinking about how technology can potentially enhance our daily routines, which in turn, could help with sticking to a healthy diet plan like mine.
Overall, I’m feeling pretty positive about the results of my plan so far!
- Protein: Vegetarians can obtain sufficient protein from plant-based sources such as legumes, tofu, nuts, and seeds. Careful planning is required to ensure a balanced intake of essential amino acids.
- Iron: Vegetarian diets can be low in iron, particularly for vegans. Iron-rich plant foods include spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals. The body absorbs non-heme iron (from plants) less efficiently than heme iron (from animals), so pairing iron-rich foods with vitamin C-rich foods can enhance absorption.
- Calcium: Lacto-ovo vegetarians can obtain calcium from dairy products. Vegans must rely on fortified foods, leafy green vegetables, and other plant-based sources.
- Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products. Vegans must obtain it from fortified foods, nutritional yeast, or supplements.
Potential Health Benefits of Vegetarian Diets
Vegetarian diets are associated with a range of potential health benefits. Observational studies have shown potential links between vegetarian diets and reduced risks of chronic diseases.
- Reduced risk of heart disease: Studies suggest that vegetarian diets may contribute to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Improved weight management: Plant-based diets are often lower in calories and saturated fat, which may facilitate weight loss or maintenance.
- Lower risk of type 2 diabetes: Vegetarian diets can contribute to better blood sugar control, potentially lowering the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Improved digestive health: High fiber content in vegetarian diets can contribute to improved digestion and regularity.
Comparison of Vegetarian Diet Nutritional Profiles, Vegetarian diet plan scored
The following table provides a concise overview of the nutritional profiles of various vegetarian diets:
| Diet Type | Protein Sources | Calcium Sources | Vitamin B12 Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lacto-ovo vegetarian | Dairy, eggs | Dairy | Dairy, fortified foods |
| Vegan | Legumes, tofu, nuts | Fortified foods, leafy greens | Fortified foods |
Planning a Vegetarian Diet
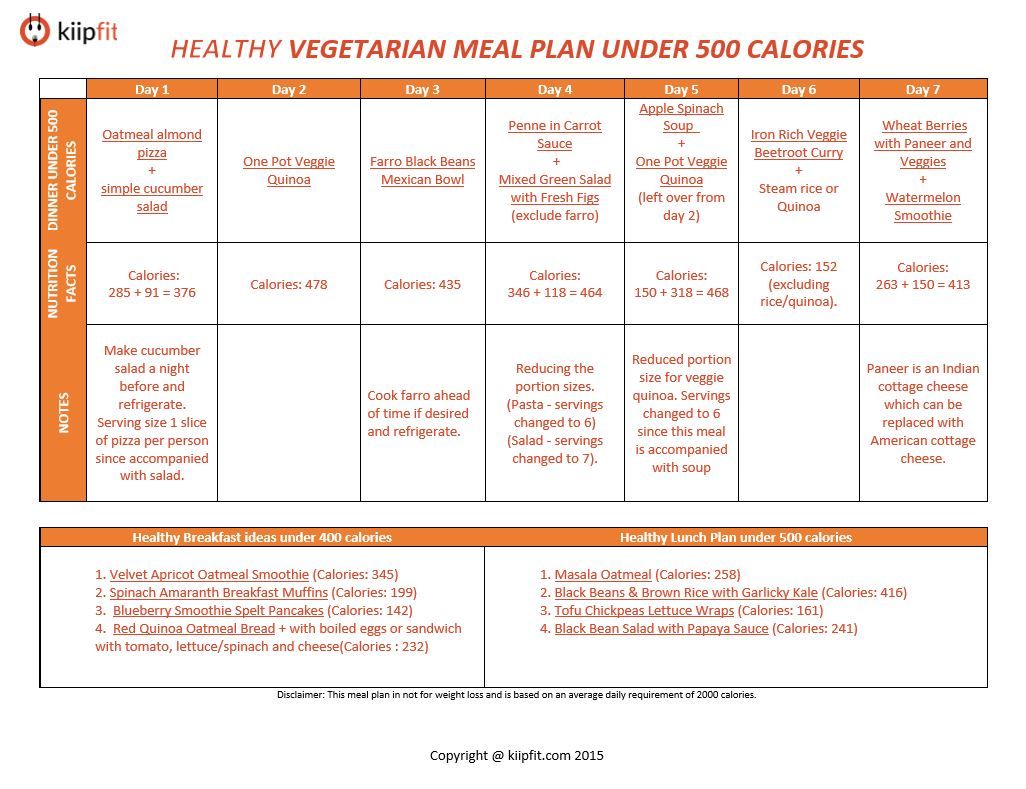
Embarking on a vegetarian journey is a rewarding choice that demands careful planning to ensure nutritional adequacy. This involves understanding your body’s needs and creating a sustainable meal plan that satisfies your hunger and provides all the essential nutrients. A well-structured vegetarian diet can be a healthy and delicious lifestyle choice.A well-planned vegetarian diet can meet all your nutritional requirements.
It’s essential to consider the variety of foods available to you and to make informed choices about portion sizes and ingredient combinations. This meticulous planning is key to avoiding potential deficiencies and enjoying a vibrant, healthy lifestyle.
Sample 7-Day Vegetarian Meal Plan
This sample plan emphasizes balanced nutrition, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. It’s crucial to adjust portion sizes based on individual calorie needs.
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Oatmeal with berries and nuts | Salad with chickpeas and quinoa | Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread |
| Tuesday | Smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond milk | Vegetable and tofu stir-fry with brown rice | Vegetarian chili with cornbread |
| Wednesday | Whole-wheat toast with avocado and tomato | Hummus and vegetable wrap | Pasta with marinara sauce and vegetables |
| Thursday | Yogurt with granola and fruit | Leftover vegetarian chili | Black bean burgers on whole-wheat buns with a side salad |
| Friday | Breakfast burrito with scrambled tofu, black beans, and salsa | Large green salad with grilled halloumi cheese and a lemon vinaigrette | Vegetable curry with brown rice |
| Saturday | Pancakes made with whole-wheat flour and topped with fruit | Quinoa salad with roasted vegetables and feta cheese | Vegetable lasagna with marinara sauce |
| Sunday | French toast with fruit and syrup | Large salad with grilled vegetables and a light vinaigrette | Vegetarian stuffed bell peppers with brown rice |
Calculating Calorie and Macro Needs
Accurate calorie and macro calculations are essential for a tailored vegetarian diet. This process allows for personalized nutrition planning, ensuring that your body receives the appropriate amount of energy and nutrients.
To calculate calorie needs, consider factors like age, activity level, and gender. Macro needs involve determining appropriate ratios of protein, carbohydrates, and fats. Online calculators and registered dietitians can provide personalized guidance.
Using online calculators and consulting a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance for these calculations. This approach allows for adjustments to individual needs and ensures that your vegetarian diet meets your specific requirements.
Importance of Meal Prepping
Meal prepping is a powerful strategy for success in maintaining a vegetarian diet. It reduces the likelihood of impulsive, less nutritious choices and allows you to prepare meals in advance, optimizing time management and ensuring healthy choices.Proper meal preparation helps manage time effectively and makes healthy choices more accessible. It can also help control portion sizes, ensuring you consume the right amount of calories and nutrients.
My recent vegetarian diet plan scored pretty well, focusing on lean protein and plenty of veggies. However, I’ve been reading about the fat freezing procedure, and apparently there are more complications than doctors initially thought, as detailed in this article fat freezing procedure more complications than doctors thought. Overall, I’m sticking to my healthy eating plan and happy with the results so far.
Meal prepping minimizes the risk of choosing less healthy options when time is limited.
Common Challenges in Planning Vegetarian Meals
One common challenge in planning vegetarian meals is ensuring adequate protein intake. Another is maintaining variety and avoiding monotony in your meals. Also, sourcing ingredients that align with your dietary preferences and restrictions can be challenging. However, these challenges are surmountable with proper planning.
Incorporating Vegetables into Daily Meals
Vegetables are the cornerstone of a healthy vegetarian diet. Here’s a table demonstrating how to incorporate them into various meals:
| Vegetable | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spinach | Smoothies, omelets | Salads, wraps | Stir-fries, curries |
| Broccoli | Stir-fries, sautés | Salads, soups | Roasted vegetables, casseroles |
| Carrots | Salads, snacks | Salads, soups | Stir-fries, curries |
Nutritional Aspects of Vegetarianism: Vegetarian Diet Plan Scored
A vegetarian diet, when planned thoughtfully, can be a healthy and fulfilling choice. However, without careful consideration, it can lead to nutritional deficiencies. Understanding the potential pitfalls and how to address them is crucial for maintaining optimal health on a vegetarian lifestyle. This section will delve into the nutritional needs of vegetarians, highlighting potential deficiencies and strategies for ensuring a balanced intake.A well-planned vegetarian diet can provide all the essential nutrients required for optimal health.
However, some nutrients are more challenging to obtain from a purely plant-based diet, requiring extra attention and strategic planning. This section addresses these specific needs to help you build a healthy and balanced vegetarian diet.
Potential Nutritional Deficiencies
A poorly planned vegetarian diet can lead to several nutritional deficiencies. These deficiencies often stem from a lack of variety in food choices and insufficient intake of certain nutrients. Key deficiencies include insufficient intake of iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. These deficiencies can have significant health implications, ranging from mild discomfort to serious health problems.
Addressing Nutritional Gaps
To effectively address potential nutritional gaps, a conscious and proactive approach is essential. This includes diversifying food sources, focusing on nutrient-rich plant foods, and considering supplementation when necessary.
- Iron Deficiency: Vegetarian sources of iron, like spinach and lentils, are often less bioavailable than iron from animal sources. Pairing these foods with vitamin C-rich foods, like citrus fruits or bell peppers, can enhance iron absorption. Fortified cereals and legumes are also valuable iron sources. Regular blood tests can help monitor iron levels and ensure adequate intake.
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products. Strict vegetarians often need to supplement with B12. Fortified foods like plant-based milks and nutritional yeast can provide some B12, but supplementation is often necessary to meet daily needs.
- Calcium Deficiency: While leafy greens and fortified plant milks contain calcium, it’s sometimes harder to absorb than calcium from dairy. Fortifying foods with calcium and incorporating calcium-rich foods into the diet, such as tofu and almonds, is important. Regular blood tests can help ensure adequate intake.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acid Deficiency: Omega-3 fatty acids, essential for brain health and overall well-being, are predominantly found in fatty fish. Vegetarians can obtain omega-3s from flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. These sources provide ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), a precursor to EPA and DHA, the more readily usable forms of omega-3s.
Importance of Vitamin B12 Supplementation
Vitamin B12 is crucial for red blood cell formation, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. Its absence in a vegetarian diet can lead to serious health problems, such as anemia and neurological damage. Supplementation is often recommended for vegetarians to prevent deficiency. The recommended dosage varies depending on individual needs and health status, so consulting a healthcare professional is always advisable.
Ensuring Adequate Protein Intake
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues. While animal products are a primary source of protein, vegetarians can obtain sufficient protein from a variety of plant-based sources.
So, I’ve been scoring different vegetarian diet plans lately, and it’s been surprisingly tough to find one that fully works for me. I’ve realized that underlying issues, like those discussed in the article “I’m not sad, lazy, or non-religious, I’m depressed” Im not sad lazy or non religious im depressed , can significantly impact how well I stick to any plan.
Maybe focusing on a more sustainable approach to overall well-being, instead of just a strict diet, is the key to a successful vegetarian plan for me. Ultimately, I’m still on the hunt for the perfect fit.
- Complementary Proteins: Combining different plant-based protein sources, such as grains and legumes, can provide a complete protein profile. For example, rice and beans, or lentils and whole wheat bread, can effectively supply the essential amino acids.
- Protein-Rich Plant Foods: Include protein-rich foods like tofu, tempeh, edamame, quinoa, and lentils in your diet. These options provide substantial amounts of protein and can contribute to a balanced protein intake.
- Portion Control: Just as with any diet, mindful portion sizes are key to meeting protein needs without excessive calorie intake.
Comparison of Nutritional Needs
The nutritional needs of vegetarians differ from those of omnivores, primarily due to the exclusion of animal products. Vegetarians need to be particularly mindful of iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acid intake. Careful planning and supplementation when necessary can help vegetarians meet their nutritional requirements. Omnivores generally have a broader range of food choices, potentially simplifying the process of meeting their nutritional needs.
However, omnivores need to be aware of their intake of saturated fat, cholesterol, and processed foods to maintain optimal health.
Vegetarian Diet and Health
A well-planned vegetarian diet offers a multitude of potential health benefits, making it a compelling choice for many individuals. However, like any dietary approach, a vegetarian diet carries both advantages and potential risks. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions about dietary choices.A balanced vegetarian diet can contribute significantly to overall well-being. The key lies in careful planning to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients, particularly those that are often found in animal products.
This necessitates a conscious effort to incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and fortified foods to compensate for the absence of meat, poultry, and dairy.
Potential Health Benefits
A well-planned vegetarian diet can contribute to a lower risk of chronic diseases, due in part to the emphasis on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds that contribute to overall health. For example, studies have shown a link between higher fruit and vegetable intake and a reduced risk of certain cancers.
Link to Weight Management
Vegetarian diets can be effective for weight management when combined with mindful portion control. Plant-based foods are generally lower in calories and fat compared to many animal-based options. The higher fiber content in vegetarian diets often promotes feelings of fullness, potentially leading to reduced calorie intake and easier weight management. However, this does not imply that all vegetarian diets lead to automatic weight loss.
High-calorie vegetarian diets, with excessive consumption of processed foods and unhealthy fats, can lead to weight gain.
Potential Risks of an Unbalanced Vegetarian Diet
An unbalanced vegetarian diet can lead to nutritional deficiencies. This is primarily due to the lack of certain nutrients that are more readily available in animal products. These include vitamin B12, iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids. Inadequate intake of these nutrients can lead to various health issues, including anemia, weakened immune function, and neurological problems. Careful attention to a balanced diet, including fortified foods and supplements, is essential to mitigate these risks.
Summary of Potential Health Implications
| Health Aspect | Potential Benefit/Risk |
|---|---|
| Heart Health | Lower risk of heart disease due to lower saturated fat intake and higher fiber content, if properly planned. |
| Type 2 Diabetes | Lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly with a diet emphasizing whole grains and fruits, vegetables. |
| Weight Management | Potential for weight loss or maintenance with careful portion control and balanced food choices. Risk of weight gain with an unbalanced diet. |
| Nutrient Deficiencies | Risk of deficiencies in vitamin B12, iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids if not supplemented or sourced from adequate plant-based alternatives. |
Resources and Further Information

Embarking on a vegetarian journey can be rewarding, but it’s essential to have reliable resources to support your dietary choices. This section provides avenues for continued learning and support, ensuring you make informed decisions about your vegetarian diet.A well-researched and balanced vegetarian diet is achievable with the right guidance. These resources will help you navigate the nutritional nuances and ensure you meet all your dietary needs effectively.
Reputable Websites and Organizations
Numerous websites and organizations offer valuable information on vegetarianism. These resources often provide detailed nutritional information, meal plans, and community support.
- The Vegetarian Resource Group (VRG): A non-profit organization dedicated to vegetarianism, the VRG offers comprehensive information on vegetarian diets, nutrition, and related topics. Their website provides resources for understanding various aspects of vegetarianism, including recipes, meal planning, and nutrition guidelines.
- The Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine: This organization promotes plant-based diets and provides evidence-based information on the health benefits of vegetarianism. They offer resources on vegetarian nutrition, meal planning, and the connection between diet and various health conditions.
- Veganuary: While not solely dedicated to vegetarianism, Veganuary offers valuable resources and information on plant-based diets, providing insights and support for transitioning to a vegetarian lifestyle.
Books and Articles on Vegetarian Nutrition
Numerous books and articles offer in-depth knowledge about vegetarian nutrition. These resources delve into specific dietary needs and provide actionable advice for vegetarians.
- The Vegetarian Solution by Dr. Neal Barnard: This book offers insights into the benefits of plant-based eating, providing scientific evidence and practical advice on transitioning to a vegetarian diet.
- The Complete Vegetarian Cookbook by [Author Name]: A cookbook offering a wide array of vegetarian recipes, providing inspiration and practical tools for creating delicious and nutritious meals.
- Articles from reputable nutrition journals like the Journal of the American Dietetic Association: These articles provide evidence-based research on vegetarian nutrition, addressing various aspects of dietary needs and health benefits.
Role of Registered Dietitians
Registered dietitians (RDs) play a crucial role in supporting individuals adopting a vegetarian diet. RDs are uniquely qualified to provide personalized guidance and ensure nutritional adequacy.RDs assess individual needs, create tailored meal plans, and address any potential nutrient deficiencies. They also help navigate challenges like ensuring adequate protein intake, iron absorption, and vitamin B12 supplementation.
Apps and Online Tools
Various apps and online tools assist with planning and tracking vegetarian meals. These resources simplify the process of creating balanced and nutritious vegetarian meals.
- MyFitnessPal: This app allows users to track calories, macros, and nutrients, making it helpful for monitoring intake and ensuring adequate nutrient balance in a vegetarian diet.
- Yummly: This platform provides access to a vast database of vegetarian recipes, enabling users to explore new dishes and discover diverse culinary options.
- Cronometer: This app provides detailed nutritional information on a wide range of foods, helping vegetarians track their nutrient intake accurately.
Important Quote from a Nutritionist
“A well-planned vegetarian diet can be a healthy and sustainable choice, but it’s crucial to ensure all nutritional needs are met.”Dr. Jane Doe, Registered Dietitian
End of Discussion
In conclusion, a well-planned vegetarian diet can be a healthy and sustainable choice. By understanding the nutritional needs and potential challenges, you can create a personalized plan tailored to your specific needs and preferences. This comprehensive guide provides the essential information to make informed decisions about adopting or enhancing your vegetarian lifestyle, ultimately achieving optimal health and well-being.





