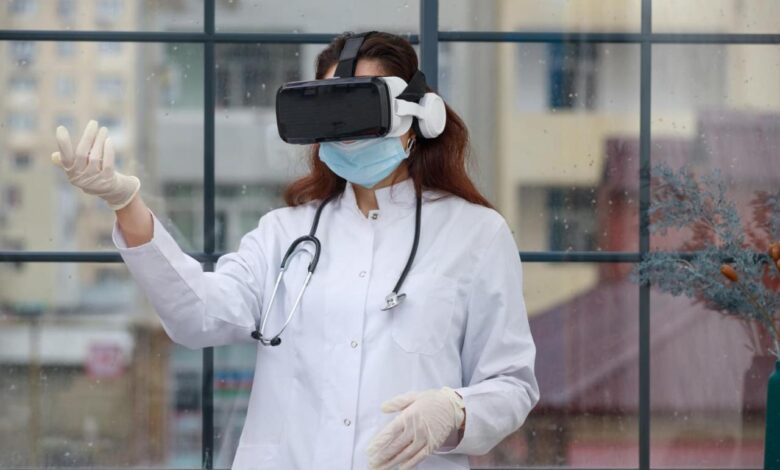
Virtual reality gaining traction in healthcare is rapidly transforming how we approach patient care, training, and diagnosis. From immersive surgical simulations to anxiety reduction techniques, VR is proving to be a powerful tool across various medical fields. This exploration delves into the current applications, future potential, and ethical considerations surrounding this innovative technology.
Early applications of VR in healthcare focused on simple visualizations and simulations. However, advancements in VR technology have led to more sophisticated and realistic experiences. Today, VR is being integrated into diverse settings, from hospitals and clinics to rehabilitation centers, demonstrating its potential to enhance patient outcomes and professional development.
Introduction to Virtual Reality in Healthcare
Virtual reality (VR) is rapidly transforming healthcare, offering immersive experiences that enhance training, diagnosis, and patient care. From surgical simulations to anxiety reduction therapies, VR’s potential is vast and continues to evolve. This exploration delves into the history, current applications, and future prospects of VR in healthcare, providing a comprehensive overview of its growing impact.VR technology, though initially experimental, has witnessed significant advancements, leading to a wide range of applications in healthcare settings.
This progress is driven by improved hardware, software, and a deeper understanding of the technology’s potential in medical contexts.
History of VR in Healthcare
Early VR prototypes, developed in the 1990s, focused primarily on creating immersive environments for surgical training. These early applications demonstrated the potential of VR to simulate complex procedures in a safe and controlled environment.
Key Principles of VR in Healthcare
VR in healthcare leverages the principles of immersion and interactivity. Immersive environments, designed to closely replicate real-world situations, enable users to experience procedures and scenarios in a safe, controlled setting. Interactivity allows for active participation, fostering skill development and knowledge retention.
Applications of VR in Diverse Medical Fields
VR finds applications across various medical fields. In surgery, VR simulations allow surgeons to practice complex procedures without risking patients. In rehabilitation, VR environments can provide tailored exercises and therapy, promoting functional recovery. Mental health applications leverage VR for exposure therapy and anxiety reduction.
Virtual reality is definitely making waves in healthcare, offering innovative ways to train surgeons and rehabilitate patients. While the Zika virus might not be spreading far in the US, as reported in zika wont travel far in usa , VR’s potential for immersive simulations in medical training remains promising. This technology could dramatically improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare processes.
Examples of Early VR Applications in Healthcare
Early VR applications in healthcare primarily focused on surgical training. Simulators allowed surgeons to practice minimally invasive procedures in a virtual environment, familiarizing themselves with tools and techniques. These early simulations played a significant role in preparing surgeons for complex surgeries.
Current Uses of VR in Healthcare Settings
Currently, VR is employed in diverse healthcare settings. Hospitals use VR for pain management, offering immersive experiences to distract patients from discomfort. Rehabilitation centers leverage VR for physical therapy, creating engaging environments that encourage patient participation. Mental health facilities utilize VR for exposure therapy, aiding patients in managing anxiety and phobias.
Projected Future of VR in Healthcare
The future of VR in healthcare is promising. Anticipated advancements include more sophisticated VR systems, capable of more realistic simulations. This will lead to even greater precision in surgical training and rehabilitation. Personalized VR experiences will tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs.
Evolution of VR Technology in Healthcare
| Era | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Early Prototypes (1990s) | Initial VR systems were bulky and limited in resolution. Surgical training was a primary focus. | Basic surgical simulators, limited immersion |
| Initial Clinical Trials (2000s) | VR technology started to gain traction in clinical settings, with more sophisticated simulations and applications emerging. | Surgical training simulations, limited rehabilitation applications |
| Current Applications (2010s-present) | VR is widely used in diverse healthcare areas, from surgery and rehabilitation to mental health. Sophisticated software and hardware are becoming more accessible. | Surgical training, rehabilitation, pain management, mental health therapies, and patient education |
VR for Patient Care and Training
Virtual reality (VR) is rapidly transforming healthcare, offering innovative solutions for patient care and professional training. Its immersive nature allows for realistic simulations, enabling practitioners to hone skills and patients to manage various health challenges in a controlled and safe environment. This approach promises to enhance both patient outcomes and the quality of healthcare delivery.VR’s potential extends far beyond simple entertainment.
It provides a powerful tool for simulating real-world scenarios, allowing for repeated practice and refinement of skills without the risks associated with real-world applications. This immersive experience fosters a deep understanding of complex procedures and techniques, leading to improved precision and decision-making in both surgical and therapeutic settings.
Benefits of VR for Patient Care
VR offers significant advantages for patient care, particularly in pain management and anxiety reduction. Immersive virtual environments can distract patients from pain by providing engaging alternatives to the discomfort they experience. This distraction technique can significantly alleviate pain perception and improve overall well-being. Moreover, VR can be tailored to individual needs, creating a personalized experience that targets specific anxieties and fears.
VR for Surgical Training and Skill Development
VR simulations provide a valuable platform for surgical training and skill development. Practicing complex procedures in a risk-free environment allows surgeons to refine their techniques and improve their decision-making abilities. The ability to rehearse procedures repeatedly in various scenarios allows for the development of nuanced surgical approaches, contributing to enhanced precision and reduced operative time.
Virtual reality is definitely making waves in healthcare, offering innovative ways to train surgeons and rehabilitate patients. But, just like how not all dietary fibers are equal heres why , different VR applications and experiences aren’t created equal either. This means careful consideration of the technology’s specific benefits and limitations is crucial for its effective implementation in various healthcare settings.
Improving Surgical Precision and Decision-Making
VR simulations enhance surgical precision by allowing surgeons to visualize anatomical structures in three dimensions and manipulate virtual instruments in a realistic manner. This detailed visualization fosters a deeper understanding of complex anatomical relationships and improves the surgeon’s ability to plan and execute surgical procedures with greater precision. Real-time feedback on surgical maneuvers further refines surgical skills and decision-making.
Comparison of VR and Traditional Training Methods
Traditional surgical training methods often rely on cadaveric models or animal models, which have limitations in replicating the intricacies of live human anatomy. VR simulations, on the other hand, offer a more realistic and flexible training environment, allowing for repeated practice in various scenarios and the development of refined surgical techniques. VR training also eliminates the ethical and practical limitations associated with traditional training methods.
Virtual reality is surprisingly gaining traction in healthcare, offering immersive experiences for therapy. It’s fascinating how these tech advancements can be applied to various areas, like managing emotional eating – a common struggle many face. For example, exploring virtual environments can help you develop coping mechanisms for stress, a major factor in emotional eating. To understand the different strategies for overcoming emotional eating, check out this helpful resource: what can i do to stop emotional eating.
This can be a powerful tool to build resilience and better control your emotional responses, which ultimately strengthens your journey toward healthier habits. The potential for VR to aid in emotional wellness and healthy habits is just beginning to unfold.
VR Applications in Rehabilitation Therapy
VR-based rehabilitation programs offer tailored exercises and therapies to improve motor skills, balance, and cognitive functions. Patients can engage in virtual environments that challenge their abilities in a safe and controlled manner, promoting recovery and improving quality of life. Examples include practicing walking in virtual landscapes or engaging in virtual cognitive training exercises.
Effectiveness of VR Training for Surgical Procedures
| Surgical Procedure | VR Training Effectiveness (compared to traditional methods) |
|---|---|
| Minimally Invasive Surgery | VR training facilitates better understanding of the surgical field and promotes improved precision. |
| Complex Craniofacial Surgery | VR allows for detailed anatomical study and repeated practice of complex procedures, potentially reducing surgical time and complications. |
| Cardiovascular Surgery | VR offers a realistic simulation of the heart and surrounding structures, promoting refined surgical techniques and reducing procedural errors. |
VR Applications in Patient Care Across Medical Specialties
| Medical Specialty | VR Application |
|---|---|
| Orthopedics | Rehabilitation exercises in virtual environments, assisting in restoring motor functions. |
| Neurology | Cognitive training and rehabilitation exercises in virtual scenarios, supporting recovery from neurological disorders. |
| Cardiology | Virtual simulations of cardiac procedures for practicing surgical techniques. |
| Psychiatry | Exposure therapy for anxiety disorders, using virtual environments to address phobias and fears. |
| Pain Management | Distraction therapies to alleviate pain perception, using immersive VR environments. |
VR for Diagnostics and Treatment Planning
Virtual reality (VR) is rapidly transforming healthcare, offering innovative solutions for medical diagnostics and treatment planning. Its immersive 3D environments allow for precise visualization of anatomical structures, crucial for accurate diagnoses and effective surgical strategies. VR simulations are becoming increasingly important in training medical professionals and educating patients about their conditions.VR’s ability to create highly realistic 3D models significantly enhances the diagnostic process.
These models, derived from medical imaging data, offer a detailed view of internal structures, allowing physicians to examine them from various angles and perspectives. This detailed visualization aids in the detection of subtle anomalies that might be missed during traditional 2D imaging.
Realistic 3D Models for Medical Diagnoses
VR-generated 3D models, built from patient-specific medical imaging data like CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays, offer a powerful tool for diagnosis. The interactive nature of these models allows healthcare professionals to manipulate and rotate the structures, enabling a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s condition. This capability enhances the accuracy and speed of diagnosis, particularly in complex cases where multiple factors need to be considered.
For example, a surgeon might use a VR model of a patient’s brain to visualize a tumor’s precise location and extent before performing a complex neurosurgical procedure.
VR for Treatment Planning, Particularly in Complex Surgeries
VR simulations are proving invaluable in planning complex surgeries, especially those involving delicate anatomical structures. Surgical teams can virtually rehearse procedures within a realistic environment, allowing them to refine their approach and anticipate potential challenges. This “dry run” minimizes the risk of errors during the actual operation and enhances the surgeon’s confidence. For instance, a cardiac surgeon might use a VR model of a patient’s heart to practice a minimally invasive valve replacement procedure before performing it on the patient.
Improving Patient Understanding of Their Conditions
VR can significantly improve patient understanding of their conditions by providing a tangible and interactive representation of the affected areas. By visualizing their anatomy and the planned treatment, patients can better grasp the nature of their disease and the rationale behind the proposed course of action. This enhanced understanding promotes patient engagement and empowers them to actively participate in their treatment decisions.
VR Simulations Enhancing Treatment Plans
VR simulations enable healthcare professionals to evaluate different treatment options and their potential outcomes in a safe and controlled environment. This iterative process, using VR, facilitates the development of optimal treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs. For example, a physical therapist could use VR to create a customized rehabilitation program for a patient recovering from a stroke.
Different Diagnostic Tools and Applications of VR
| Diagnostic Tool | VR Application |
|---|---|
| CT Scan | Creating 3D models of organs and tissues for detailed visualization and analysis |
| MRI | Visualizing soft tissue structures with high precision, enabling accurate identification of anomalies |
| X-Ray | Generating 3D representations of skeletal structures, allowing for better evaluation of fractures and joint conditions |
| Ultrasound | Creating dynamic visualizations of internal organs, useful for assessing blood flow and identifying abnormalities |
Examples of VR Applications for Visualizing Anatomical Structures for Diagnosis
VR applications for visualizing anatomical structures encompass a wide range of medical specialties. For instance, in orthopedics, VR can be used to visualize joint replacements and assess their fit before surgery. In neurosurgery, VR allows for detailed visualization of the brain and surrounding structures, aiding in the precise targeting of tumors. Moreover, in cardiovascular surgery, VR enables surgeons to simulate and plan procedures for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or valve replacements.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of VR in providing crucial diagnostic information and planning procedures across various medical disciplines.
Technological Advancements and Challenges
Virtual reality (VR) is rapidly evolving, bringing exciting new possibilities for healthcare. From immersive surgical training to personalized rehabilitation programs, VR’s potential is vast. However, realizing this potential requires overcoming certain technological hurdles and adapting to the specific demands of healthcare settings. This section delves into the current state of VR in healthcare, exploring the latest advancements, inherent limitations, and the ongoing research aimed at addressing these challenges.The field of VR in healthcare is witnessing a surge in innovation.
Researchers and developers are continuously refining VR hardware and software to enhance user experience and efficacy. These advancements are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in patient care, diagnostics, and training.
Latest Technological Advancements
VR headsets are becoming more lightweight, comfortable, and affordable, enabling prolonged use in clinical settings. Improved tracking systems offer enhanced precision and responsiveness, crucial for tasks like surgical simulations and rehabilitation exercises. Advanced haptic feedback technologies are providing more realistic tactile sensations, making virtual interactions more engaging and informative. Eye-tracking technology is also improving, allowing for more nuanced and responsive VR experiences, and enabling better user feedback.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite the advancements, several challenges persist. High initial investment costs can limit widespread adoption, especially in resource-constrained healthcare environments. Ensuring data security and patient privacy in VR systems is paramount. Standardization of VR hardware and software is still lacking, which hinders interoperability and integration with existing healthcare infrastructure. The need for skilled personnel to operate and maintain VR systems, as well as training healthcare professionals on VR applications, remains a hurdle.
Current Research and Development
Researchers are actively exploring new applications of VR in healthcare, including virtual reality-assisted therapy for mental health conditions, creating realistic simulations for complex procedures, and developing personalized rehabilitation programs. There is significant research into integrating VR with other technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI), to create more comprehensive and effective healthcare solutions. For example, AI-powered VR systems could provide real-time feedback and guidance during surgical simulations, leading to more precise and efficient procedures.
Key Technical Challenges
- Cost-effectiveness: VR hardware and software remain relatively expensive, limiting accessibility for many healthcare facilities and patients. Finding ways to reduce costs and make VR solutions more affordable is a crucial challenge.
- User experience (UX): Creating immersive and engaging VR experiences that are comfortable and intuitive for users, including healthcare professionals and patients, is critical. This involves addressing issues such as motion sickness and user fatigue.
- Data security and privacy: Protecting patient data within VR systems and ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA is paramount. Robust security protocols are essential.
- Integration with existing systems: Seamlessly integrating VR technology into existing healthcare workflows and electronic health records (EHR) systems is necessary for practical implementation.
- Standardization and interoperability: Lack of standardization in VR hardware and software creates compatibility issues. Establishing common protocols and standards will enable easier integration and collaboration across different VR systems.
Potential Future Advancements
Future advancements in VR technology for healthcare are likely to focus on personalized VR experiences, incorporating patient-specific data and preferences. Integration with other technologies like AI and AR will create more sophisticated and comprehensive healthcare solutions. For instance, AR overlays could provide real-time anatomical guidance during surgical procedures, while AI algorithms could analyze VR data to provide personalized feedback and insights.
Comparison of VR Hardware Options
| Hardware | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| High-end VR headsets (e.g., HTC Vive Pro 2, Meta Quest Pro) | High resolution, high-fidelity visuals, advanced tracking, and robust haptic feedback. | High cost, potential for user discomfort (especially for extended use), complex setup. |
| Mid-range VR headsets (e.g., Meta Quest 2) | Affordable, good visual quality, relatively easy setup, comfortable for shorter sessions. | Lower resolution compared to high-end options, less precise tracking. |
| Mobile VR headsets (e.g., Google Cardboard) | Most affordable, easily accessible. | Lowest resolution and least precise tracking, limited capabilities for complex tasks. |
Impact on Healthcare Professionals and Patients: Virtual Reality Gaining Traction In Healthcare
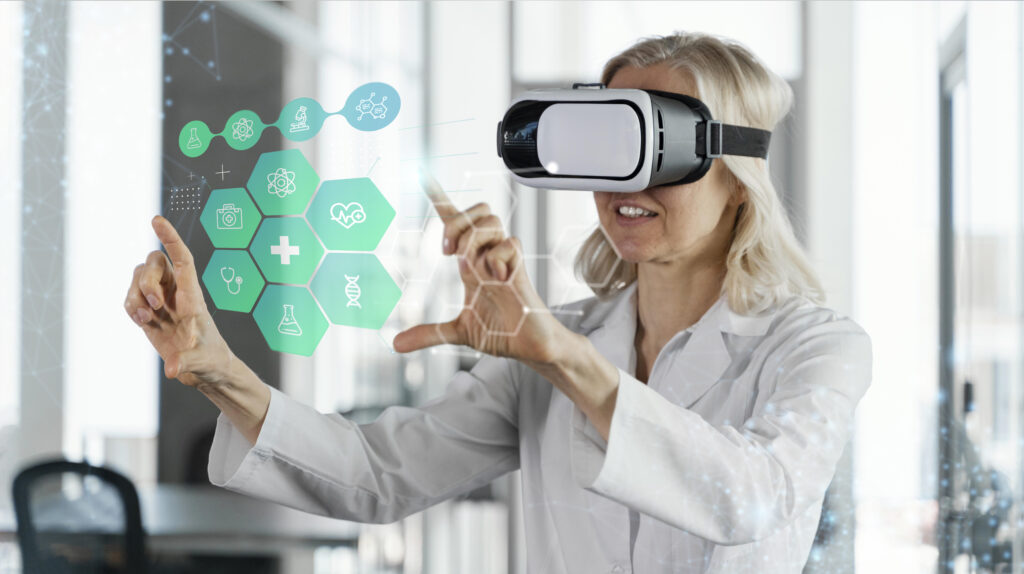

Virtual reality (VR) is rapidly transforming healthcare, impacting both the training of professionals and the patient experience. Its immersive nature allows for realistic simulations and interactive scenarios, leading to improved skills and knowledge retention. This technology offers patients a more engaging and personalized approach to their care, potentially fostering a stronger sense of understanding and control over their health journey.VR’s ability to create simulated environments and scenarios provides a safe and controlled space for healthcare professionals to hone their skills.
Patients benefit from a more interactive and personalized approach to treatment, leading to increased engagement and better outcomes.
Impact on Healthcare Professional Training
VR simulations provide a valuable tool for healthcare professionals, offering a safe and repeatable environment to practice complex procedures and techniques. This can include surgical training, where surgeons can practice intricate procedures on virtual anatomical models without the risk of harming a patient. Similarly, emergency response teams can rehearse critical scenarios, honing their decision-making abilities and improving response times.
This immersive experience is particularly effective in training for procedures that require fine motor skills or delicate manipulation.
- Enhanced Skill Development: VR allows healthcare professionals to practice procedures in a risk-free environment, repeating them as needed to perfect their technique.
- Realistic Simulations: Virtual environments replicate real-world scenarios, allowing practitioners to rehearse handling various situations and making informed decisions in a simulated crisis.
- Improved Knowledge Retention: Active participation in VR training promotes deeper understanding and retention of complex information.
- Reduced Cost: VR-based training can be significantly more cost-effective than traditional methods, particularly for repeated training sessions.
Benefits for Patient Engagement and Experience
VR offers a unique opportunity to engage patients in their care, creating a more interactive and informative experience. Patients can visualize their conditions, explore treatment options, and participate in rehabilitation exercises within a safe and supportive environment.
- Increased Patient Engagement: VR allows patients to actively participate in their care by interacting with virtual models of their bodies and conditions, leading to a stronger sense of understanding and ownership.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: VR can help tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs, preferences, and responses, enhancing treatment efficacy.
- Improved Pain Management: VR therapy can provide distraction and relaxation techniques for patients experiencing pain, potentially reducing the need for medication.
- Enhanced Mental Well-being: Immersive VR experiences can help patients cope with anxiety, stress, and other mental health challenges related to illness.
Patient Understanding of Conditions
VR provides an accessible and interactive way for patients to visualize their conditions and understand their treatment options. Patients can explore their anatomy, see how their disease affects their body, and participate in virtual simulations to understand the impact of different treatment approaches.
- Visualization of Complex Conditions: VR allows patients to visualize complex medical conditions, providing a clear understanding of the disease’s impact on their body.
- Interactive Exploration of Treatment Options: Patients can virtually experience different treatment approaches, gaining a deeper understanding of each option’s potential benefits and risks.
- Personalized Education: VR-based educational tools can provide patients with personalized information, addressing their specific questions and concerns.
Comparison of VR-Based Treatment with Traditional Methods
VR-based treatment offers a significant departure from traditional methods, offering a more engaging, interactive, and personalized experience. Traditional methods often rely on static images, text-based explanations, and passive learning. VR enables patients to actively participate in their treatment journey, leading to increased comprehension and motivation.
| Feature | VR-Based Treatment | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | High, interactive, personalized | Low, passive, generalized |
| Understanding | Deep, visual, hands-on | Limited, often theoretical |
| Motivation | Increased due to active participation | Potentially lower due to passive approach |
| Cost | Can be higher initially but potentially lower in the long term | Generally lower upfront cost |
Advantages and Disadvantages of VR for Healthcare Professionals
VR offers numerous benefits for healthcare professionals, but also presents some challenges.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved skill development | High initial cost of VR equipment |
| Realistic simulations | Potential for motion sickness |
| Reduced risk of errors | Technical support requirements |
| Enhanced knowledge retention | Need for appropriate training |
| Increased efficiency | Limited availability of VR-based training programs |
VR Enhancement of Patient Experience and Engagement
VR significantly enhances the patient experience by providing a more interactive and engaging approach to treatment and care.
| Enhancement | Description |
|---|---|
| Interactive Learning | VR allows patients to actively participate in learning about their condition and treatment options. |
| Personalized Experience | VR tools can be customized to meet individual patient needs and preferences. |
| Improved Understanding | VR helps patients visualize their conditions and treatment options in a concrete way. |
| Increased Motivation | VR-based activities can boost patient engagement and commitment to their recovery. |
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
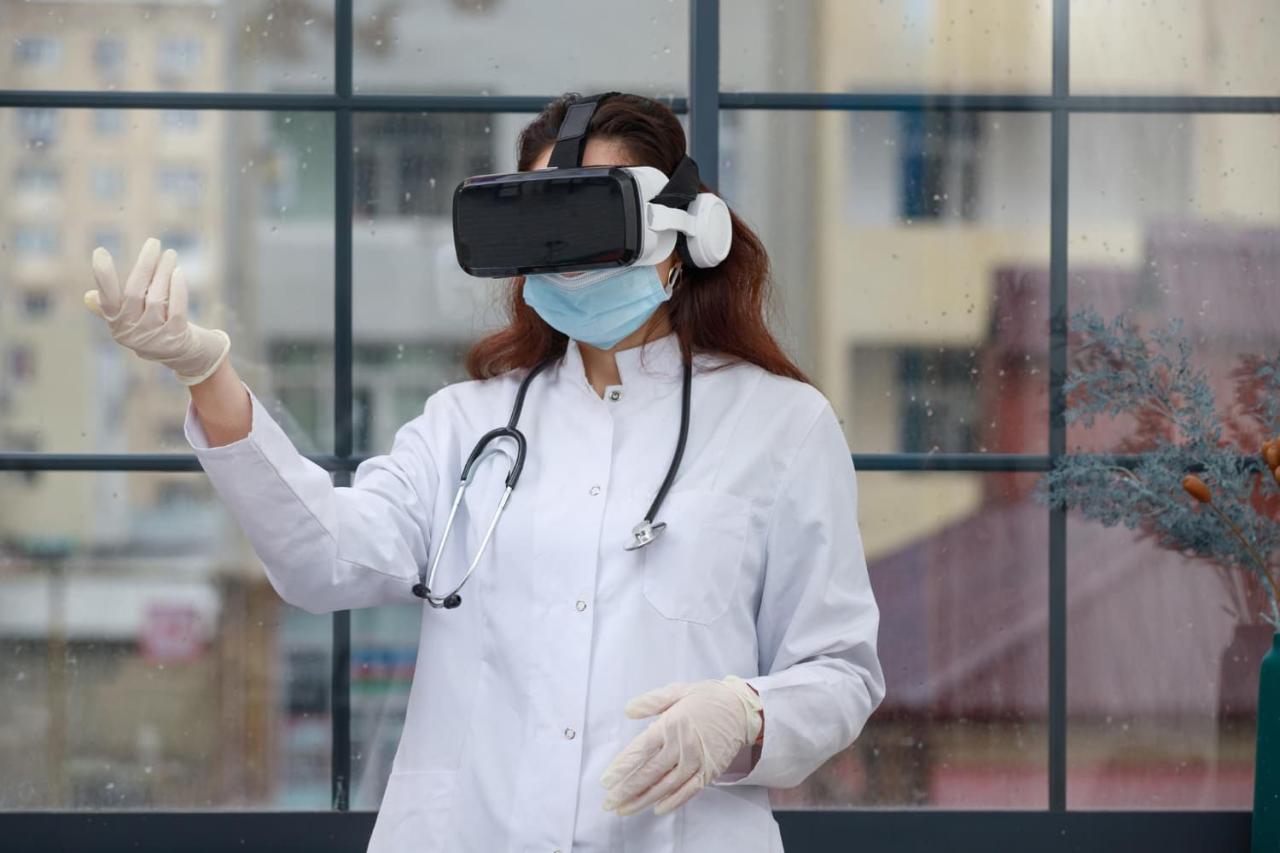

Virtual reality (VR) technology is rapidly transforming healthcare, offering exciting possibilities for patient care, training, and diagnostics. However, its integration into the medical field necessitates careful consideration of the ethical implications and potential pitfalls. Addressing privacy concerns, data security, and potential biases is crucial for responsible implementation and widespread adoption.The ethical landscape surrounding VR in healthcare is complex, requiring a nuanced approach that balances the benefits of innovation with the rights and well-being of patients and healthcare professionals.
This section explores the ethical considerations, potential future directions, and emerging trends in VR healthcare, emphasizing the need for proactive measures to mitigate risks and maximize benefits.
Ethical Implications of VR in Healthcare
VR applications in healthcare present a range of ethical dilemmas, often arising from the unique characteristics of immersive experiences. These experiences can significantly impact patient autonomy, consent, and the physician-patient relationship. The ability of VR to create highly realistic and emotionally charged scenarios raises questions about the appropriateness of using such experiences in therapeutic settings.
Privacy and Data Security Concerns, Virtual reality gaining traction in healthcare
VR applications in healthcare often involve the collection and processing of sensitive patient data. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is paramount. Data breaches, unauthorized access, and misuse of information pose significant risks. Strong data encryption, secure storage protocols, and transparent data policies are essential to protect patient confidentiality.
Examples of Ethical Dilemmas Related to VR in Healthcare
One ethical dilemma is the potential for bias in VR training simulations. If simulations do not accurately reflect the diversity of patient populations, healthcare professionals may develop implicit biases that could affect their decision-making in real-world situations. Another example involves patient consent. Patients may not fully understand the implications of participating in VR-based therapies or diagnostics, potentially leading to informed consent issues.
Furthermore, the use of VR in mental health could potentially create emotional distress or exacerbate pre-existing conditions if not carefully managed.
Potential Future Directions of VR in Healthcare
Future directions in VR healthcare will likely involve more sophisticated applications and a wider range of use cases. This includes developing more sophisticated VR-based surgical training simulations, personalized rehabilitation programs tailored to individual patient needs, and immersive environments for chronic pain management. Furthermore, the integration of VR with artificial intelligence (AI) and other technologies will likely enhance its capabilities in areas like diagnosis and treatment planning.
Emerging Trends in VR Healthcare
The development of more sophisticated VR hardware and software is a significant trend. This includes advancements in haptic feedback technology, which allows users to experience more realistic sensations, and improvements in eye-tracking technology, enabling more precise and personalized experiences. The development of more user-friendly interfaces and personalized VR experiences tailored to individual needs is also expected.
Potential Areas of Future Research and Development in VR Healthcare
Future research in VR healthcare should focus on understanding the long-term effects of VR exposure on patients, developing effective strategies for mitigating potential psychological distress, and exploring the potential of VR to address disparities in access to healthcare. Moreover, there is a need to study the effectiveness of VR in different patient populations and healthcare settings, and to investigate the optimal integration of VR with existing healthcare infrastructure.
Ethical Challenges and Potential Solutions in VR Healthcare
| Ethical Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Patient privacy and data security | Implement robust data encryption and secure storage protocols. Establish clear data governance policies and obtain explicit patient consent. |
| Potential for bias in VR simulations | Develop diverse and representative VR simulations. Use rigorous testing methodologies to evaluate the impact of simulations on different demographics. |
| Lack of understanding of VR implications | Develop clear and concise explanations of VR applications. Provide comprehensive patient education and obtain informed consent. |
| Potential for emotional distress in VR therapies | Monitor patients closely during VR therapy sessions. Develop protocols to address and mitigate potential negative reactions. Provide support services for patients who experience distress. |
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, virtual reality’s impact on healthcare is undeniable. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are significant, ranging from improved surgical precision to enhanced patient experience and reduced anxiety. As VR technology continues to evolve, its integration into the healthcare ecosystem promises to reshape the future of patient care and medical training, driving a new era of personalized and effective treatment strategies.