What is flurona and how serious can it be? This new viral combination, a co-infection of influenza and COVID-19 variants, raises important questions about its transmission, severity, and public health response. Understanding the specific viruses involved, how they interact, and the potential impact on individuals and communities is crucial.
This article delves into the characteristics of flurona, exploring its definition, transmission patterns, potential severity, and the necessary public health strategies. We will examine the common symptoms, how they might differ from those of individual infections, and the diagnostic and treatment approaches. The article also highlights the risk factors, potential long-term effects, and the critical role of public health measures in managing this emerging threat.
Understanding Flurona
Flurona, a term coined for the co-infection of influenza and COVID-19, presents a unique challenge in terms of diagnosis and treatment. While not a new phenomenon, the increasing prevalence of both viruses highlights the potential for more complex clinical presentations. This understanding is crucial for healthcare professionals to effectively manage cases and for individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Defining Flurona
Flurona refers to the simultaneous infection of a person with both influenza and SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19). This co-infection can occur with various influenza strains and COVID-19 variants. The scientific basis for the term lies in the independent transmission and replication of these viruses within the host. Both viruses can infect the respiratory tract, creating an environment where they can multiply and potentially interact, although the interaction mechanisms are not fully understood.
The presence of both viruses leads to a co-infection, increasing the likelihood of a more severe or prolonged illness, compared to either infection alone. The specific conditions for co-infection are generally the same as for single infections, with the important caveat that exposure to both viruses simultaneously increases the likelihood.
Common Symptoms of Flurona
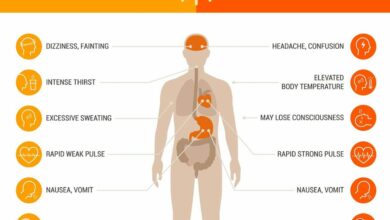
The symptoms of Flurona often overlap with those of influenza and COVID-19, making accurate diagnosis challenging. Individuals experiencing Flurona may exhibit a range of symptoms, which can vary in severity. Common symptoms include fever, cough, body aches, and fatigue. The severity and duration of symptoms can also vary significantly, depending on the individual’s overall health and the specific strains of influenza and COVID-19 involved.
Comparing Symptoms of Influenza, COVID-19, and Flurona
| Symptom | Influenza | COVID-19 | Flurona |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | Likely | Possible | Likely |
| Cough | Likely | Possible | Likely |
| Body Aches | Possible | Possible | Possible |
| Runny Nose | Likely | Possible | Possible |
| Sore Throat | Likely | Possible | Possible |
| Headache | Possible | Possible | Possible |
| Fatigue | Possible | Likely | Likely |
Note: The presence and severity of symptoms can vary significantly between individuals. The table provides a general overview, and individual experiences may differ.
Transmission and Spread

The emergence of Flurona, a co-infection of influenza and SARS-CoV-2, raises concerns about its transmission dynamics. Understanding how this combined infection spreads is crucial for effective preventative measures and public health responses. While the underlying mechanisms are similar to those of individual viruses, the combined presence introduces potential complexities.The potential routes of transmission for Flurona are essentially the same as for influenza and SARS-CoV-2.
Respiratory droplets, produced through coughing, sneezing, or talking, are the primary mode of transmission for both viruses. Close contact with infected individuals, particularly within confined spaces, significantly increases the risk of exposure. Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the face can also play a role in transmission. Understanding that Flurona combines these routes makes the importance of hygiene and social distancing paramount.
So, flurona, a combination of flu and COVID, is definitely something to be aware of. While it can sometimes cause unpleasant symptoms, it’s generally not considered as serious as a severe case of the flu alone, or even a serious case of COVID-19, especially in those who are vaccinated. But honestly, managing the exhaustion that comes with a little one who just won’t sleep can be incredibly tough.
Learning how to manage that exhaustion is crucial for your overall well-being, and this article on how to manage exhaustion when your kid still wont sleep could be a game-changer. Ultimately, staying informed about flurona and taking precautions, like getting vaccinated, is key to keeping yourself and your family healthy.
Potential Transmission Differences
The combined presence of influenza and SARS-CoV-2 in a single individual may alter the infection’s characteristics, potentially affecting transmission rates. Studies have shown that co-infections can sometimes lead to a more severe or prolonged illness. This is a significant factor in assessing the potential impact of Flurona on community transmission. The overall severity of a Flurona infection could potentially influence the duration of contagiousness, although further research is necessary to determine the precise impact.
It is important to remember that co-infections may not always be more severe, and the severity can vary significantly from person to person.
Prevention Measures
Maintaining robust preventative measures remains crucial in mitigating the spread of Flurona. These measures mirror those for influenza and SARS-CoV-2, and their efficacy is essential.
- Vaccination: Vaccination against influenza and SARS-CoV-2 is a critical preventive measure. Vaccinations reduce the likelihood of infection and, critically, lower the severity of illness. Up-to-date vaccination against both viruses should be prioritized.
- Hygiene Practices: Frequent handwashing with soap and water, or hand sanitizers containing at least 60% alcohol, are fundamental hygiene practices to prevent transmission. Covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or elbow is equally important in limiting the spread of respiratory droplets. Avoiding close contact with infected individuals, especially in crowded environments, can substantially reduce the risk of transmission.
- Social Distancing: Maintaining appropriate social distancing, particularly in indoor settings, can help reduce the risk of transmission. Maintaining physical space from others can minimize exposure to respiratory droplets and aerosol particles carrying the viruses.
Impact on Community Transmission
The impact of Flurona on community transmission is a subject of ongoing research and study. Modeling studies and real-world data are needed to fully understand the dynamics of co-infection outbreaks.
- Increased Transmission Rates: The combined presence of both viruses could potentially increase the overall transmission rate within a community compared to separate outbreaks of either virus alone. A possible scenario is the rapid spread, especially in vulnerable populations. This is a complex dynamic that requires continuous monitoring.
- Super-Spreader Events: Super-spreader events, where a single individual transmits the infection to numerous others, could be amplified in the case of Flurona. These events could significantly accelerate community transmission, highlighting the importance of preventative measures.
- Shifting Epidemiology: The combined presence of the viruses might shift the epidemiology of respiratory infections in a community. This could potentially impact hospital capacity and healthcare resource allocation. Ongoing monitoring is crucial to understand these shifts.
Severity and Risk Factors

Understanding the severity of a Flurona infection is crucial for proactive health management. Factors like underlying health conditions and individual immune responses play a significant role in determining how the body reacts to the combined viral load. This section delves into the potential risk factors and the spectrum of severity, from mild to life-threatening cases.
Risk Factors for Severe Complications
Several factors increase the risk of severe complications from Flurona. Age is a prominent one, with individuals at the extremes of age—very young children and older adults—often exhibiting a higher vulnerability to severe illness. Pre-existing health conditions also significantly influence the potential severity of the infection. Chronic respiratory illnesses like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cystic fibrosis are major risk factors, as these conditions already compromise lung function, making the individual more susceptible to respiratory complications.
Cardiovascular conditions such as heart failure, high blood pressure, and coronary artery disease also increase the risk of severe illness. Weakened immune systems, whether due to medical treatments or underlying conditions, can lead to more severe outcomes. Obesity is another significant risk factor.
Underlying Health Conditions
Numerous underlying health conditions can exacerbate the severity of Flurona. Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder, can lead to impaired immune function and increased susceptibility to infections. Kidney disease, affecting the body’s filtration system, can make it harder for the body to fight off infections. Individuals with liver disease may have compromised immune responses, increasing their vulnerability. Weakened immune systems, such as those resulting from HIV/AIDS or organ transplantation, significantly increase the risk of severe complications from Flurona.
Flurona, a combination of influenza and COVID-19, is a relatively new concern, but thankfully, it’s usually not as severe as a double infection. While symptoms can be unpleasant, it’s important to be aware that some CBD products are frequently mislabeled, sometimes containing THC, which is a psychoactive compound. For more info on that, check out this article about cbd products often mislabeled some containing thc what to know.
Ultimately, understanding the severity of flurona is key for staying informed and making responsible decisions about your health.
The impact of pre-existing conditions on the body’s ability to fight off the infection is a critical aspect of evaluating the potential for severe illness.
Potential Severity Levels of Flurona Infection
The severity of Flurona infection can range from mild to severe, impacting individuals differently. The following table Artikels the potential severity levels and associated characteristics:
| Severity Level | Description | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | Self-limiting illness, usually resolving within a week or two. | Mild fever, cough, sore throat, fatigue, and occasional body aches. | Rest, fluids, over-the-counter medications for symptom relief. |
| Moderate | Requires medical attention, potentially necessitating hospitalization. | High fever, persistent cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain, and rapid heart rate. | Hospitalization, supportive care, and potential use of antiviral medications or oxygen therapy. |
| Severe | Life-threatening, requiring intensive care. | Severe respiratory distress, low blood oxygen levels, and organ dysfunction. | Intensive care unit (ICU) admission, mechanical ventilation, and supportive therapies. |
Long-Term Effects of Flurona
While most individuals recover fully from Flurona, some may experience long-term effects, often referred to as long COVID. These effects can vary significantly, from persistent fatigue and breathing problems to cognitive impairments and cardiovascular issues. The long-term consequences are still being investigated, and the exact prevalence and impact are yet to be fully understood. More research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects and develop appropriate strategies for managing them.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Navigating a Flurona infection requires a multifaceted approach that combines accurate diagnosis with appropriate treatment strategies. Understanding the nuances of testing and treatment protocols is crucial for managing this dual viral infection effectively and minimizing potential complications.The diagnostic process for Flurona involves confirming the presence of both influenza viruses and SARS-CoV-2. This often necessitates multiple tests, targeting each virus separately.
Rapid antigen tests can be helpful for initial screening, but confirmation often relies on polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for both viruses. These tests identify the genetic material of the viruses, providing a definitive diagnosis.
Diagnostic Process for Flurona
A comprehensive diagnostic strategy is essential to accurately identify and manage Flurona. Initial screening with rapid antigen tests can be valuable, but confirmation typically requires PCR testing. This dual testing approach allows healthcare providers to distinguish between co-infection and separate infections.
Flurona, a combination of influenza and COVID-19, is a concern, but generally, the severity seems to be similar to a typical flu infection. However, underlying health conditions can make anyone more vulnerable, and the link between a condition like incontinence, particularly in women over 50, as highlighted in this article ( half of women over 50 have had incontinence 2 ), could influence how the body handles viral infections.
This underscores the importance of considering individual health factors when assessing the potential impact of flurona.
- Rapid Antigen Tests: These tests detect viral proteins, offering quick results. However, they might yield false negatives, necessitating further confirmation.
- PCR Testing: This molecular technique amplifies viral genetic material, providing highly accurate results. Separate PCR tests are typically performed to identify both influenza viruses and SARS-CoV-2.
Standard Treatments for Flurona
Standard treatments for Flurona primarily focus on managing symptoms and supporting the body’s immune response. There’s no specific antiviral medication explicitly designed for both viruses simultaneously. Instead, treatments address each infection individually.
- Symptom Management: Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications like pain relievers and fever reducers can alleviate discomfort associated with the infection.
- Supportive Care: Maintaining adequate hydration and nutrition is essential. If complications arise, such as pneumonia or severe respiratory distress, hospitalization may be necessary for supportive care.
Antiviral Medications
Several antiviral medications are available for influenza and SARS-CoV-2. However, the optimal strategy for Flurona involves using these medications based on the specific viral types detected.
- Influenza Antivirals: Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir are examples of antiviral medications that can be effective against influenza. Early initiation is crucial to limit the severity of the infection.
- SARS-CoV-2 Antivirals: Paxlovid and molnupiravir are examples of antiviral medications that can be used for SARS-CoV-2. These medications are often prescribed for high-risk individuals to prevent severe illness.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment, What is flurona and how serious can it be
Early diagnosis and treatment of Flurona are crucial to minimize complications and improve outcomes. Early intervention can help prevent the progression of the illness and reduce the risk of severe respiratory complications. This is particularly important for vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions.
- Prevention of Severe Illness: Prompt diagnosis and treatment can reduce the risk of severe respiratory complications, including pneumonia.
- Reduced Hospitalization: Early intervention can often prevent the need for hospitalization, especially for those at higher risk.
Public Health Response
The emergence of flurona, a co-infection of influenza and COVID-19, necessitates a nuanced public health response. This response must consider the unique challenges presented by the dual viral threat while building upon established strategies for individual viruses. The approach needs to be flexible, adaptive, and prioritize public health measures that are effective and scalable.The response to flurona outbreaks must account for the combined effect of two viruses on the population.
While individual strategies for influenza and COVID-19 have proven effective, their combined impact on transmission, severity, and resource allocation needs to be evaluated and adapted. This includes careful consideration of potential overlaps and redundancies in existing public health infrastructure.
Public Health Measures
Public health measures in response to flurona outbreaks are likely to build upon existing strategies for influenza and COVID-19. This means a multifaceted approach encompassing vaccination, hygiene, and social distancing. The key lies in adapting these measures to the combined threat, possibly implementing stricter guidelines or more targeted interventions where necessary.
Differing Measures from Influenza or COVID-19 Alone
The response to flurona might differ from the response to influenza or COVID-19 in several key aspects. For example, the combined nature of flurona necessitates a more comprehensive approach to vaccination, potentially involving a combined vaccine or a more proactive vaccination strategy. Enhanced hygiene measures, already well-established in the COVID-19 era, may be further reinforced to account for the dual threat.
Similarly, while social distancing played a crucial role in the COVID-19 response, a similar strategy may be adopted or enhanced for flurona, particularly in vulnerable populations or high-risk settings.
Comparative Analysis of Strategies
The following table compares public health strategies for influenza, COVID-19, and flurona, highlighting potential differences.
| Strategy | Influenza | COVID-19 | Flurona |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccination | Annual, focused on seasonal strains | Ongoing, evolving based on variant emergence | Combined or separate, possibly with enhanced booster campaigns |
| Hygiene Measures | Standard recommendations (handwashing, covering coughs) | Enhanced recommendations (frequent handwashing, mask-wearing, avoiding crowds) | Standard + enhanced, with a focus on sustained adherence to hygiene protocols |
| Social Distancing | Possible in high-risk settings or during outbreaks | Essential, with varying levels of restrictions in place | Possible + enhanced, with a need to identify high-risk scenarios and implement targeted measures |
Public Health Communication Framework
A robust public health communication framework for flurona is crucial for effective response and public understanding. This framework should:
- Emphasize clear and consistent messaging across all channels, using easily understandable language. This is vital to ensure clarity and avoid confusion.
- Highlight the importance of continued vaccination efforts, perhaps with information on how to combine influenza and COVID-19 vaccination for optimal protection.
- Provide up-to-date information on transmission routes, risk factors, and symptoms, recognizing the dual nature of the virus.
- Encourage adherence to hygiene practices, including regular handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick.
- Promote responsible social distancing measures, including mask-wearing in crowded areas and avoiding unnecessary gatherings.
Epilogue: What Is Flurona And How Serious Can It Be
In conclusion, flurona presents a unique challenge for public health. While the severity often aligns with typical influenza or COVID-19 infections, understanding the combined impact is crucial. The need for comprehensive preventative measures, including vaccinations (where available), diligent hygiene, and potentially enhanced social distancing protocols, remains paramount. The article has provided insights into various aspects of flurona, emphasizing the significance of proactive public health strategies and individual responsibility in managing this co-infection risk.