
What is polio like disease affecting kids – What is polio-like disease affecting kids? This exploration dives deep into the world of debilitating illnesses mimicking polio, focusing on their impact on young lives. We’ll uncover the common symptoms, historical context, and geographical spread, shedding light on these often overlooked conditions.
Understanding these illnesses is crucial for recognizing the symptoms, aiding in early diagnosis, and ultimately supporting the well-being of affected children. We’ll also delve into the causes, transmission methods, and available treatments, equipping readers with a comprehensive understanding of the challenges faced by families.
Introduction to Polio-like Diseases Affecting Children
Polio-like diseases, characterized by the sudden onset of muscle weakness and paralysis, represent a significant threat to children’s health globally. While polio itself has been largely eradicated, other viral and infectious conditions can mimic its symptoms, demanding careful diagnosis and treatment. Understanding these diseases is crucial for effective prevention and management.These conditions, though distinct in their etiology, share common characteristics, including the potential for debilitating paralysis and the disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations.
Polio, a debilitating disease, once crippled many children. Thankfully, vaccines have largely eradicated it. While we’re making strides in treating other childhood illnesses, like the potential breakthrough with a patch for peanut allergies shows promise, the need to find better ways to prevent and treat diseases like polio remains vital. This kind of research helps us understand and address the complex challenges of childhood illnesses.
Early recognition of symptoms and appropriate medical intervention are essential to mitigating the long-term consequences of these diseases.
Common Symptoms of Polio-like Diseases
Children experiencing polio-like diseases often exhibit a range of symptoms, which can vary depending on the specific condition. These symptoms frequently include fever, headache, sore throat, nausea, and vomiting. Muscle weakness, particularly in the limbs, is a prominent feature, often progressing to paralysis in severe cases. The progression of symptoms can differ significantly between diseases.
Historical Context of Polio-like Diseases, What is polio like disease affecting kids
The history of polio-like diseases is intertwined with human health challenges. These diseases have plagued communities for centuries, causing significant morbidity and mortality, particularly among children. Historical records detail outbreaks that led to widespread fear and public health interventions. Efforts to understand and control these diseases have evolved alongside advancements in medical knowledge and technology.
Geographical Distribution of Polio-like Diseases
The geographical distribution of polio-like diseases varies considerably. While some diseases may have a more global presence, others are concentrated in specific regions. Factors such as sanitation, hygiene, and access to healthcare influence the prevalence and distribution of these diseases. The ongoing monitoring of these diseases is crucial to identify potential outbreaks and implement preventive measures effectively.
Comparison of Polio-like Diseases
| Disease | Symptoms | Transmission | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Flaccid Myelitis (AFM) | Sudden onset of muscle weakness, often affecting the limbs; fever, headache, sore throat; some cases with mild or no symptoms. | Likely viral, but the exact cause is unknown. | Can range from mild muscle weakness to permanent paralysis. Prognosis varies considerably. |
| West Nile Virus | Often mild or asymptomatic; fever, headache, body aches, nausea, vomiting; in some cases, more serious neurological complications like encephalitis or meningitis. | Transmitted primarily by mosquitoes. | Serious neurological complications are possible but are less common in children. |
| Japanese Encephalitis | High fever, headache, stiff neck, disorientation, seizures; potentially leading to brain swelling (encephalitis). | Transmitted by infected mosquitoes. | Can lead to severe neurological damage and even death, particularly in children. |
| Poliomyelitis (Polio) | Initial symptoms include fever, headache, sore throat, nausea, and vomiting; progressing to muscle weakness and paralysis in severe cases. | Fecal-oral transmission. | Paralysis, in some cases, can be permanent. The severity varies considerably. |
The table above provides a general comparison of different polio-like diseases. Specific symptoms, transmission routes, and severity can vary based on individual cases and the specific disease. Consulting a medical professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Causes and Transmission of Polio-like Diseases
Understanding the causes and transmission pathways of polio-like diseases is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies. These illnesses, while often mimicking polio in their symptoms, can have diverse origins and modes of spread. This knowledge empowers healthcare providers and communities to take proactive measures to protect children.
Polio-like diseases in kids can be devastating, impacting their ability to move freely. These illnesses often target the nervous system, making simple tasks like walking or lifting their arms difficult. Understanding the intricate workings of the body, like the superficial muscles of the neck, superficial muscles of neck , is crucial in comprehending the impact these diseases have on the body’s overall function.
It’s important to remember that these illnesses can hinder a child’s physical development and overall well-being.
Causes of Polio-like Diseases
Polio-like diseases encompass a spectrum of conditions, each with its unique set of causative agents. Viral infections are frequently implicated, with enteroviruses being prominent culprits. Bacterial infections can also trigger similar symptoms. In some cases, the underlying cause might be a combination of factors, including nutritional deficiencies or pre-existing health conditions that weaken the immune system. Certain toxins or environmental exposures can also contribute to the development of polio-like symptoms.
Transmission Methods
The transmission of polio-like diseases varies depending on the specific causative agent. Fecal-oral transmission is a common mechanism, where the virus or bacteria present in contaminated food or water enters the body through the mouth. Direct contact with infected individuals can also spread the illness, especially in close-knit communities. In some cases, airborne transmission might play a role, although this is less frequent than other routes.
Role of Hygiene and Sanitation
Maintaining proper hygiene and sanitation practices are fundamental in preventing the spread of polio-like diseases. Washing hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially after using the restroom and before eating, is a simple yet effective measure. Safe disposal of waste and ensuring access to clean water sources are critical aspects of public health interventions. Improved sanitation infrastructure plays a vital role in mitigating the risk of outbreaks.
Risk Factors for Children
Several factors increase a child’s susceptibility to polio-like diseases. Malnutrition weakens the immune system, making children more vulnerable to infections. Crowded living conditions and poor sanitation in communities can facilitate the rapid spread of diseases. Lack of access to healthcare and vaccination programs can also increase the risk. Children with pre-existing medical conditions, such as weakened immune systems, are at higher risk of developing severe complications from these illnesses.
Transmission Routes for Polio-like Diseases
| Disease | Transmission Route(s) |
|---|---|
| Enteroviral Infections | Fecal-oral, respiratory droplets (less common) |
| Bacterial Infections (e.g., meningitis) | Respiratory droplets, direct contact, contaminated food/water |
| Parasitic Infections (e.g., giardiasis) | Fecal-oral |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Indirectly increasing susceptibility to infections; poor immune response |
This table summarizes the various transmission routes for different types of polio-like diseases, highlighting the importance of recognizing the specific mode of transmission to develop targeted preventive measures.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Polio-like Diseases
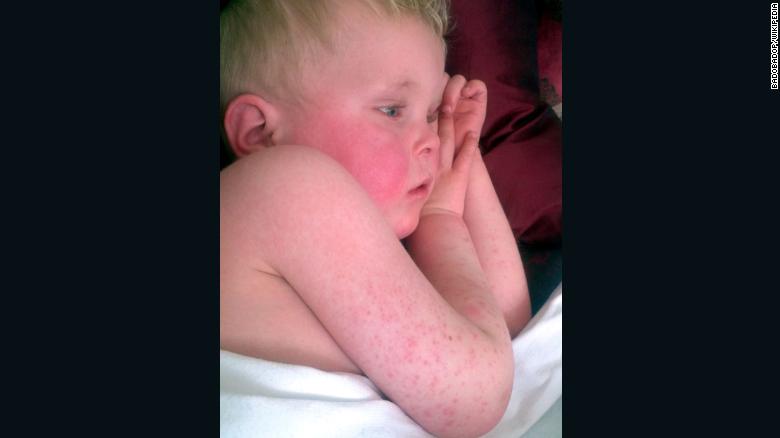
Diagnosing and treating polio-like diseases requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing a range of diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies tailored to the specific clinical presentation. Early detection and intervention are crucial in minimizing the severity of the illness and improving long-term outcomes. The availability and accessibility of these diagnostic and therapeutic methods vary significantly across different regions and healthcare systems.The diagnostic process for polio-like illnesses often involves a combination of clinical assessments, laboratory tests, and sometimes, imaging studies.
Treatment strategies, similarly, can involve antiviral medications, supportive care, and rehabilitation programs, each with varying levels of efficacy and potential side effects. Careful consideration of individual patient factors and disease characteristics is paramount in determining the most appropriate course of action.
Common Diagnostic Methods
Accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective treatment for polio-like illnesses. Initial assessment involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, focusing on the onset, progression, and associated symptoms. Physical examination, including neurological assessments, helps identify specific signs and symptoms indicative of the disease. Neurological examination assesses muscle strength, reflexes, and sensory function to identify potential nerve damage.Laboratory tests play a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis and differentiating polio-like diseases from other neurological conditions.
These tests may include cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis to detect inflammatory markers or viral agents. In some cases, specific viral cultures or molecular tests might be employed to identify the causative pathogen. These diagnostic methods can aid in differentiating between various types of polio-like illnesses and guide treatment decisions.
Polio, a disease that used to be a serious threat to kids, can leave lasting physical effects. Beyond the physical toll, chronic pain can significantly impact mental well-being. Learning how to manage chronic pain and its effects on mental health is crucial, as seen in this helpful resource on chronic pain can worsen mental health what can be done.
Understanding how to support children facing these challenges is vital, as is recognizing the parallels to polio-like symptoms, like muscle weakness and fatigue, in the context of chronic pain. Ultimately, supporting kids’ well-being in the face of these challenges is key.
Available Treatments
Treatment for polio-like diseases primarily focuses on managing symptoms and supporting the body’s recovery. Supportive care is often the mainstay of treatment, encompassing measures to alleviate pain, manage fever, and prevent secondary infections. Rehabilitation programs play a vital role in helping patients regain lost function and improve their quality of life. In some cases, antiviral medications may be considered, but their effectiveness varies greatly depending on the causative agent.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in mitigating the long-term effects of polio-like illnesses. Prompt medical attention allows for the initiation of appropriate treatment, potentially limiting the extent of nerve damage and muscle weakness. Early intervention can also reduce the risk of complications, such as respiratory failure or long-term disability.
Role of Supportive Care
Supportive care plays a critical role in managing polio-like diseases. It encompasses a wide range of interventions aimed at alleviating symptoms and improving the patient’s overall well-being. Pain management, nutritional support, and respiratory assistance are integral components of supportive care, helping to maintain comfort and promote recovery. Physical therapy and occupational therapy are also critical to helping patients regain strength and function.
Comparison of Treatment Approaches
| Disease Type | Treatment Approach | Effectiveness | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Polio-like illness (caused by a specific virus) | Antiviral medications + Supportive Care | Moderate to High, depending on early intervention | Potential for drug-specific side effects, such as nausea or vomiting; Supportive care generally has low side effects |
| Type 2 Polio-like illness (caused by a different virus) | Antiviral medications + Supportive Care + Immunomodulators | Variable, depends on the specific case and viral agent | Potential for drug-specific side effects, including immune system suppression; Supportive care generally has low side effects |
| Polio-like illness with significant muscle weakness | Supportive Care + Physical Therapy + Occupational Therapy | High, especially when started early | Physical therapy and occupational therapy may have minor side effects like muscle soreness or discomfort; Supportive care generally has low side effects |
Prevention and Control Strategies
Protecting children from polio-like diseases requires a multifaceted approach encompassing vaccination, public health initiatives, and rigorous hygiene practices. Effective strategies are crucial in preventing the spread and ensuring the well-being of vulnerable populations. A comprehensive understanding of these strategies empowers individuals and communities to actively participate in disease prevention efforts.
Effective Preventive Measures
A range of preventive measures are essential to combat polio-like diseases. These measures focus on strengthening immunity, disrupting transmission pathways, and fostering community engagement. Effective strategies are crucial in preventing the spread and ensuring the well-being of vulnerable populations.
Role of Vaccination
Vaccination remains a cornerstone in preventing polio-like diseases. Immunization programs have been instrumental in drastically reducing the global burden of these diseases. The effectiveness of vaccines is well-documented, demonstrating their ability to build immunity and protect individuals from debilitating illnesses.
Importance of Public Health Campaigns and Awareness Programs
Public health campaigns play a vital role in educating communities about the importance of vaccination and preventive measures. These campaigns often highlight the risks associated with the disease and the benefits of vaccination, fostering a culture of proactive health protection. Educational materials and awareness campaigns help disseminate crucial information, motivating individuals and families to prioritize their health and the health of their communities.
Community engagement is critical for successful implementation of vaccination programs.
Significance of Hygiene Practices
Maintaining meticulous hygiene practices is paramount in reducing the transmission of polio-like diseases. These practices, which include regular handwashing, proper sanitation, and food safety measures, are essential for interrupting the cycle of infection. These practices are crucial for reducing transmission rates and protecting individuals from infection. Thorough hygiene practices, combined with vaccination, are essential to prevent the spread of these illnesses.
Vaccination Schedules and Recommendations
The following table Artikels recommended vaccination schedules for various polio-like diseases. These schedules are subject to change and should be consulted with a healthcare professional for the most up-to-date information.
| Polio-like Disease | Recommended Vaccination Schedule | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Polio | IPV (Inactivated Polio Vaccine) at 2, 4, 6-8, and 18 months of age. Booster doses may be recommended. | IPV is safe and effective in preventing polio. |
| Type 2 Polio | IPV at 2, 4, 6-8, and 18 months of age. Booster doses may be recommended. | IPV is safe and effective in preventing polio. |
| Type 3 Polio | IPV at 2, 4, 6-8, and 18 months of age. Booster doses may be recommended. | IPV is safe and effective in preventing polio. |
| Other Polio-like Diseases (e.g., Acute Flaccid Myelitis – AFM) | No specific vaccine exists for all AFM cases. Vaccination against other viral infections may reduce risk. | Current research is ongoing to determine the cause of AFM and potential preventive measures. |
Impact on Children’s Health and Development
Polio-like diseases, while often treatable, can have profound and lasting effects on a child’s health and well-being. The consequences extend far beyond the initial illness, impacting not only physical capabilities but also cognitive development, social interactions, and emotional well-being. Understanding these ramifications is crucial for implementing effective prevention and support strategies.These diseases, while treatable, can lead to a range of long-term complications.
The impact varies depending on the specific disease, the severity of the initial infection, and the promptness and quality of medical care. The long-term effects can significantly alter a child’s life trajectory, impacting their educational opportunities, employment prospects, and overall quality of life. Recognizing these potential consequences is essential for proactive healthcare interventions and support systems.
Long-Term Health Consequences
Children who experience polio-like diseases can face a spectrum of long-term health challenges. These complications can manifest as physical disabilities, impacting their ability to perform everyday tasks. Furthermore, these diseases can affect the child’s overall well-being, potentially leading to decreased physical activity and limitations in social participation.
Impact on Physical and Cognitive Development
Polio-like diseases can hinder a child’s physical development, leading to muscle weakness, paralysis, or deformities. These physical limitations can restrict their participation in activities, potentially affecting their social and emotional growth. Furthermore, some polio-like diseases can impact cognitive function, although this is less common. Cases have shown a link between severe illness and slight developmental delays, requiring tailored educational support.
Socio-economic Consequences for Families and Communities
The burden of caring for a child with long-term disabilities associated with polio-like diseases falls heavily on families. Financial strain, emotional stress, and the need for specialized care can significantly impact family finances and well-being. Furthermore, the community also bears the responsibility of supporting these families, providing resources and opportunities for integration. Communities need to understand the socioeconomic burden to offer appropriate assistance.
Psychological Effects on Children and Families
The experience of a polio-like disease can have a profound psychological impact on both the child and the family. Children may experience feelings of frustration, isolation, and low self-esteem due to their limitations. The family may experience anxiety, stress, and grief as they navigate the challenges of long-term care and support. Addressing these psychological needs is crucial for the well-being of both the child and the family unit.
Table of Potential Long-Term Disabilities
| Polio-like Disease | Potential Long-Term Disabilities |
|---|---|
| Acute Flaccid Myelitis (AFM) | Muscle weakness, paralysis, reduced range of motion, respiratory problems, and speech difficulties. |
| Post-infectious Neurological Syndromes | Muscle weakness, paralysis, cognitive impairments, and sensory deficits. |
| Other Viral Infections | Varying degrees of neurological involvement, such as muscle weakness, paralysis, and cognitive impairment, depending on the virus and its severity. |
This table provides a general overview of potential long-term disabilities. Individual experiences can vary significantly. It is crucial to remember that early intervention and supportive care can significantly improve outcomes for children affected by these diseases.
Illustrative Cases and Examples
Polio-like diseases, while often less severe than polio itself, can still cause significant hardship for affected children and their families. Understanding the diverse ways these illnesses manifest is crucial for developing effective preventative and treatment strategies. Real-world examples highlight the importance of access to quality healthcare and the resilience of children and families facing these challenges.The experiences of children with polio-like diseases are as varied as the diseases themselves.
Some children may experience mild symptoms, while others face more debilitating consequences. These cases underscore the importance of prompt diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. Access to quality healthcare plays a pivotal role in both the diagnosis and the management of these conditions.
Real-World Cases of Polio-like Diseases
Children across the globe are affected by a range of illnesses mimicking polio. These conditions may present with varying symptoms and severity. Recognizing these patterns is critical for appropriate interventions.
- A 6-year-old girl presented with sudden onset of muscle weakness in her legs, accompanied by fever and headache. Initial diagnoses included several possibilities, including viral infections. Ultimately, a detailed neurological examination and blood tests led to a diagnosis of a specific polio-like disease. The child’s recovery was gradual, requiring physical therapy and supportive care. This case illustrates the importance of a thorough diagnostic process in distinguishing polio-like diseases from other conditions.
- A 3-year-old boy developed flaccid paralysis in his right arm. The paralysis initially seemed to progress rapidly, causing significant concern for the family. With prompt medical attention, including intravenous fluids, pain management, and physiotherapy, the child began showing signs of recovery within weeks. This example showcases the positive impact of timely intervention in managing polio-like diseases.
Challenges Faced by Families
The challenges faced by families caring for children with polio-like diseases extend beyond the child’s physical suffering. Financial burdens, emotional stress, and the need for extensive care are significant considerations.
- Financial constraints often limit access to specialized care, impacting the child’s prognosis and the family’s well-being. Families may face high medical costs, lost wages, and additional expenses associated with home care or transportation to medical facilities.
- The emotional toll on families is substantial. Uncertainty surrounding the diagnosis, the physical and emotional impact on the child, and the need for continuous care can be overwhelming.
Importance of Access to Quality Healthcare
Access to quality healthcare is essential for managing polio-like diseases effectively. This encompasses prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and long-term support.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for improving outcomes. Prompt intervention can limit the progression of the disease and reduce long-term complications. This necessitates readily available and skilled healthcare providers.
- Access to rehabilitation services, including physical therapy and occupational therapy, is crucial for maximizing recovery and improving the child’s quality of life.
Inspiring Stories of Recovery and Resilience
Despite the challenges, many children with polio-like diseases demonstrate remarkable resilience and inspire hope.
- Stories of children overcoming significant obstacles and achieving remarkable recoveries serve as powerful reminders of the human spirit’s ability to adapt and thrive. These narratives highlight the importance of support systems, both within the family and the community.
- Many children with polio-like diseases, with the right medical care, supportive environment, and strong family support, can lead fulfilling lives, demonstrating their exceptional strength and resilience.
Table of Illustrative Cases
| Case | Age | Symptoms | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 6 years | Muscle weakness, fever, headache | Gradual recovery with physical therapy |
| Case 2 | 3 years | Flaccid paralysis in right arm | Recovery within weeks with intensive care |
| Case 3 | 8 years | Progressive muscle weakness in legs | Partial recovery, requiring ongoing support |
Global Health Perspective: What Is Polio Like Disease Affecting Kids
Polio-like diseases, while often less severe than polio in their acute presentation, pose a significant global health concern, particularly in under-resourced communities. Understanding their prevalence, distribution, and the challenges in eradication efforts is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect children worldwide. The global burden of these diseases extends beyond individual cases, impacting families, communities, and national healthcare systems.The global response to polio-like diseases relies heavily on international cooperation and coordinated efforts.
This includes not only the provision of vaccines and treatment but also the strengthening of healthcare infrastructure in affected regions. Addressing these diseases necessitates a multi-pronged approach that combines public health interventions with community engagement and education.
Global Burden of Polio-like Diseases
The global burden of polio-like diseases varies significantly depending on factors like access to healthcare, sanitation, and vaccination programs. Certain regions experience higher rates of these diseases due to ongoing challenges in implementing effective preventive measures. These challenges include inadequate infrastructure, limited access to clean water and sanitation, and insufficient public health awareness campaigns. Accurate data collection and epidemiological surveillance remain crucial for understanding the scope of the problem and for directing resources to where they are most needed.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations play a vital role in coordinating global efforts to combat polio-like diseases. Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) are instrumental in developing guidelines, providing technical assistance, and mobilizing resources for immunization campaigns and surveillance programs. They facilitate collaborations among nations and provide support to countries in developing robust public health systems.
These organizations also provide training to local healthcare workers, enhancing their capacity to identify, diagnose, and treat these diseases.
Challenges in Eradicating Polio-like Diseases
Eradicating polio-like diseases faces numerous obstacles across the globe. Political instability, conflict, and displacement can disrupt vaccination programs and limit access to healthcare. In some regions, cultural and religious beliefs may hinder the acceptance of vaccination campaigns. Moreover, logistical challenges, such as access to remote areas and maintaining cold-chain logistics for vaccines, can hinder efforts. Funding limitations and the need for sustained global commitment also present significant obstacles.
Comparison of Prevalence Across Countries
The prevalence of polio-like diseases varies significantly across different countries. Factors such as vaccination coverage, sanitation levels, and access to healthcare resources influence the incidence of these illnesses. Countries with lower vaccination rates and poorer sanitation tend to experience higher prevalence. For example, countries in sub-Saharan Africa may have a higher incidence compared to developed nations in Europe or North America, highlighting the disparities in healthcare access.
Global Distribution of Polio-like Diseases
| Region | Affected Countries | Prevalence Rate (estimated) | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-Saharan Africa | Multiple countries | High | Limited access to healthcare, ongoing conflicts |
| South Asia | Several countries | Moderate to High | Low vaccination coverage, inadequate sanitation |
| Southeast Asia | Several countries | Moderate | Dispersed populations, limited access to remote areas |
| Middle East | Some countries | Low to Moderate | Political instability, varying vaccination rates |
Note: Prevalence rates are estimates and may vary depending on the specific polio-like disease and the year. Data collection in some regions may be incomplete. This table provides a general overview of the global distribution.
Concluding Remarks

In conclusion, polio-like diseases affecting kids present a complex array of challenges, impacting children’s health, development, and families. From the historical context to the global health perspective, we’ve explored the intricate aspects of these illnesses. Prevention and early intervention play a crucial role in mitigating the long-term consequences. This discussion highlights the need for continued research, public awareness, and access to quality healthcare to better support these vulnerable children.
