What needs to be fixed in Obamacare is a critical question demanding careful consideration. The Affordable Care Act, while aiming to expand access to healthcare, faces significant challenges in accessibility, affordability, and overall effectiveness. This exploration delves into the key areas requiring attention, from market dynamics to coverage limitations and administrative hurdles. We’ll examine the current state of the healthcare system under Obamacare, highlighting both its successes and shortcomings, and discuss potential solutions to strengthen and improve the law.
The ACA has undoubtedly brought positive changes, but its implementation has also uncovered areas that require improvement. This analysis considers diverse perspectives, including those of consumers, providers, and policymakers, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the complexities involved in reforming the system.
Accessibility and Affordability
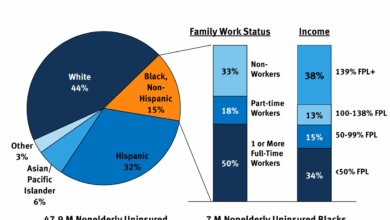
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) aimed to expand health insurance coverage and make healthcare more accessible and affordable. However, challenges persist in achieving these goals, particularly for vulnerable populations. Understanding these hurdles and exploring potential solutions is crucial for improving the overall health of the nation.Current challenges faced by individuals in accessing affordable healthcare under the ACA include high premiums, especially in high-cost areas.
Cost-sharing, including deductibles and copays, can create financial barriers, preventing individuals from seeking necessary care. The availability of affordable plans varies significantly across states and regions, further complicating access for some. These factors contribute to the ongoing struggle for many to obtain and maintain affordable health insurance.
ACA Subsidies and Cost-Sharing Reductions
The ACA’s subsidies and cost-sharing reductions aim to lower the cost of healthcare for individuals and families with moderate incomes. However, the effectiveness of these programs varies depending on individual circumstances and plan choices. Some argue that the subsidies are insufficient to fully address affordability issues, particularly for those with higher medical needs. Others highlight the positive impact on access to care for many, emphasizing that these programs have helped many gain coverage and reduce out-of-pocket costs.
Strategies to Improve Accessibility and Affordability for Vulnerable Populations
Expanding the range of affordable plans, particularly in underserved areas, is critical. This can involve promoting plans with lower premiums and more comprehensive benefits. Another strategy is increasing outreach and education to vulnerable populations, helping them understand their options and navigate the complexities of the health insurance marketplace. Targeted subsidies and financial assistance programs can further ease the financial burden of healthcare for those with limited resources.
Community health centers and mobile clinics can increase access to care in remote or underserved communities.
Comparison of Healthcare Plan Costs
| Plan Type | Premium (Annual) | Deductible | Out-of-Pocket Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bronze | $250 | $1,500 | $6,000 |
| Silver | $350 | $2,000 | $8,000 |
| Gold | $450 | $2,500 | $10,000 |
| Platinum | $550 | $3,000 | $12,000 |
Note: These are illustrative examples and actual costs will vary based on location, provider, and individual circumstances.
Potential Solutions to Reduce Prescription Drug Costs
Negotiating lower drug prices with pharmaceutical companies is a key strategy. This can involve government-led negotiations or through collective bargaining by large insurance providers. Promoting generic drug use can also reduce costs significantly. Encouraging the development of more affordable biosimilars and alternative treatments can provide cheaper alternatives to expensive brand-name medications. Improving transparency in drug pricing and increasing public awareness of cost-saving strategies can also help patients make informed decisions.
Market Dynamics and Competition
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) aimed to expand health insurance coverage and improve market dynamics. However, the current state of the insurance market under the ACA presents a complex picture, with both successes and ongoing challenges. Understanding these complexities is crucial for developing effective strategies to further improve the system.The current insurance market under the ACA displays a mix of competition and consolidation.
While the law fostered the creation of new insurance marketplaces, some areas still show limited competition among insurers. This lack of competition can lead to higher premiums and fewer choices for consumers.
State of Competition in the ACA Market
The ACA’s marketplaces, designed to increase competition, have seen varying degrees of success. In some states, the presence of multiple insurers and competitive pricing is evident. However, in others, fewer insurers participate, which can restrict consumer choice and potentially lead to higher premiums. This variation is often influenced by state-level regulations and the specific characteristics of the insurance market within each state.
Effectiveness of Different Market Models
Different insurance market models under the ACA exhibit unique strengths and weaknesses. The individual market, which allows individuals to purchase coverage directly, often faces challenges in attracting enough healthy individuals to maintain affordability. The small group market, designed to offer coverage to small businesses, can sometimes be impacted by the varying size and needs of these businesses. Furthermore, the Medicaid expansion programs, while crucial for expanding coverage, sometimes face budget constraints, which can impact their ability to provide comprehensive benefits.
Potential for Increased Competition
Increased competition in the healthcare insurance market has the potential to significantly impact healthcare costs and quality. More insurers vying for customers would likely lead to more competitive pricing and a wider range of plans. This, in turn, could provide consumers with better choices and potentially drive down healthcare costs. Competitive pressures could also encourage insurers to offer more comprehensive plans and innovative benefits packages, leading to a higher quality of care.
Obamacare, while a landmark achievement, definitely needs some tweaking. High premiums and confusing coverage options are major pain points. Plus, understanding the impact of certain substances on driving ability is important, and research into whether marijuana increases the risk of vehicle crashes is crucial. Does marijuana increase risk of vehicle crashes? This type of data is essential to crafting a more robust and user-friendly healthcare system.
Ultimately, fixing these aspects of Obamacare is key to creating a more accessible and affordable healthcare solution for everyone.
Strategies for Increasing Competition
Several strategies could foster greater competition among insurance providers within the ACA’s framework. Implementing policies that encourage the entry of new insurers into the marketplace, especially in underserved areas, could strengthen competition. Additionally, regulatory reforms aimed at reducing barriers to entry for new providers could also be considered. Facilitating greater transparency in pricing and plan offerings could empower consumers to make informed decisions.
Impact of Insurance Market Trends on Premiums and Plan Choices
| Insurance Market Trend | Impact on Premium Rates | Impact on Plan Choices |
|---|---|---|
| Increased competition | Lower premiums | Wider range of plans |
| Reduced competition | Higher premiums | Limited plan choices |
| Expansion of Medicaid | Potentially reduced premiums for some low-income individuals | Increased access to coverage for some populations |
| Expansion of the individual market | Potentially higher premiums if healthy individuals do not enroll | More options for individuals |
| Technological advancements in insurance administration | Potential for lower administrative costs, which could translate to lower premiums | Potential for more tailored plans and personalized service |
Coverage and Benefits

The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has significantly expanded health insurance coverage, but crucial gaps remain in its benefits structure. Many Americans still face challenges accessing comprehensive care due to limitations in coverage for specific conditions, treatments, and preventive services. Addressing these limitations is essential for ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare for all.The ACA’s coverage provisions, while a step forward, don’t fully meet the needs of all individuals, particularly those with pre-existing conditions or those seeking specialized treatments.
This necessitates a critical review of the current coverage framework to identify and address existing deficiencies. Such a review should also explore potential expansions or modifications to coverage benefits while maintaining financial sustainability.
Current Coverage Limitations
The ACA’s coverage limitations often create significant hurdles for individuals seeking treatment for chronic conditions or specialized care. This is particularly true for individuals with pre-existing conditions, who may find that certain treatments or procedures are not fully covered, or that out-of-pocket costs remain high. The lack of consistent coverage across plans can also lead to inequitable access to care.
Examples of Coverage Gaps
Many individuals face significant financial hardship due to coverage gaps in the ACA. For example, mental health services, including therapy and counseling, may not be adequately covered in some plans, leaving individuals struggling with mental health conditions with limited access to care. Similarly, certain types of experimental or innovative treatments for rare diseases may not be covered, creating a barrier to accessing potentially life-saving interventions.
Moreover, some plans may limit coverage for specific prescription medications, creating a considerable burden for individuals relying on those medications for chronic conditions.
Obamacare definitely needs some tweaks, like making coverage more affordable and accessible. But the pandemic really highlighted another critical issue – the worsening mental health crisis among teens. This, sadly, is something that needs to be addressed alongside any healthcare reform. For more on how the pandemic impacted teen mental health, check out this insightful article: how the pandemic made the mental health crisis worse for teens.
Ultimately, fixing Obamacare involves not just cost, but also comprehensive support for the well-being of our youth. We need to make sure our healthcare system is robust enough to handle both the physical and mental needs of everyone.
Need for Coverage Expansions and Modifications
Expanding coverage to include a broader range of preventative services and treatments is essential. Mental health services, substance abuse treatment, and coverage for chronic conditions should be expanded to ensure individuals can access comprehensive care. Addressing the limitations of coverage for experimental or innovative treatments for rare diseases is also critical. A potential modification could involve establishing a national formulary of covered medications to ensure consistent and equitable access to essential medicines.
Approaches to Improve Coverage Quality
Several approaches can improve the quality and comprehensiveness of healthcare coverage under the ACA. These include establishing clear and transparent standards for coverage benefits, including mental health and substance abuse services, and establishing a national formulary for essential medicines. Encouraging greater competition among insurance providers, while ensuring the availability of affordable plans, is another crucial factor. Finally, providing financial assistance to individuals who struggle to afford coverage will help close the coverage gap.
Table Illustrating Areas for ACA Coverage Improvement
| Area of Coverage | Current Status | Needed Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Mental Health Services | Limited coverage in some plans; inconsistent access. | Expand coverage to include a wider range of mental health services, such as therapy and counseling, and ensure consistent access across plans. |
| Prescription Drugs | Coverage varies widely by plan; some essential medications excluded. | Establish a national formulary of covered medications to ensure consistent and equitable access to essential medicines. |
| Experimental/Innovative Treatments | Limited or no coverage for many experimental or innovative treatments. | Establish clear guidelines and criteria for coverage of experimental or innovative treatments, particularly for rare diseases. |
| Preventive Services | Generally covered, but may have limitations. | Expand coverage to include a wider range of preventative services, such as screenings and vaccinations, and ensure consistent access across plans. |
Administrative Efficiency and Compliance

The Affordable Care Act (ACA) aimed to expand health insurance access, but its administrative complexities have proven a significant hurdle. Inefficient processes, coupled with intricate compliance requirements, can drive up healthcare costs and create a frustrating experience for both providers and patients. Streamlining these procedures is crucial to the ACA’s long-term success.The current administrative framework within the ACA has several inherent weaknesses.
These inefficiencies translate directly into higher healthcare costs. For example, navigating the various insurance exchanges, processing claims, and ensuring compliance with a multitude of regulations often involves redundant steps and considerable paperwork. This complexity not only burdens providers and insurers but also contributes to delays in receiving necessary care.
Administrative Inefficiencies and Cost Increases, What needs to be fixed in obamacare
Administrative inefficiencies within the ACA framework directly impact healthcare costs. Redundant processes, lack of interoperability between different systems, and a fragmented approach to claim processing increase the administrative burden and cost. This burden ultimately falls on consumers through higher premiums or reduced benefits.
Challenges in Maintaining ACA Compliance
Maintaining compliance with ACA regulations presents numerous challenges. The sheer volume of regulations, evolving interpretations by different jurisdictions, and the need for ongoing updates create a dynamic and complex environment. Providers must stay informed about changes in regulations, which can be a significant undertaking, especially for smaller practices. Failure to comply can lead to costly penalties, further increasing the burden on providers and ultimately affecting the affordability of care.
Obamacare, while a significant step, definitely needs some tweaks. One glaring issue is its impact on preventative care, especially considering the recent alarming rise in alcohol-related deaths, doubling in the past two decades ( alcohol related deaths double in two decades ). This suggests a possible disconnect between current healthcare initiatives and addressing the root causes of such a concerning trend.
Ultimately, a more holistic approach to healthcare, encompassing mental wellness and substance abuse programs, needs to be integrated into Obamacare for a more effective system.
Streamlining Administrative Processes
Several methods can streamline administrative processes within the ACA to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Implementing standardized claim forms and processes, promoting interoperability between different healthcare systems, and simplifying the enrollment process are key steps. Utilizing technology to automate tasks like claim processing and regulatory compliance checks can dramatically reduce the workload and associated costs.
Technology for Improved Administrative Efficiency and Compliance
Technology offers significant potential to enhance administrative efficiency and compliance within the ACA. Electronic health records (EHRs) can streamline data exchange between providers and insurers, facilitating quicker and more accurate claim processing. Automated systems can help identify and resolve compliance issues proactively, minimizing potential penalties. Furthermore, secure online portals for patients and providers can improve communication and transparency, allowing for more efficient management of healthcare information.
Healthcare Claims Process Under the ACA
The following table illustrates the various steps involved in the healthcare claims process under the ACA. This standardized approach facilitates efficiency and minimizes errors.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Patient Visit | Patient receives care from a healthcare provider. |
| 2. Claim Initiation | Provider submits a claim electronically to the insurance company. |
| 3. Claim Processing | Insurance company processes the claim, verifying eligibility and coverage. |
| 4. Payment Approval | If the claim is approved, the insurance company releases payment to the provider. |
| 5. Payment Receipt | Provider receives the payment for services rendered. |
| 6. Patient Billing | Patient receives a statement detailing the charges and payment amount. |
Cost-Effectiveness and Value: What Needs To Be Fixed In Obamacare
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has significantly expanded health insurance coverage, but its cost-effectiveness remains a crucial area for improvement. Optimizing the value proposition of ACA benefits for both consumers and providers is essential to ensuring the sustainability and success of the program. This necessitates a thorough examination of potential areas for enhanced cost-effectiveness in service delivery, along with robust methods for evaluating the overall value of covered treatments.
Potential Areas for Enhanced Cost-Effectiveness
The ACA has introduced innovative approaches to healthcare delivery, but room exists for further streamlining and optimization. Strategies focusing on preventive care, telemedicine, and value-based care models can significantly lower overall healthcare costs while improving patient outcomes. Early intervention and proactive management of chronic conditions through preventative measures can reduce the need for costly emergency room visits and hospitalizations in the long run.
Improving the Value Proposition of ACA Benefits
Ensuring optimal outcomes for consumers and providers requires a shift towards value-based care models. This involves incentivizing providers to focus on preventative care, patient engagement, and improved health outcomes rather than simply volume of services. Value-based care arrangements, such as capitation or bundled payments, can incentivize providers to deliver high-quality care at a lower cost. Transparency in pricing and cost-effectiveness of procedures will empower consumers to make informed decisions.
Measuring Cost-Effectiveness of Healthcare Services
Measuring the overall cost-effectiveness of various healthcare services requires a multifaceted approach. This involves comparing the cost of a particular treatment or intervention to its clinical outcomes. Economic evaluations, such as cost-benefit analysis and cost-effectiveness ratios, can quantify the value of different healthcare interventions. These analyses typically consider the costs of treatment, the duration of treatment, and the expected outcomes, including improvements in quality of life and reductions in disease progression.
For example, a cost-effectiveness analysis might compare the cost of a new drug treatment to the cost of standard care, considering factors such as efficacy, side effects, and patient adherence.
Optimizing Resource Allocation
Efficient resource allocation within the ACA is crucial to maximizing cost-effectiveness. This involves strategic investments in preventive care programs, telehealth infrastructure, and community health centers. Prioritizing evidence-based interventions and supporting innovative healthcare delivery models can yield significant returns. For instance, a comprehensive program addressing social determinants of health, such as housing insecurity or food insecurity, can significantly reduce healthcare costs associated with preventable illnesses and chronic conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness Comparison of Healthcare Treatments
| Treatment | Estimated Cost | Clinical Outcomes (e.g., Length of Stay, Recurrence Rate) | Cost-Effectiveness Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive Care (e.g., Vaccinations, Health Screenings) | Low | Reduced hospitalizations, improved health | High |
| Telemedicine Consultations | Lower than In-Person Visits | Effective for many conditions, reduced travel time | High |
| Value-Based Care Models | Potentially Lower, depending on structure | Improved patient outcomes, increased efficiency | High |
| Hospital-Acquired Infections Prevention Programs | Moderate | Reduced infections, shorter hospital stays | High |
| Chronic Disease Management Programs | Moderate | Improved patient outcomes, reduced hospital readmissions | High |
Note: Cost estimates are approximate and may vary depending on specific circumstances and healthcare provider. Cost-effectiveness ratios are hypothetical and should be calculated based on specific programs and data.
Public Perception and Political Landscape
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) continues to be a subject of intense public debate and political maneuvering. Public perception plays a crucial role in shaping its future, and understanding the factors influencing this perception is essential for any discussion of potential reforms. The political landscape surrounding the ACA is characterized by deep partisan divides, which significantly impact the likelihood of bipartisan support for any proposed changes.
This section delves into the complexities of public opinion, political challenges, and the varied perspectives of key stakeholders regarding the ACA’s impact.The ACA’s success hinges, in part, on public acceptance. Common concerns, often fueled by misinformation and political rhetoric, include perceived increases in premiums, limited choices in healthcare plans, and the overall complexity of the system. These concerns, while sometimes valid, need to be contextualized within the broader healthcare landscape and the specific benefits offered by the ACA.
Public Concerns Regarding the ACA
Public criticism of the ACA often centers on perceived affordability issues, particularly for individuals and families with lower incomes. Concerns about limited plan choices and rising premiums are often amplified by a lack of comprehensive understanding of the complexities of the insurance marketplace. Furthermore, the perception of the ACA’s bureaucratic nature contributes to public dissatisfaction.
Political Challenges Facing the ACA
The ACA’s future is inextricably linked to the political climate. Significant partisan divides hinder bipartisan efforts at reform, leading to gridlock in legislative processes. Potential legislative reforms could include measures aimed at increasing affordability, expanding coverage, or streamlining administrative processes. The success of these reforms, however, depends on securing broad political support, which remains a significant challenge.
Impact of Political Ideologies on Public Opinion
Political ideologies strongly influence public opinion regarding the ACA. Conservatives often express concerns about government intervention in the healthcare market, emphasizing individual responsibility and free-market principles. Conversely, liberals often support government regulation to ensure equitable access to healthcare for all citizens. Understanding these ideological underpinnings is vital for crafting strategies that promote broader acceptance of the ACA.
Strategies to Improve Public Support for the ACA
Strategies to enhance public support for the ACA include transparent communication about its benefits and addressing specific concerns. For instance, targeted outreach to vulnerable populations and increased educational initiatives about the ACA’s provisions could help alleviate misinformation and enhance public understanding. Furthermore, promoting success stories of individuals who have benefited from the ACA could serve as a powerful tool to improve public perception.
Stakeholder Perspectives on Healthcare Access and Affordability
Different stakeholders hold varying views on the ACA’s impact on healthcare access and affordability. Consumers, particularly those with pre-existing conditions, often praise the ACA’s protections. However, small business owners frequently voice concerns about the associated costs and administrative burdens. Healthcare providers, insurers, and government agencies also have distinct perspectives, influenced by their specific roles and responsibilities within the healthcare system.
A comprehensive understanding of these diverse viewpoints is essential for effective reform.
| Stakeholder Group | General Perspective | Specific Concerns/Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Consumers with Pre-Existing Conditions | Positive; ACA protects access | Premiums, limited plan choices |
| Small Business Owners | Mixed; concerns about costs and administrative burden | Impact on employee benefits, increased costs |
| Healthcare Providers | Varied; depends on specific practice | Payment rates, access to care, changes in patient demographics |
| Insurers | Mixed; profitability concerns | Regulatory changes, market dynamics |
| Government Agencies | Responsible for implementation and oversight | Compliance, administrative efficiency |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, fixing Obamacare requires a multifaceted approach addressing accessibility, affordability, market dynamics, coverage, and administrative efficiency. While the law has undoubtedly improved access for many, persistent issues remain. By examining the root causes of these problems and exploring potential solutions, we can work towards a more equitable and effective healthcare system for all. The future of healthcare reform hinges on finding pragmatic and sustainable solutions to these challenges.