When will we know if reopening states has worked or backfired? This question hangs heavy in the air, a complex puzzle with no easy answers. The effects of reopening strategies ripple through communities, impacting everything from local economies to public health. We’re left wondering if the decisions made were the right ones, and when the long-term consequences will become clear.
To understand this, we need to dissect the factors involved. How do we measure success? Is it the rebound of the economy, the return to pre-pandemic normalcy, or perhaps something more nuanced? Analyzing the timeframe for evaluation is crucial, considering the impact on different demographics, external factors, and the role of public health measures. A deep dive into these aspects will shed light on the answers, helping us understand the full scope of the reopening process.
Defining Metrics for Success
Reopening states after pandemic lockdowns presented a complex challenge. Assessing the success or failure of these efforts requires a multifaceted approach, considering both economic and public health impacts. This necessitates a robust framework of metrics, allowing for a nuanced understanding of the effects of reopening across various sectors.A simple binary assessment of “success” or “failure” is insufficient. The impact of reopening is a dynamic process, influenced by numerous factors and exhibiting varying degrees of success in different regions and communities.
To understand this, we need to develop specific and measurable criteria.
Economic Indicators for Evaluating Reopening
Understanding the economic ramifications of reopening requires a comprehensive examination of various indicators. These metrics help us gauge the recovery and resilience of businesses, industries, and the overall economy.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth: Tracking GDP growth rates before, during, and after reopening provides insights into the economic health of a state. Comparing these rates to pre-pandemic trends allows for a more informed analysis of the reopening’s impact. For example, a state that experiences a slower-than-expected GDP recovery might suggest difficulties in specific sectors.
- Job Creation and Unemployment Rates: Analyzing employment figures and unemployment rates before, during, and after reopening is crucial. A significant increase in job losses or a persistent high unemployment rate might indicate the reopening strategy didn’t effectively support the workforce. Conversely, a sustained decline in unemployment suggests the strategy is working.
- Retail Sales and Consumer Spending: Monitoring retail sales and consumer spending can reveal how effectively the reopening stimulated economic activity. A significant increase in these metrics often indicates that reopening spurred consumer confidence and spending. Conversely, a decrease suggests that reopening might not have generated the anticipated economic rebound.
Public Health Metrics for Evaluating Reopening
Evaluating the public health consequences of reopening necessitates a comprehensive assessment of several key indicators. These metrics provide valuable insights into the impact of reopening on the spread of the virus.
- Hospitalization Rates: Monitoring hospitalization rates for COVID-19 before, during, and after reopening offers a crucial perspective on the strain on healthcare systems. A significant increase in hospitalizations could indicate that reopening strategies were insufficient to mitigate the spread of the virus. Conversely, stable or decreasing hospitalization rates suggest effective mitigation.
- Infection Rates: Tracking infection rates (new cases) before, during, and after reopening is crucial to understand the spread of the virus. A surge in infection rates might indicate that reopening strategies were inadequate in controlling the virus. Conversely, a steady decline or a plateau in infection rates might signify that the reopening strategy is having a positive effect.
- Mortality Rates: Analyzing mortality rates before, during, and after reopening provides a critical perspective on the impact of reopening on public health. A significant increase in mortality rates might suggest that reopening strategies did not sufficiently protect vulnerable populations. A steady decline in mortality rates indicates that reopening is not negatively impacting public health.
Comparative Methodologies for Evaluating Reopening
Different methodologies for evaluating the success or failure of reopening efforts can provide different perspectives. Employing a combination of approaches offers a more comprehensive understanding of the complex issue.
- Pre-Post Analysis: Comparing data before and after reopening can provide a baseline for assessing the impact of reopening. This method helps isolate the effects of reopening from other factors.
- Regional Comparisons: Comparing reopening strategies and outcomes across different regions provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of various approaches. This approach allows us to examine how different factors impact the results.
- Sector-Specific Analysis: Assessing the impact of reopening on specific sectors (e.g., healthcare, education, tourism) allows for a more nuanced understanding of the complexities. A focused examination reveals which sectors have been most impacted by the reopening and how they might need different support strategies.
Comparing Metrics for Different Sectors
| Sector | Economic Indicators | Public Health Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Hospital capacity utilization, healthcare worker burnout, staffing levels | Hospitalization rates, ICU bed occupancy, healthcare worker infections |
| Education | Student enrollment, teacher retention, school budget impacts | Infection rates in schools, absenteeism, need for remote learning |
| Tourism | Hotel occupancy rates, restaurant sales, visitor numbers | Infection rates in tourist hotspots, compliance with health protocols |
Analyzing the Timeframe for Evaluation

Assessing the long-term impacts of reopening decisions requires a careful consideration of the timeframe involved. Simply declaring a reopening date and then evaluating results immediately afterward is insufficient. The effects of such decisions ripple through the economy, society, and public health, often manifesting over extended periods. Understanding the appropriate timeframe for evaluation is critical for drawing accurate conclusions and formulating effective future strategies.A thorough evaluation necessitates considering the interplay of various factors, including the nature of the impacts, the inherent variability in data, and the influence of seasonal trends.
This analysis explores the nuances of establishing an appropriate evaluation period, factoring in diverse perspectives and the potential for seasonal variations to distort data interpretation.
Establishing a Suitable Evaluation Period
Determining an appropriate period for evaluating the effects of reopening decisions is crucial for understanding the true long-term impact. A short timeframe might not capture the full extent of the consequences, while an excessively long period could be influenced by other external factors. The optimal evaluation period should be long enough to observe the significant consequences of reopening, but not so long as to be confounded by unrelated events.
Figuring out if reopening states was a good idea or a blunder is tricky. It’s like waiting for the results of a long experiment, and sometimes, the effects of sugar free gummy bears laxatives can take a while to manifest. We’ll only truly know when the long-term health and economic data starts to settle, showing us whether the initial positive gains were temporary or truly sustainable.
So, while we’re all eagerly awaiting the verdict, maybe we should all consider the potential for long-term health consequences of these types of laxatives. We’ll probably need a while to really see if the reopening plan worked or backfired.
Factors Influencing Evaluation Time
Several factors can significantly impact the length of time required for evaluating the outcomes of reopening decisions. These factors include the specific sectors affected, the nature of the restrictions lifted, and the overall health and economic conditions before and after the reopening. The duration of time needed to observe meaningful shifts in various sectors may vary. For instance, the recovery of the tourism sector might take longer than the recovery of the retail sector, depending on the particular circumstances.
Similarly, the effects of reduced restrictions on social gatherings may manifest differently depending on the pre-existing cultural norms and behaviors.
Considering Seasonal Variations in Data
Seasonal variations can significantly impact data collection and interpretation when evaluating reopening efforts. For example, spikes in hospitalizations or infections during specific seasons might not necessarily be attributed to reopening policies but rather to the typical seasonal patterns. It’s crucial to account for these patterns to avoid misinterpreting data. Data collected during a peak flu season, for example, might wrongly suggest a correlation with reopening policies if the seasonal effect is not considered.
Wondering when we’ll truly know if reopening states has worked or backfired? It’s a tricky question, but we’ll likely see a clearer picture as the CDC provides valuable insight on returning to work. For example, the CDC gives advice on how to go back to work what the experts say regarding safety protocols and infection rates will help us understand the long-term effects of these decisions.
Ultimately, the true test will be measured by public health metrics over the coming months and years.
Consequently, a thorough analysis must incorporate seasonal adjustments or comparisons to previous years’ data to ascertain the true impact of the reopening decisions.
Perspectives on the Timeframe for Full Effects
Different perspectives exist regarding how long it takes for the full effects of reopening to become apparent. Some argue that the initial effects are immediately visible, while others maintain that a more extended period is needed to observe the full consequences. The speed at which the effects manifest depends on factors such as the level of pre-existing restrictions, the nature of the reopening, and the specific demographics being considered.
The tourism sector, for instance, may demonstrate a rapid recovery following a reopening, while sectors requiring a substantial shift in workforce behavior might take longer to adjust.
Illustrative Timeline for Assessing Long-Term Impacts
A reasonable timeline for assessing the long-term impacts of reopening might span 12 to 24 months. This allows for observation of trends in key indicators, such as employment rates, hospitalizations, and economic growth, while minimizing the influence of short-term fluctuations.
Examining the Impact on Different Demographics: When Will We Know If Reopening States Has Worked Or Backfired
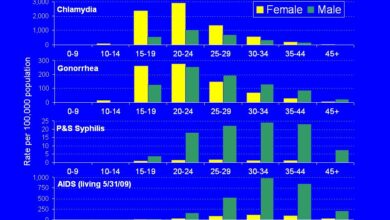
Reopening states after pandemic lockdowns presented a complex challenge, demanding careful consideration of the potential disparate impacts on various demographic groups. The differing vulnerabilities and resources available to various communities played a crucial role in shaping the outcomes of these reopening strategies. Understanding these impacts is essential for formulating future pandemic response strategies that are more equitable and effective.The uneven distribution of resources, access to healthcare, and pre-existing health conditions significantly influenced the responses of different demographics to the reopening decisions.
Analyzing the consequences of these decisions on vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, low-income communities, and individuals with pre-existing conditions, is crucial to understanding the true effectiveness of these measures. This examination allows for a nuanced understanding of the pandemic’s impact beyond aggregated data.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations
Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions, often face higher risks from infectious diseases. Reopening decisions significantly impacted their well-being. The disruption to essential services, such as access to healthcare and social support networks, often exacerbated pre-existing vulnerabilities and created new challenges.
Impact on Low-Income Communities
Low-income communities frequently lack access to quality healthcare and adequate resources. Reopening strategies that did not prioritize the needs of these communities could have led to disproportionate health consequences. Economic hardship, limited access to childcare, and essential services often presented unique obstacles for these communities during the reopening period. For example, job losses and closures in essential sectors disproportionately affected low-income communities.
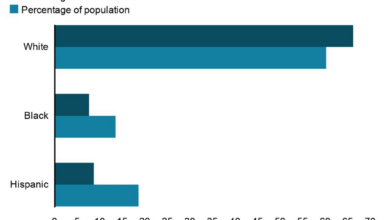
Impact on Racial and Ethnic Minorities
Racial and ethnic minorities often face systemic health disparities, including limited access to quality healthcare and higher rates of certain health conditions. Reopening strategies that did not address these pre-existing disparities risked exacerbating health inequities.
Impact on Children and Adolescents
Children and adolescents experienced unique challenges during the pandemic and the reopening process. The impact on their education, social development, and mental health needs careful consideration. School closures and social distancing measures had lasting effects on their learning and emotional well-being.
Comparative Analysis Table
| Demographic Group | Potential Impacts of Reopening | Evidence of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Elderly | Increased risk of severe illness, disruption of social support networks | Studies showing higher mortality rates among older adults during periods of community transmission |
| Low-Income Communities | Increased job loss, reduced access to healthcare, exacerbation of existing vulnerabilities | Economic data demonstrating disproportionate job losses in low-income sectors; reports of decreased access to essential services |
| Racial and Ethnic Minorities | Exacerbation of existing health disparities, limited access to quality healthcare | Data on racial and ethnic disparities in COVID-19 outcomes; reports of inequities in access to healthcare |
| Children and Adolescents | Impact on education, social development, and mental health; potential increase in learning gaps | Reports on increased rates of mental health issues and learning gaps among children and adolescents |
Considering External Factors Influencing Outcomes
Reopening states after lockdowns presented a complex interplay of internal and external factors. While local public health measures and citizen behaviors played crucial roles, external forces significantly impacted the success or failure of these initiatives. Understanding these influences is critical to evaluating the long-term effects of reopening and informing future strategies.External factors often masked or amplified the impact of local decisions, making a straightforward assessment challenging.
International events, economic fluctuations, and the emergence of new virus variants were not always predictable or easily controlled, affecting the trajectory of reopening efforts in ways that weren’t initially anticipated.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies at both the state and federal levels exerted a powerful influence on reopening strategies. Differing approaches to mask mandates, business restrictions, and economic aid packages led to diverse outcomes across states. For example, states that prioritized economic recovery might have seen a quicker return to normalcy but potentially higher infection rates initially, while states prioritizing public health may have experienced slower economic recovery but potentially lower rates of infection.
The specific regulations implemented played a crucial role in shaping the public’s behavior and ultimately influencing the trajectory of reopening.
Public Health Guidance and Citizen Behavior
Public health guidance significantly impacted the success of reopening efforts. Clear communication about infection prevention measures, vaccination rates, and risk levels directly affected public behavior. Variations in compliance with these guidelines across different communities led to varying outcomes. High levels of public compliance with recommended precautions, coupled with strong local public health measures, likely resulted in smoother reopenings.
Conversely, lower compliance levels, especially in the absence of effective local strategies, could have contributed to more significant outbreaks during the reopening period.
Global Events, Economic Downturns, and Emerging Variants
Global events, economic downturns, and emerging variants significantly complicated the assessment of reopening outcomes. International travel restrictions, trade disruptions, and economic uncertainties could have altered the spread of the virus and the impact of reopening. For instance, a sudden economic downturn could have made it difficult for businesses to reopen, regardless of local regulations, potentially leading to increased unemployment and reduced consumer spending.
The emergence of new variants could have jeopardized the effectiveness of public health measures and necessitated a return to stricter lockdowns.
Impact of International Travel and Border Restrictions
International travel and border restrictions were crucial external factors that influenced the effects of reopening. Restrictions on international travel could have limited the introduction of new variants into a region, potentially impacting the severity of outbreaks. Conversely, the lifting of travel restrictions could have led to a rapid influx of cases, overwhelming local healthcare systems and necessitating a swift return to more stringent measures.
The interplay between domestic reopening and international travel policies created a complex dynamic in assessing the success or failure of reopening efforts. For example, the lifting of border restrictions during an emerging variant period might have introduced a surge in infections, even in areas with stringent domestic regulations.
Data Interpretation Considerations
Several factors could influence the interpretation of data regarding reopening. The timing of data collection, the availability of testing, and the reliability of reporting mechanisms could all create bias. A surge in cases observed immediately after reopening might not necessarily indicate a failure of the reopening strategy if the surge is linked to a new variant or increased testing.
A more accurate assessment would require a comprehensive analysis that considers both the local reopening strategy and the external factors influencing the data.
Evaluating the Role of Public Health Measures
The reopening of states after pandemic lockdowns presented a complex challenge. Successfully navigating this transition hinged on factors beyond just economic considerations; public health measures played a critical role in determining the success or failure of these reopenings. Understanding the impact of these measures is crucial for informing future responses to public health crises.The effectiveness of reopening strategies was intricately tied to the level of adherence to public health recommendations.
Figuring out if reopening states was a good idea or a disaster is tricky. It’s like waiting for the results of a long-term experiment, and honestly, we’re still in the data collection phase. A big factor in this uncertainty is the long-term health effects of COVID-19, and whether those effects are being fully understood. Ultimately, determining the success or failure of reopening will likely depend on a variety of factors, and will take time.
For parents, a safer way to keep kids protected while traveling is by choosing the best convertible car seat. This crucial safety decision can be greatly simplified with a guide like best convertible car seat to help navigate the market. So, while we wait for those long-term data points, we’re all just trying to make the best decisions possible, based on the information we have now.
Successful reopenings were often characterized by high rates of mask-wearing, social distancing, and vaccination. Conversely, regions with low adherence rates frequently experienced surges in cases, necessitating renewed restrictions and undermining economic recovery efforts. This interplay between public health and economic activity underscores the need for a nuanced understanding of how these factors interact.
Importance of Public Health Interventions
Public health interventions, such as mask mandates, social distancing guidelines, and vaccination campaigns, are vital tools for mitigating the spread of infectious diseases. They create a protective barrier, reducing transmission rates and the burden on healthcare systems. The effectiveness of these measures in shaping the outcomes of reopening is undeniable. Their impact can be seen in the differing experiences of regions with varying degrees of compliance.
Effectiveness of Different Public Health Interventions
Mask mandates, when consistently enforced and widely adopted, demonstrably reduce the spread of airborne pathogens. Social distancing guidelines, while challenging to enforce consistently, can significantly reduce transmission risk. Vaccination campaigns, when coupled with other interventions, can dramatically alter disease dynamics, protecting both individuals and communities. The success of vaccination campaigns depends heavily on public trust and accessibility.
Adherence to Public Health Measures and Reopening Success
The degree to which individuals and communities adhered to public health measures significantly influenced the outcomes of reopening strategies. High adherence rates often correlated with fewer cases and hospitalizations, allowing for more gradual and sustained reopenings. Conversely, low adherence rates led to surges in cases, requiring swift and potentially economically damaging responses. The relationship between adherence and reopening outcomes is a critical consideration for future public health strategies.
Relationship Between Public Health Interventions and Reopening Strategies
Effective reopening strategies must be intertwined with robust public health interventions. These interventions act as a safety net, mitigating the risk of widespread transmission and allowing for controlled and gradual economic recovery. The success of reopening hinges on a clear understanding of the interplay between these two factors, enabling a balanced approach that prioritizes both health and economic well-being.
Correlation Between Adherence and Outcomes
| Adherence to Public Health Measures | Outcomes of Reopening |
|---|---|
| High | Fewer cases, gradual reopening, fewer hospitalizations, sustained economic recovery |
| Moderate | Some cases, potential for controlled reopening, limited economic impact |
| Low | Surges in cases, potential for economic setbacks, need for renewed restrictions, higher hospitalizations |
Illustrating Successes and Failures
The reopening of states after the COVID-19 pandemic presented a complex challenge, demanding careful consideration of public health, economic factors, and social well-being. Different states employed varying strategies, leading to diverse outcomes. Analyzing these successes and failures can provide valuable lessons for future public health crises.
Successful Reopening Strategies
Successful reopenings often involved a phased approach, carefully monitoring key metrics like infection rates and hospitalizations. Public health measures, including mask mandates and vaccination campaigns, played a crucial role in mitigating the spread of the virus.
- Phase-based approach: States that implemented a gradual reopening, allowing businesses to reopen in stages, while consistently monitoring and adjusting public health measures, often experienced smoother transitions. For example, states like North Dakota, which prioritized vaccination rates and adherence to safety protocols, saw a relatively controlled reopening process.
- Emphasis on vaccination: High vaccination rates were a common denominator in states that successfully navigated reopening. These states demonstrated that vaccination, combined with other public health measures, significantly lowered transmission and hospitalizations, facilitating a safer return to normalcy.
- Data-driven decision-making: States that relied on data to inform their reopening decisions, tracking key metrics such as hospital bed availability, positivity rates, and new cases, were better positioned to adjust strategies as needed. This allowed for timely responses to emerging outbreaks and ensured that measures were proportionate to the risk.
Negative Consequences of Reopening, When will we know if reopening states has worked or backfired
Conversely, some states experienced a surge in cases and hospitalizations following reopening, often due to a combination of factors.
- Inadequate public health measures: A lack of consistent mask mandates, social distancing guidelines, and vaccination efforts in some states created an environment conducive to the spread of the virus. This led to significant outbreaks and a strain on healthcare resources.
- Resistance to public health measures: Resistance to mask mandates and vaccination efforts in some areas hampered the overall effectiveness of public health measures. This created an environment where the virus could spread more easily, regardless of economic incentives.
- Rapid lifting of restrictions: States that lifted restrictions too quickly, without sufficient precautions, often faced a rebound in cases and hospitalizations. This demonstrates the importance of a gradual and cautious approach to reopening, particularly in areas with lower vaccination rates.
Comparison of Successful and Unsuccessful Strategies
The following table illustrates a comparison of successful and unsuccessful strategies for reopening, highlighting key differences.
| Characteristic | Successful Reopening | Unsuccessful Reopening |
|---|---|---|
| Public Health Measures | Consistent and comprehensive implementation of mask mandates, social distancing, and vaccination programs | Limited or inconsistent enforcement of public health measures; resistance to vaccination |
| Economic Considerations | Balanced approach; careful consideration of public health alongside economic needs | Prioritization of economic reopening over public health |
| Data-Driven Decision Making | Regular monitoring and analysis of key metrics to inform decisions | Limited or no data-driven decision making |
| Gradual Approach | Phased reopening to allow for monitoring and adjustment | Rapid lifting of restrictions without adequate safeguards |
Summary
Ultimately, determining whether reopening strategies succeeded or failed requires a comprehensive evaluation. It involves considering multiple metrics, analyzing long-term impacts, and examining the disparate effects on various demographic groups. External factors and the effectiveness of public health measures play critical roles in the equation. This intricate process demands careful consideration and a nuanced understanding of the variables at play.
The answers will help us learn valuable lessons for future crisis management and ensure a more informed approach to similar challenges in the future.