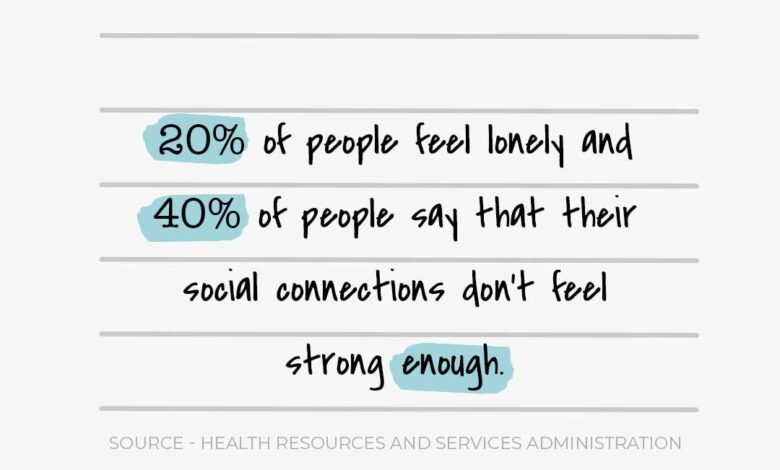
Why are we in the middle of a loneliness epidemic one reason could be an aging population 2 – Why are we in the middle of a loneliness epidemic? One reason could be an aging population 2. This isn’t just a societal issue; it’s a profound human experience affecting individuals across generations. The shift in demographics, coupled with changing social structures, highlights the critical need to understand the complex interplay between aging, loneliness, and societal support systems.
From historical shifts in population demographics to the impact of technology on social interactions, this exploration dives deep into the multifaceted problem of loneliness in an aging world.
This article delves into the multifaceted issue of loneliness, focusing on the aging population as a key contributing factor. It examines the historical context of demographic shifts, explores the impact on social structures, and compares support systems across countries. Furthermore, it analyzes the evolving nature of social interactions, the role of technology, and the changing dynamics of family structures.
The discussion will also touch upon mental and physical health implications, potential solutions, and cultural considerations. The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of this complex issue, paving the way for potential interventions and strategies for a more connected future.
The Aging Population as a Contributing Factor
The global population is aging at an unprecedented rate. This demographic shift, driven by increased life expectancy and declining birth rates, is reshaping societies and presenting unique challenges, particularly concerning the well-being of the elderly. Understanding the impact of this trend on loneliness is crucial for developing effective strategies to address this growing issue.The aging population is a complex phenomenon with profound societal consequences.
It is no longer a future concern, but a present reality with far-reaching implications for social structures, healthcare systems, and economic stability. The shift towards an older population is not uniform across the globe; some countries are experiencing this transition more rapidly than others, creating disparities in resources and support systems.
Historical Overview of Demographic Shifts
Demographic shifts related to aging populations have been observed throughout history, though the current pace and scale are unprecedented. Historically, mortality rates were significantly higher, and life expectancy was considerably shorter. The 20th century witnessed a dramatic increase in life expectancy, largely due to advancements in medicine, sanitation, and nutrition. This led to a gradual but steady increase in the proportion of older adults within the population.
Today, this trend is accelerating, and the implications are more profound than ever before.
Impact on Social Structures and Support Systems
An aging population necessitates adjustments to social structures and support systems. The traditional family unit, often the primary source of support for the elderly, is evolving. Nuclear families and increased geographic mobility often mean that elderly individuals are less likely to have immediate family nearby to provide assistance. This shift can lead to increased social isolation and loneliness, particularly in societies with weakened community ties.
Changes in social support systems are necessary to accommodate the needs of the growing elderly population.
Social Support Systems Across Countries, Why are we in the middle of a loneliness epidemic one reason could be an aging population 2
Social support systems for the elderly vary significantly across countries. Some nations, such as those in Scandinavia, have robust social welfare systems that provide extensive support for the elderly, including access to healthcare, housing assistance, and social activities. Other countries may rely more heavily on family support, which can be inadequate or inconsistent. This disparity in social support systems underscores the need for tailored approaches to combat loneliness among the elderly, recognizing the unique context of each nation.
Financial Strain on Families and Governments
The increasing care needs of the elderly place a significant financial strain on both families and governments. Long-term care, healthcare costs, and potential housing adaptations can create a substantial financial burden, especially for those with limited resources. The burden on government budgets is substantial, demanding strategic investments in social welfare programs and infrastructure to support an aging population.
Governments need to anticipate and plan for these financial implications to ensure adequate resources are available.
Strategies for Mitigating Loneliness
Several strategies can mitigate the impact of loneliness in aging populations. These include promoting social connections through community programs, encouraging intergenerational activities, and fostering digital literacy to enable elderly individuals to stay connected with loved ones and the community. Investing in accessible transportation options and community centers can enhance opportunities for social interaction. This proactive approach necessitates collaboration among governments, communities, and families.
Government Policies to Combat Loneliness
| Country | Policy Examples |
|---|---|
| Sweden | Comprehensive social welfare programs, subsidized senior housing, robust community centers, and initiatives fostering intergenerational interactions. |
| Japan | Emphasis on family support, community-based care programs, and initiatives to promote social engagement among the elderly. |
| United States | Varied approaches; some states and localities have initiatives focusing on senior centers, volunteer programs, and community outreach, but consistent national policy is lacking. |
| United Kingdom | Government initiatives focused on social prescribing, community support services, and programs encouraging social interaction for older adults. |
Impact on Social Connections: Why Are We In The Middle Of A Loneliness Epidemic One Reason Could Be An Aging Population 2

The evolving landscape of social interaction is profoundly impacting individual well-being, and loneliness is a significant consequence. As our world becomes increasingly digital, the nature of human connection is undergoing a dramatic shift. This transformation, while offering some benefits, presents unique challenges, particularly concerning the vulnerability of individuals to feelings of isolation. We need to understand how these shifts affect different communities and generations to address the growing problem of loneliness effectively.The ways we connect have changed dramatically.
Face-to-face interactions, once the cornerstone of social life, are increasingly being replaced by digital communication. While technology offers unprecedented opportunities to connect with people across geographical boundaries, it can also contribute to feelings of isolation, particularly when it replaces meaningful, in-person interactions. Furthermore, the changing structure of families and communities has altered support networks, potentially leaving individuals feeling more disconnected.
Understanding these trends is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat the loneliness epidemic.
Evolving Nature of Social Interactions
Social interactions are evolving at an unprecedented pace. The rise of social media and online communication platforms has fostered new forms of connection. However, this shift has also led to a decline in face-to-face interactions, potentially weakening the depth and richness of relationships. Digital communication often lacks the nonverbal cues and nuances that are crucial for building strong bonds.
The rapid pace of technological advancement further complicates the situation, making it difficult for individuals to adapt and maintain meaningful connections in this ever-changing environment.
Potential Role of Technology in Social Connections
Technology’s impact on social connections is multifaceted. It can facilitate communication across vast distances, connecting individuals with shared interests and creating virtual communities. However, excessive reliance on digital platforms can also lead to feelings of isolation and disconnection from the physical world. The curated nature of online profiles and the potential for cyberbullying further complicate the picture.
The balance between leveraging technology for connection and avoiding its potential pitfalls is a crucial consideration in addressing loneliness.
Changing Dynamics of Family Structures
Family structures are experiencing significant transformations. Increased geographic mobility, smaller family sizes, and changing roles within families have altered the traditional support systems that many individuals relied upon. Multi-generational households are becoming less common, potentially diminishing the availability of emotional and practical support. These shifts have profound implications for social connections and can contribute to feelings of isolation, especially for those living alone or in geographically dispersed families.
Examples of Social Isolation in Various Communities
Social isolation manifests differently across various communities and populations. For instance, rural communities often face challenges in maintaining social connections due to limited access to transportation and opportunities for social interaction. Similarly, marginalized groups may experience higher rates of isolation due to systemic discrimination and social exclusion. Elderly individuals, living alone, may struggle to maintain social connections, while young adults navigating new social landscapes may also be vulnerable to feelings of loneliness.
The need for culturally sensitive approaches to addressing social isolation is evident in these diverse contexts.
Comparison of Loneliness Rates in Different Generations
Loneliness rates vary significantly across generations. Different generations have experienced varying levels of social support, technological advancements, and societal norms. For example, Baby Boomers may experience loneliness due to changes in family structures and the increasing prevalence of single-person households, while Gen Z may experience loneliness due to the hyper-connected but potentially isolating nature of the digital world.
So, why are we in the middle of a loneliness epidemic? One major factor is the aging population. But, let’s be honest, juggling newborn needs, and the endless sleep deprivation, leaves little time for anything else. Finding the best eye creams for new parents here can help combat those tired eyes, which can contribute to a sense of overwhelm.
In the grand scheme of things, though, the isolation and loneliness that often accompany the aging population are still serious concerns.
Understanding these generational differences is crucial for developing tailored interventions to address loneliness across the spectrum of ages.
Correlation Between Technology Use and Loneliness Across Age Groups
| Age Group | High Technology Use | Moderate Technology Use | Low Technology Use | Reported Loneliness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18-25 | High | Moderate | Low | High |
| 26-45 | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate |
| 46-65 | Moderate | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| 65+ | Low | Moderate | High | High |
This table illustrates a potential correlation between technology use and reported loneliness across different age groups. It highlights the need for a nuanced approach to understanding how technology use impacts social connections, recognizing that the relationship between technology and loneliness is not uniform across generations. Further research is needed to establish definitive causal relationships.
Mental and Physical Health Implications

Loneliness, a pervasive issue in modern society, has profound effects on both mental and physical well-being. The absence of meaningful social connections can lead to a cascade of negative consequences, impacting everything from emotional stability to physical health indicators. Understanding these implications is crucial for developing effective interventions and support systems.The correlation between loneliness and mental health conditions is well-documented.
Prolonged feelings of isolation can significantly increase the risk of developing various mental health disorders. Studies have shown a strong link between loneliness and depression, anxiety, and even suicidal ideation. The absence of social support systems can exacerbate these conditions, creating a vicious cycle of isolation and poor mental health.
Correlation Between Loneliness and Mental Health Conditions
Loneliness significantly increases vulnerability to mental health issues. Individuals experiencing chronic loneliness often report higher levels of anxiety and depression. The lack of social interaction and emotional support can hinder coping mechanisms and contribute to feelings of hopelessness and worthlessness. A lack of social connection can create a breeding ground for negative thoughts and emotions. This, in turn, can affect self-esteem, leading to further isolation.
Impact of Loneliness on Physical Health
Loneliness is not just a mental health concern; it also has a tangible impact on physical health. Research consistently demonstrates a correlation between loneliness and a heightened risk of various physical ailments. Studies have linked loneliness to weakened immune function, cardiovascular issues, and increased risk of chronic diseases. The stress response triggered by loneliness can have a direct impact on physiological processes, contributing to poor physical health outcomes.
For instance, individuals experiencing loneliness often have elevated blood pressure and cortisol levels, both of which are linked to various health problems.
Examples of Support Groups and Interventions
Numerous support groups and interventions are designed to address loneliness and promote social connection. These include community centers offering social activities, support groups for seniors, and online forums connecting individuals with shared interests. Volunteer organizations often play a vital role in fostering social interaction and providing opportunities for meaningful connections. These initiatives can help combat loneliness by providing opportunities for social interaction and emotional support.
A crucial element of these interventions is tailoring support to the specific needs of the population being served.
Strategies for Promoting Social Connection
Promoting social connection requires a multifaceted approach. This includes encouraging participation in community events, promoting intergenerational interactions, and facilitating opportunities for individuals to connect with others who share similar interests. Simple actions, such as fostering conversations in public spaces or organizing group activities, can contribute significantly to a more connected community. Encouraging participation in hobbies and shared activities can break down social barriers and promote a sense of belonging.
Mental Health Challenges Associated with Loneliness
| Mental Health Challenge | Symptoms | Potential Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Depression | Persistent sadness, loss of interest, fatigue, changes in appetite and sleep | Therapy (CBT, interpersonal therapy), medication, support groups |
| Anxiety | Excessive worry, fear, nervousness, physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat | Therapy (CBT, mindfulness), medication, relaxation techniques |
| Social Isolation | Withdrawal from social activities, difficulty forming relationships, avoidance of interaction | Therapy (social skills training), support groups, encouragement of social activities |
| Suicidal Ideation | Thoughts of death or self-harm | Immediate professional help (crisis hotline, mental health professional), therapy, medication |
Potential Solutions and Interventions
Combating loneliness, particularly among the elderly, requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the social, emotional, and practical needs of individuals. Effective interventions must go beyond simply providing companionship and aim to foster genuine social connections and a sense of belonging. This involves creating opportunities for meaningful interaction and empowering individuals to actively participate in their communities.Existing programs and initiatives offer valuable insights into strategies that can be adapted and scaled to reach a wider audience.
Innovative solutions are needed to overcome the challenges of isolation and promote well-being in an aging population. This includes recognizing the diverse needs of older adults and tailoring interventions to specific circumstances and preferences.
The loneliness epidemic hitting us hard, especially with an aging population, is a serious concern. Learning how to properly prepare beets, for example, might seem unrelated, but mastering techniques like how to cut beets could be a surprisingly helpful skill. This attention to detail, honed through tasks like preparing vegetables, might be a small part of a larger solution to combatting the isolation often felt by older generations.
It could be as simple as a shared meal prepared together.
Existing Programs Aimed at Combating Loneliness
Various organizations and communities have developed programs to combat loneliness among older adults. These programs often incorporate a combination of social activities, volunteer opportunities, and mental health support. Successful programs emphasize building social networks and providing a sense of purpose. Examples include senior centers offering activities like book clubs, exercise classes, and social gatherings. These structured activities provide opportunities for interaction and shared experiences, fostering a sense of community.
Potential Solutions for Fostering Social Connection
Several potential solutions can foster social connections and reduce isolation among the elderly. These solutions range from technology-based interventions to community-based initiatives. Digital platforms, such as video conferencing and online social groups, can connect individuals who are geographically distant. These platforms can also help older adults maintain contact with family and friends. Furthermore, promoting intergenerational programs, where older adults interact with younger generations, can foster mutual understanding and support.
Such interactions can provide opportunities for mentorship and companionship.
Role of Community Centers and Volunteer Organizations
Community centers and volunteer organizations play a critical role in addressing loneliness among the elderly. These organizations often act as hubs for social activities, providing a safe and welcoming environment for interaction. They offer a range of programs, including social gatherings, educational workshops, and opportunities for volunteering. Volunteering provides a sense of purpose and belonging, which can counteract feelings of isolation.
Community centers often act as meeting places, fostering social connections and facilitating interactions between individuals.
Examples of Successful Community Initiatives
Numerous successful community initiatives have demonstrated the effectiveness of addressing loneliness. For example, some communities have established “friendship benches,” designated spots where individuals can sit and engage in conversation. These benches provide a neutral space for spontaneous interactions and build a sense of community. Other communities have organized “senior walks,” encouraging physical activity and social interaction in a group setting.
Such activities not only improve physical health but also promote social connections.
Comparison of Approaches to Combatting Loneliness
| Approach | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Community Centers | Provide a central location for social activities; Offer diverse programs; Often have established staff and resources. | May not reach individuals who live far from the center; Programs may not always cater to specific needs; May face funding limitations. |
| Volunteer Organizations | Provide opportunities for meaningful engagement and purpose; Foster connections between different generations. | May rely heavily on volunteers; May not always have sufficient resources or staff to cater to a large number of individuals; May not be accessible to all individuals due to geographical constraints. |
| Technology-Based Interventions | Enable communication and interaction across distances; Accessible to individuals with limited mobility. | Requires access to technology and digital literacy; May not replace face-to-face interaction completely; Can exacerbate feelings of isolation if not used appropriately. |
Cultural Considerations
Loneliness, a pervasive issue in our modern world, is profoundly shaped by cultural contexts. Our understanding of social interaction, support systems, and even the expression of emotional distress varies significantly across cultures. Recognizing these differences is crucial for developing effective interventions and support strategies for individuals experiencing loneliness in diverse communities. This section explores how cultural norms and values influence social interactions and the impact of cultural factors on loneliness experiences.
Cultural Norms and Social Interactions
Cultural norms dictate acceptable social behaviors and expectations. In collectivist cultures, strong emphasis is placed on family and community ties. Social interaction often centers around shared activities and responsibilities, fostering a sense of belonging and mutual support. Conversely, individualistic cultures prioritize independence and personal achievement. While this can lead to a sense of self-reliance, it may also result in a reduced emphasis on close-knit social connections and potentially contribute to feelings of isolation, depending on the individual circumstances.
The varying degrees of emphasis on social interactions within families and communities shape the level of social support available and perceived as necessary.
Levels of Social Support Across Cultures
Social support systems vary significantly across cultures. In some cultures, extended family members play a vital role in providing emotional and practical assistance. In others, support networks may be more limited or less formalized. The level of social support available can influence the likelihood of experiencing loneliness. Individuals in cultures with strong social support systems may find it easier to cope with stressful situations and maintain a sense of connection.
Conversely, those in cultures with less formalized support structures may face greater challenges in accessing needed assistance, increasing the risk of loneliness.
The loneliness epidemic, especially among aging populations, is a growing concern. It’s a complex issue, but one contributing factor is the simple lack of connection. Interestingly, while engaging in baby talk, a technique shown to dramatically speed up infants’ language development, having a conversation in baby talk can speed up infants language development , perhaps a similar approach could be used to foster connections in older generations.
This could be a valuable tool in combating the growing issue of loneliness in our aging population.
Impact of Cultural Factors on Loneliness Experiences
Cultural norms influence how individuals perceive and experience loneliness. In some cultures, expressing feelings of loneliness might be considered a sign of weakness or inadequacy, leading individuals to suppress these emotions. Conversely, in other cultures, open expression of emotional distress, including loneliness, is more accepted. These differences in expression can affect the recognition and treatment of loneliness.
Cultural beliefs about aging and the roles of older adults can also contribute to the experience of loneliness.
Cultural Differences in Expressing and Addressing Loneliness
The ways in which individuals express and address loneliness differ across cultures. In some cultures, seeking professional help for emotional distress might be stigmatized, hindering individuals from accessing support services. Cultural beliefs about mental health and well-being can influence the willingness to engage in mental health interventions for loneliness. Furthermore, cultural understanding of loneliness, including its causes and treatment, plays a crucial role in addressing the issue effectively.
Table Summarizing Cultural Differences in Social Norms and Their Impact on Loneliness
| Cultural Dimension | Social Norm | Potential Impact on Loneliness |
|---|---|---|
| Collectivist | Strong emphasis on family and community ties, shared responsibilities | Potentially lower rates of loneliness due to readily available social support. However, pressure to conform can lead to feelings of isolation if individual needs are not met. |
| Individualistic | Prioritization of independence and personal achievement, less emphasis on extended family ties | Potentially higher rates of loneliness if strong social connections are not actively cultivated. Greater autonomy can lead to a sense of freedom, but also isolation. |
| High-context cultures | Emphasis on nonverbal communication and implicit understanding | May lead to a reduced expression of loneliness if feelings are not openly communicated. Misunderstandings in nonverbal cues can potentially exacerbate feelings of isolation. |
| Low-context cultures | Emphasis on explicit communication and direct expression | May lead to a greater likelihood of expressing loneliness if feelings are openly shared. However, individuals may experience pressure to verbalize emotions that are not felt deeply. |
Future Trends and Projections
The aging population is a global phenomenon, and its impact on loneliness is a complex issue that will continue to shape our societies. Understanding future trends in this area is crucial to developing effective preventative measures and support systems. Projecting the future requires considering societal changes, technological advancements, and cultural shifts.The long-term implications of societal changes on social isolation are far-reaching.
As generations shift, the traditional support structures that families and communities provided may weaken. Changes in work patterns, increased urbanization, and evolving family dynamics could contribute to feelings of isolation. Furthermore, the pace of societal change can lead to feelings of displacement and alienation among older adults.
Potential Future Impact of an Aging Population on Loneliness
The increasing proportion of older adults in the global population will inevitably place pressure on social support systems. Without proactive measures, loneliness could become a more pervasive issue, leading to significant mental and physical health consequences. The strain on healthcare resources and social services will also increase. This demographic shift necessitates anticipatory planning and adaptation in healthcare systems, social policies, and community engagement initiatives.
Long-Term Implications of Societal Changes on Social Isolation
Societal changes often lead to shifts in social interaction patterns. The rise of digital communication, while connecting people in new ways, may also contribute to a decline in face-to-face interactions. This trend, coupled with changing family structures and increased urbanization, could lead to more individuals experiencing social isolation. Maintaining a balance between digital and real-world interactions will be critical to mitigating social isolation.
Possible Future Technological Advancements to Combat Loneliness
Technological advancements offer promising avenues to combat loneliness. The development of more sophisticated telehealth platforms could enable older adults to connect with healthcare providers and social support groups remotely. Wearable technology, designed to monitor well-being and encourage social interaction, could also play a role. Virtual reality (VR) applications could simulate social interactions and provide a sense of community.
Examples of Preventative Measures to Address Loneliness
Early intervention programs are essential to combat loneliness before it escalates into more serious issues. These programs could involve community-based initiatives that encourage social engagement among older adults. Promoting intergenerational programs can bridge the gap between generations and foster a sense of community. Providing access to affordable transportation can facilitate social outings and visits.
Summary Table of Potential Future Trends in Addressing Loneliness
| Potential Future Trend | Effectiveness | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Increased investment in telehealth services | High | Telehealth can provide accessible healthcare and social support, potentially reducing isolation. |
| Development of AI-powered social interaction tools | Moderate | AI could personalize support and engagement, but the effectiveness depends on proper implementation and ethical considerations. |
| Promotion of intergenerational programs | High | Intergenerational programs can foster a sense of community and combat loneliness by bridging generational gaps. |
| Improved access to affordable transportation | High | Access to transportation enables older adults to participate in social activities and maintain connections. |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the loneliness epidemic, particularly concerning the aging population, necessitates a multifaceted approach. While the aging population presents unique challenges, potential solutions exist. From strengthening social support systems to fostering technological engagement, the key lies in acknowledging the complex interplay of demographics, societal structures, and cultural norms. By understanding these factors, we can move toward a future where loneliness is not an inevitable consequence of aging but a preventable issue.
The journey toward combating loneliness in our aging communities requires a collective effort, encompassing individuals, families, governments, and communities alike.





