Why is the cost of insulin rising and what can people do about it? This critical issue affects millions, with prices skyrocketing in recent years. We’ll explore the factors driving these increases, from manufacturing processes to pharmaceutical company policies. Furthermore, we’ll examine potential solutions, including government subsidies, alternative pricing models, and patient assistance programs. The discussion will also consider the impact on various demographics and the potential consequences of inaction.
The current state of insulin prices presents a significant challenge for individuals managing diabetes. Historical data reveals a substantial gap between insulin costs and other medical necessities. Different insulin types exhibit varying price points, adding complexity to affordability. This disparity disproportionately affects low-income individuals and families, highlighting the urgency for accessible solutions. The role of pharmaceutical companies in setting these prices is also a key element in understanding this crisis.
Rising Insulin Costs
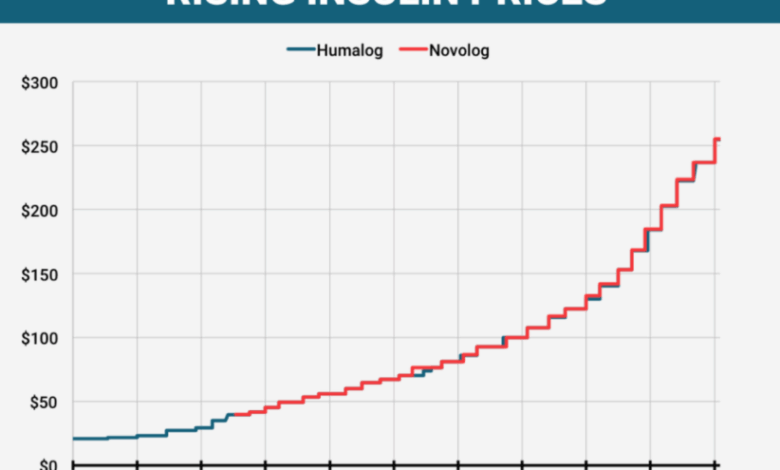
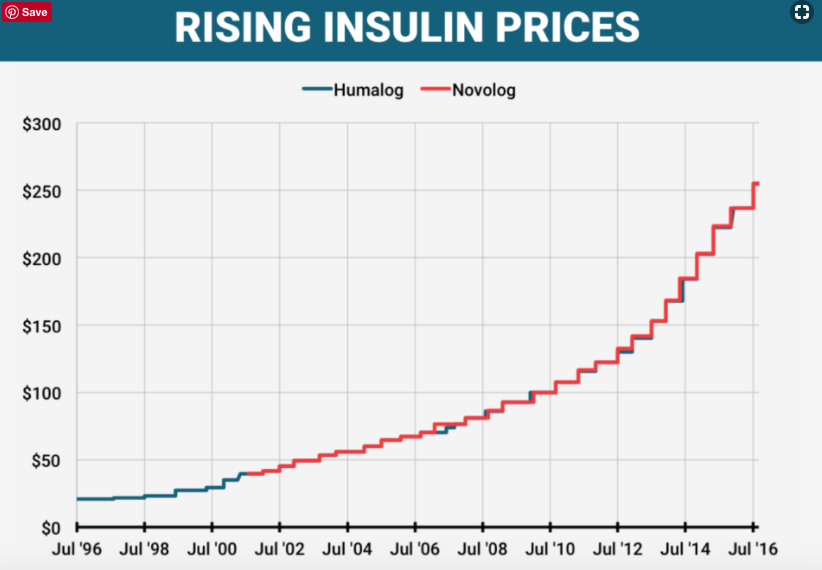
The escalating cost of insulin has become a critical issue for millions worldwide, impacting individuals with diabetes and straining healthcare systems. This dramatic price increase, particularly in recent years, has created a significant financial burden and has raised concerns about access to life-saving medication. Understanding the factors driving these costs and the impact on various demographics is essential to developing effective solutions.The rising cost of insulin is a complex issue, rooted in several factors including pharmaceutical pricing strategies, manufacturing processes, and the types of insulin available.
Historical data reveals a stark contrast between the cost of insulin and other essential medications or consumer goods, highlighting the substantial and disproportionate increase in insulin prices. This difference underscores the need for further investigation and action.
Current State of Insulin Prices
Insulin prices have risen dramatically in recent years, far outpacing the inflation rate for other consumer goods. This rapid increase has placed a considerable strain on individuals and families managing diabetes. Data from various sources, including government reports and independent analyses, demonstrate a significant upward trend in insulin prices.
Historical Price Comparison
Comparing the cost of insulin to other medical necessities and consumer goods reveals a concerning disparity. While the cost of other essential medicines and consumer products may have increased, the rate of increase for insulin has been notably higher. This comparison emphasizes the unique challenges faced by those needing insulin.
Types of Insulin and Price Variations
Several types of insulin are available, each with varying levels of efficacy and duration of action. These differences affect the price of each type of insulin. The prices for different types of insulin vary significantly, with some formulations costing considerably more than others. This price variation further complicates the issue of affordability.
Impact on Vulnerable Demographics
The rising cost of insulin disproportionately affects low-income individuals and families. These individuals often face significant financial hardships in affording the medication necessary to manage their health conditions. This is a critical concern for public health.
Role of Pharmaceutical Companies in Setting Insulin Prices
Pharmaceutical companies play a significant role in determining insulin prices. Their pricing strategies, including factors such as research and development costs, manufacturing expenses, and market competition, significantly influence the cost of insulin. Understanding the financial considerations and market dynamics is essential to address the affordability issue.
Factors Contributing to Rising Costs
The escalating price of insulin is a critical issue impacting millions worldwide. Understanding the multifaceted factors driving these increases is essential to developing effective solutions. Beyond the immediate impact on individuals, these factors reveal systemic challenges within the pharmaceutical industry and healthcare systems.The escalating cost of insulin isn’t simply a matter of supply and demand; it’s a complex interplay of various factors, from manufacturing processes to market dynamics.
Understanding these underlying forces is crucial for devising sustainable and equitable solutions.
Manufacturing Processes and Research and Development, Why is the cost of insulin rising and what can people do about it
The production of insulin, while largely automated, involves intricate steps requiring specialized equipment and skilled personnel. Technological advancements, such as genetic engineering and improved purification techniques, can enhance production efficiency and yield, but these advancements often come with substantial capital expenditures. Research and development costs for new insulin formulations, delivery methods, and companion therapies further add to the overall cost.
For example, developing a new insulin analog that offers improved efficacy or reduced side effects requires substantial investment in research and clinical trials, which are reflected in the final price.
Patent Protection and Market Competition
Patent protection plays a significant role in influencing insulin pricing. When a company holds a patent on a particular insulin formulation, it can often set prices without facing immediate competition. However, as patents expire, generic versions of insulin often enter the market, potentially reducing prices. The absence of robust market competition can, in some cases, lead to inflated prices.
For instance, the prolonged exclusivity of certain insulin formulations has contributed to sustained high prices.
Insulin Pricing Models in Different Countries
Different countries employ various pricing models for insulin. In some nations, the government sets prices, often based on cost-effectiveness and public health considerations. Other countries rely on market forces to determine prices, with varying degrees of regulatory oversight. Comparing pricing models across different countries reveals considerable disparities, highlighting the impact of healthcare system structures and policies on insulin affordability.
For instance, in countries with national health insurance, the price negotiation power of the system can impact the final price.
Role of Intermediaries
Pharmacies, insurance companies, and other intermediaries play a crucial role in shaping the final price of insulin. Markup percentages, administrative costs, and reimbursement rates can significantly influence the affordability of insulin. For example, substantial markups applied by pharmacies or complex insurance formularies can make insulin unaffordable for patients. The role of intermediaries can also include negotiating prices with manufacturers.
Administrative Overhead and Distribution Processes
The administrative overhead and distribution costs associated with insulin production and delivery contribute to the overall price. These costs include warehousing, logistics, and regulatory compliance. The complexity of the global supply chain, encompassing diverse manufacturing facilities and international distribution networks, further adds to the administrative costs. For example, the need to maintain stringent quality control standards across various distribution channels can significantly impact the final price.
Alternatives and Affordability Strategies
The escalating cost of insulin poses a significant challenge for individuals managing diabetes. While understanding the factors driving these price increases is crucial, equally important is exploring potential solutions to make insulin more accessible and affordable. This section delves into alternative insulin options, government strategies, and individual cost-saving measures.
Insulin Brand Cost Comparison
Various insulin brands offer different formulations and delivery methods, leading to varying prices. A comparison of these costs is essential for patients to make informed decisions about their treatment. Understanding the price differences empowers individuals to explore alternatives and optimize their budgets.
| Insulin Brand | Type | Typical Monthly Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Humalog (lispro) | Rapid-acting | $300-$500 |
| Lantus (glargine) | Long-acting | $250-$450 |
| NovoLog (aspart) | Rapid-acting | $350-$550 |
| Levemir (detemir) | Long-acting | $200-$400 |
| Generic Insulin Analogs | Rapid/Long-acting | $100-$300 |
Note: Prices are approximate and may vary depending on the pharmacy, insurance coverage, and specific dosage.
Affordability Strategies: Government and Policy Interventions
Addressing the high cost of insulin requires a multifaceted approach. Government subsidies and price controls can significantly impact affordability. These strategies can help mitigate the financial burden on patients.
- Government Subsidies: Direct financial support from the government, such as subsidies or coupons, can make insulin more affordable for patients. This can be achieved through programs that provide direct financial assistance or discounts to qualified individuals. Examples include government-funded prescription drug programs, which provide reduced-cost medications for low-income individuals.
- Price Controls: Implementing price controls on insulin can limit the extent to which pharmaceutical companies can raise prices. This could potentially curb excessive price increases, though the impact on supply chain and pharmaceutical innovation requires careful consideration. This approach is often implemented in countries with strong public health systems.
- Negotiating Lower Prices: Governments can negotiate lower prices with pharmaceutical companies for insulin, leveraging their purchasing power to obtain more favorable terms. This approach has been successful in some countries.
Innovative Approaches from Other Countries
Several countries and regions have implemented innovative strategies to address high insulin costs. Analyzing these approaches can provide valuable insights for policy development in other countries.
So, insulin costs are skyrocketing, leaving many struggling. It’s a serious issue, and while there’s no magic bullet, exploring alternative solutions is important. One often-discussed yet controversial area is the potential life-extending benefits of switching to e-cigarettes. Switching to e-cigarettes can lengthen your life , according to some studies, though it’s crucial to approach this with caution.
Ultimately, finding affordable and effective ways to manage your health, like exploring insulin affordability programs, is key to navigating this challenging time.
- Canada’s Public Drug Plan: Canada’s publicly funded drug plan has a system for regulating drug prices, which has been instrumental in keeping insulin costs lower compared to the United States.
- European Union’s Price Regulation: The European Union has various regulations that set limits on pharmaceutical pricing, including insulin. These regulations often factor in factors like the drug’s efficacy and innovation.
Cost-Saving Measures for Individuals
Individuals can take steps to manage their insulin costs. These strategies can help reduce the financial burden while ensuring adequate treatment.
So, insulin costs are skyrocketing. It’s a real struggle for people with diabetes. While we can’t always control the pharmaceutical market, perhaps we should consider other avenues for affordable health solutions. Maybe we should question the value of some supplements, like multivitamins, which recent research suggests don’t provide many significant health benefits. Check out this recent study on the efficacy of multivitamins: multivitamins dont provide many health benefits researchers say.
Ultimately, though, focusing on preventative care and exploring cost-effective options like a healthier diet and lifestyle is key to managing insulin costs.
| Cost-Saving Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Generic Insulin | Using generic insulin, when available, can significantly reduce costs compared to brand-name products. Generic insulins often contain the same active ingredients and provide comparable effectiveness. |
| Patient Assistance Programs | Pharmaceutical companies and other organizations often offer patient assistance programs that provide financial assistance for medications. These programs can cover a portion of the cost for eligible patients. |
| Prioritizing Affordable Options | Comparing costs of different insulin brands, delivery methods, and dosage types is crucial. Patients should prioritize the most affordable option while ensuring they receive the necessary dose and type for their specific needs. |
Public Policy and Regulation: Why Is The Cost Of Insulin Rising And What Can People Do About It
The escalating cost of insulin is a complex issue, and government intervention is increasingly seen as a crucial element in finding solutions. Policymakers face the daunting task of balancing the need to make insulin affordable for patients with the imperative to maintain a thriving pharmaceutical industry. This section explores potential regulatory approaches, examining the roles of governments and insurance companies in controlling costs, and comparing international approaches to pharmaceutical pricing.A key aspect of addressing the rising cost of insulin is the need for effective government regulations.
These regulations must consider both patient access and the financial viability of pharmaceutical companies. The goal is to create a system that ensures affordable insulin while maintaining the incentive for innovation and research in the pharmaceutical industry. Different approaches to regulation exist, each with its own set of potential benefits and drawbacks.
Potential Government Regulations
Governments can implement various regulations to influence insulin prices. These could include price controls, negotiation of lower prices by public programs, and measures to incentivize the development of cheaper alternatives. The specific regulations will vary depending on the particular economic and political context.
- Price Controls: Price controls, while potentially effective in lowering costs for consumers, can sometimes discourage investment in research and development. This could potentially impact the long-term availability of innovative insulin products. Countries like Canada and the UK have different approaches to price regulation, reflecting varying national priorities and economic realities. For example, in some European countries, national health systems negotiate bulk discounts for medications, resulting in lower costs for consumers.
- Incentivizing Biosimilar Development: Governments could implement policies that incentivize the development of biosimilar insulins. These are highly similar to the original insulin, but are often produced at lower costs, which could significantly reduce the price for consumers. The success of biosimilar adoption in the market will depend on factors like regulatory approvals, consumer acceptance, and manufacturer incentives.
- Negotiating Prices: The government or a national health service can negotiate with pharmaceutical companies for bulk discounts on insulin, much like how large retailers negotiate with suppliers. This approach is already used in some countries to manage pharmaceutical costs.
Role of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies play a significant role in determining the affordability of insulin. Their negotiating power with pharmaceutical companies can be substantial, potentially leading to lower prices for their insured members. The effectiveness of insurance company negotiations depends on factors such as the bargaining power of the insurance companies and the specific regulations in place.
- Negotiation Strategies: Insurance companies can leverage their collective purchasing power to negotiate lower prices with pharmaceutical companies. This approach can significantly reduce the cost of insulin for policyholders. The success of these negotiations depends on factors such as the insurance company’s size and influence.
- Impact on Premiums: The savings achieved through negotiations could be reflected in lower premiums for insurance policyholders, or used to offset the costs in other areas of the health insurance package. However, the savings might not always be directly passed on to consumers, and may be partially absorbed by the insurance company.
International Regulatory Frameworks
Different countries have adopted various regulatory approaches to pharmaceutical pricing. These frameworks reflect the unique economic and social contexts of each nation. Comparing these frameworks can offer insights into potential solutions for the US insulin crisis.
| Country | Regulatory Framework | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Market-based system with limited price controls | Relies heavily on market forces; insulin prices are influenced by supply and demand, with limited government intervention. |
| Canada | Publicly funded system with price controls | Negotiates drug prices; government has more control over pharmaceutical pricing. |
| United Kingdom | National Health Service system | Negotiates prices with pharmaceutical companies, with price controls influencing the cost of medications. |
Implementing Affordable Policies
Policies designed to increase insulin affordability must consider both the cost of the drug and the long-term health of the pharmaceutical industry. Finding a balance between these two factors is crucial to ensuring the sustainability of the system.
- Promoting Competition: Encouraging competition among insulin manufacturers could potentially drive down prices and increase availability of different formulations and strengths. Policies to foster competition could include streamlining regulatory approval processes for biosimilars and promoting generic alternatives.
- Ensuring Quality: The quality of insulin must be maintained regardless of the price. Regulations should ensure that lower-cost alternatives meet the same safety and efficacy standards as traditional insulin.
Potential Consequences of Price Controls
Price controls on insulin could potentially impact the pharmaceutical industry in various ways. These impacts can range from reduced investment in research and development to decreased production of insulin.
High insulin costs are a real struggle for many. Understanding the factors driving these increases, like manufacturing costs and pharmaceutical company policies, is key. Learning how to navigate these challenges requires proactive steps, like researching affordable options and advocating for change. Fortunately, a helpful resource for those preparing for similar challenges in other fields is the AR test sample lesson , which can provide valuable insights into practical problem-solving techniques.
Ultimately, empowering ourselves with knowledge and support is crucial in tackling this significant issue.
- Reduced Investment: Price controls can reduce the financial incentive for pharmaceutical companies to invest in research and development for new and improved insulin formulations. This could lead to a slower pace of innovation in the long term.
- Decreased Production: A significant reduction in the price of insulin may make it less profitable for pharmaceutical companies to produce it, potentially leading to decreased production and supply shortages.
Patient Perspectives and Experiences
The rising cost of insulin is not just a financial burden; it’s a profound impact on the lives of millions of people living with diabetes. This section delves into the human stories behind these escalating costs, exploring the challenges patients face and the resources available to help.Patients across the nation are struggling to afford the medication they need to manage their health.
The emotional and practical consequences are significant, impacting their daily routines, financial stability, and overall well-being.
Patient Stories
The personal stories of individuals living with diabetes offer a glimpse into the real-world impact of rising insulin costs. One patient might find their savings dwindling as they struggle to cover monthly insulin expenses. Another might delay necessary medical care due to the high cost of medication. These experiences illustrate the urgent need for solutions that address the financial burden on patients.
Patient Assistance Programs
Numerous patient assistance programs exist to help individuals manage the cost of insulin. These programs often provide discounts or free medications to eligible patients. Understanding the eligibility criteria and navigating the application process is crucial.
| Program Name | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|
| Patient Assistance Program 1 | Generally, those with low incomes and limited insurance coverage are prioritized. The specific requirements vary based on the program’s guidelines. |
| Patient Assistance Program 2 | Individuals with specific medical conditions or diagnoses may qualify. Documentation of medical needs is often required. |
| Patient Assistance Program 3 | Individuals enrolled in certain government programs, such as Medicaid or Medicare, may be eligible. Verification of enrollment is often needed. |
Navigating these programs can be challenging, and patients may need additional support.
Challenges in Accessing Affordable Insulin
Patients face numerous hurdles in accessing affordable insulin. The application process for assistance programs can be complex and time-consuming. Many programs have limited availability, making it difficult for all eligible individuals to receive help. The lack of clear, easily accessible information about these programs also creates a barrier.
Impact on Health Outcomes
The rising cost of insulin can directly impact patient health outcomes. Patients may delay or reduce their insulin dosage to save money, potentially leading to complications from uncontrolled blood sugar levels. This, in turn, can lead to increased hospitalizations, greater medical expenses, and a reduced quality of life.
Resources for Patients
Various resources are available to support patients struggling with insulin costs. Many patient advocacy groups offer information and assistance. Websites and helplines provide guidance on navigating assistance programs and accessing financial support. Government agencies also provide resources for patients in need.
Potential Solutions and Future Trends
The escalating cost of insulin presents a significant challenge for individuals and healthcare systems worldwide. Addressing this issue requires a multifaceted approach encompassing innovative solutions, technological advancements, and sustainable affordability models. Exploring alternative delivery methods, biosimilars, and long-term policy strategies is crucial to ensure equitable access to life-saving medication.The future of insulin management hinges on the development and adoption of cost-effective, yet high-quality, solutions.
This involves a comprehensive examination of various approaches, from technological breakthroughs to policy changes, aiming to make insulin more accessible and affordable for everyone who needs it.
Biosimilars and Innovative Insulin Alternatives
Biosimilars are a key area of potential advancement in the insulin market. These are highly similar versions of biological medicines like insulin, produced through advanced biopharmaceutical techniques. The production of biosimilars can often lead to reduced costs, as they compete with the original patented products. This competition can potentially drive down prices, making insulin more accessible.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Insulin Production and Delivery
Technological advancements are transforming insulin production and delivery, offering potential solutions for affordability and improved patient outcomes. For example, research into new methods for producing insulin using genetically engineered organisms could significantly reduce the cost of production. Furthermore, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are increasingly sophisticated, enabling more precise and personalized insulin delivery.
Long-Term Solutions for Maintaining Affordability
Maintaining affordability while preserving quality and innovation in the insulin market requires a multifaceted approach. Government subsidies, tax incentives, and public-private partnerships could be employed to support the development and implementation of innovative technologies and cost-effective solutions. Furthermore, promoting competition in the insulin market, including the use of biosimilars, is vital to keep costs down. The key is to find a balance that encourages research and development without compromising the safety and efficacy of the medication.
Different Models of Insulin Access and Affordability
Various models of insulin access and affordability are being explored globally. These include government-funded programs, subsidies for vulnerable populations, and tiered pricing structures. Each model has advantages and disadvantages, with the most effective approach likely involving a combination of strategies tailored to specific national or regional contexts. For instance, a program offering subsidized insulin for low-income patients might complement a pricing strategy that encourages the use of biosimilars.
Projected Costs of Insulin (Next 5-10 Years)
| Year | Projected Cost (USD) | Reason for Change |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | $1,500 | Current market prices, limited biosimilar availability |
| 2025 | $1,350 | Increased biosimilar adoption, reduced patent protection |
| 2026 | $1,200 | Further biosimilar competition, technological advancements in production |
| 2027 | $1,100 | Wider adoption of CGM and personalized insulin delivery |
| 2028 | $1,050 | Continued competition, potential for new innovative therapies |
| 2029 | $950 | Continued improvements in insulin production and delivery |
| 2030 | $900 | Continued market adjustments, increasing use of biosimilars |
Note: These projections are estimates and are subject to change based on market dynamics, technological advancements, and policy changes.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the escalating cost of insulin is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. While various factors contribute to the problem, from manufacturing to pricing models, there are potential strategies for achieving greater affordability. Government regulation, innovative alternatives, and patient assistance programs all play crucial roles in mitigating the crisis. Ultimately, a multi-pronged approach involving both policy changes and patient-centered solutions is essential for ensuring access to this vital medication.