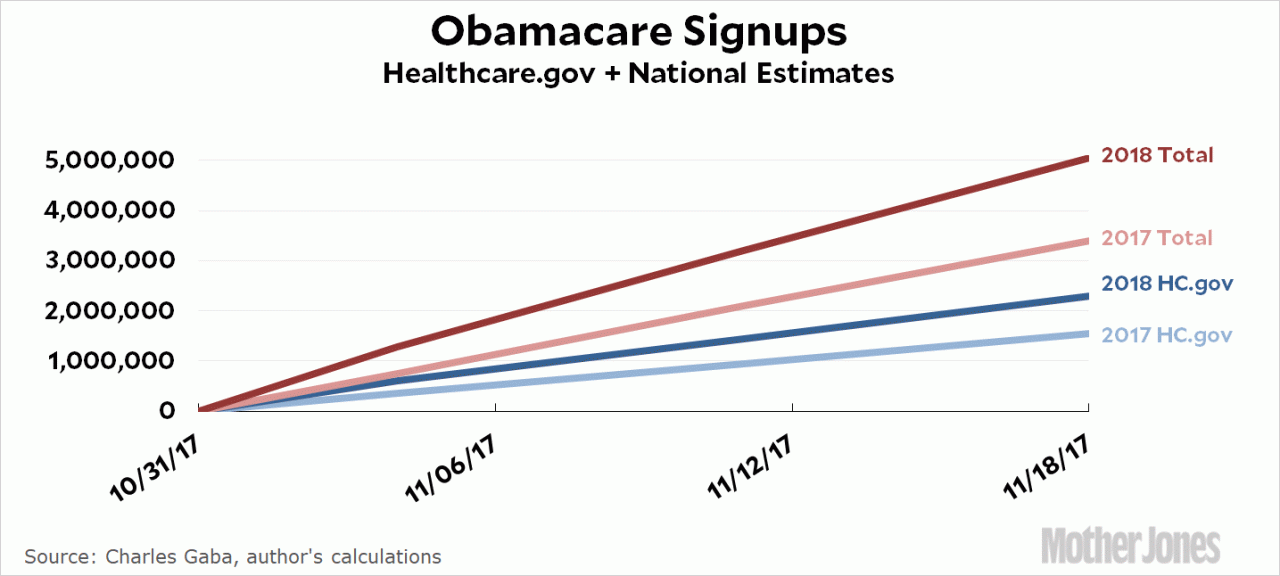
Why you should care that obamacare enrollment is down. The recent dip in Obamacare sign-ups isn’t just a statistic; it signals a potential shift in healthcare access and affordability for millions. This decline has significant implications for individuals, the healthcare system, and the broader economy. Understanding the factors behind this trend and the potential consequences is crucial for anyone concerned about the future of healthcare in America.
This drop in enrollment could disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, impacting their ability to obtain necessary medical care. It also raises concerns about the sustainability of the Affordable Care Act and the long-term health of the American healthcare system. We’ll delve into the economic, political, and demographic factors contributing to this trend, and explore potential solutions and alternative models.
Impact on Healthcare Access: Why You Should Care That Obamacare Enrollment Is Down
Declining enrollment in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace, often referred to as Obamacare, presents a significant concern for healthcare access, particularly for vulnerable populations. The potential consequences ripple through the entire healthcare system, affecting both individuals and providers. Understanding the relationship between enrollment numbers and the affordability of plans is crucial in assessing the overall impact.The ACA’s marketplace provides a critical safety net for millions of Americans, especially those who might not qualify for employer-sponsored insurance or traditional subsidies.
Lower Obamacare enrollment numbers are a serious concern because access to affordable healthcare is vital for everyone. When fewer people have insurance, it directly impacts the health of communities, especially those already facing systemic disadvantages. This directly relates to the crucial issue of racism as a health crisis; as highlighted in this important article, racism is a health crisis why aren’t we treating it like one , the cumulative effect of discrimination has devastating physical and mental health consequences.
Ultimately, declining enrollment in affordable healthcare plans hurts everyone, as a healthier population is a stronger population for everyone.
A reduction in enrollment directly translates to fewer people having access to affordable health insurance options. This, in turn, can lead to increased healthcare costs in the long run as individuals delay necessary medical care due to financial constraints.
Vulnerable Populations
Reduced enrollment in the ACA marketplace disproportionately affects vulnerable populations, such as low-income individuals and those with pre-existing conditions. Without access to affordable insurance, these individuals face a higher risk of delaying or foregoing necessary medical care, leading to potential health complications and a strain on the healthcare system. The lack of preventive care can result in more expensive treatments later on.
Healthcare Providers and Hospitals, Why you should care that obamacare enrollment is down
Decreased enrollment can negatively impact healthcare providers and hospitals, potentially leading to a decline in patient volume and revenue. This could force some providers to limit services, particularly in areas with low enrollment. For example, rural hospitals might struggle to maintain essential services if they experience a significant drop in insured patients.
Affordability of Healthcare Plans
The correlation between enrollment numbers and the affordability of healthcare plans is complex. Lower enrollment can impact the stability of the insurance marketplace, potentially leading to higher premiums for those who remain enrolled. This can be exacerbated by the interplay of market forces and the overall health of the insured population. Increased demand for coverage, particularly in areas with limited choices, can further drive up costs.
Enrollment Rates by Demographics
The impact of declining enrollment varies across different demographic groups. Analyzing enrollment rates by age, income, and location provides a more nuanced understanding of the issue.
| Demographic | Enrollment Rate | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Low-income individuals | Likely lower than average | Higher risk of delaying or forgoing necessary medical care, potentially leading to increased healthcare costs later on. |
| Individuals with pre-existing conditions | Potentially lower than average | Higher risk of delayed or forgone care, impacting their long-term health and increasing costs for the system. |
| Rural populations | Potentially lower than average | Limited access to providers and healthcare facilities, potentially leading to longer travel times for care. |
| Older adults | Potentially higher than average | Significant impact on the affordability and availability of healthcare plans, impacting their ability to access necessary care. |
Economic Implications
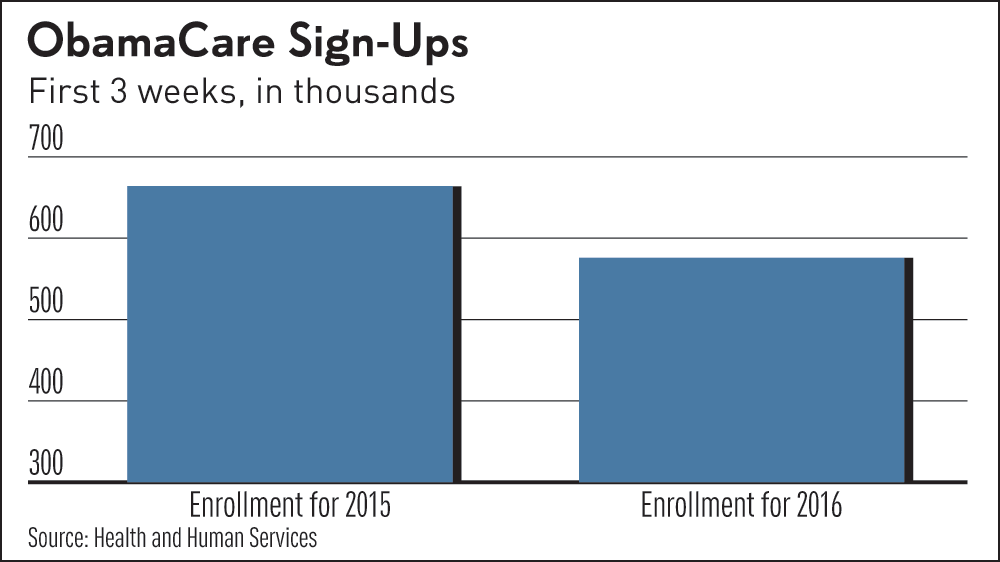
Reduced Obamacare enrollment has significant ramifications for the overall healthcare system, impacting both individuals and the government. The financial strain on various sectors, from insurance companies to hospitals, warrants careful examination. Understanding these implications is crucial for crafting informed policies and strategies to ensure healthcare affordability and accessibility.
Financial Burden on Individuals
The decrease in enrollment affects individuals’ access to affordable health insurance. This can lead to higher out-of-pocket costs for medical services, especially for those who lack alternative coverage options. The financial burden on individuals is often amplified by rising healthcare prices, which can strain personal budgets and create financial instability.
Financial Burden on the Government
Decreased enrollment can lead to a reduction in government revenue from premium taxes and subsidies. This directly impacts the government’s ability to fund healthcare programs and initiatives. The reduced pool of insured individuals can also result in an increase in the number of uninsured individuals, potentially requiring more public spending on emergency services and uncompensated care. The government’s financial position is closely tied to the health of the healthcare system, highlighting the importance of maintaining adequate insurance coverage.
Impact on Insurance Companies
Lower enrollment can negatively affect insurance companies’ profitability. Decreased demand for coverage leads to reduced premiums and potentially lower investment returns. This can cause insurers to struggle to maintain their financial stability, especially if they are not adequately prepared for a shrinking pool of insured individuals.
Influence on Healthcare Costs
Reduced enrollment can influence healthcare costs in various ways. Lower demand for services might result in decreased pricing for some procedures or medications. However, the potential for increased costs in other areas, such as uncompensated care, remains a significant concern. Understanding the interplay of these factors is crucial for policymakers aiming to manage healthcare costs effectively.
Projected Financial Impact of Decreased Enrollment
| Sector | Potential Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Insurance Companies | Reduced premiums, lower investment returns, potential profitability issues. | A decrease in the number of policyholders may result in a decrease in the revenue for an insurance company, impacting its ability to pay out claims and maintain financial stability. |
| Hospitals | Potential decrease in revenue from insured patients, increased burden of uncompensated care. | Hospitals might see a decrease in revenue from patients with insurance coverage, which can lead to reduced funding for operations, staffing, and equipment. Simultaneously, the increase in uninsured individuals may translate into a greater financial burden due to uncompensated care. |
| Government | Reduced tax revenue from premiums and subsidies, potential increase in spending on uncompensated care and emergency services. | Decreased tax revenue from premiums and subsidies could strain the government’s ability to fund healthcare initiatives and programs. This, in turn, may lead to a higher financial burden on the public sector. |
| Individuals | Increased out-of-pocket costs, potential difficulty accessing necessary care. | Individuals might face higher costs for medical services and procedures, which could impact their financial stability and access to quality healthcare. |
Political and Policy Implications
The declining enrollment in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace has significant political ramifications, potentially impacting future healthcare policy and government intervention strategies. This shift in participation necessitates a careful examination of the political landscape surrounding healthcare reform and the various viewpoints on the issue. Understanding the implications of declining enrollment is crucial for crafting effective policy responses.The political implications of declining enrollment extend beyond simple party lines.
It prompts a critical reevaluation of the ACA’s effectiveness and raises questions about the role of government intervention in healthcare markets. The ongoing debate surrounding the ACA’s future underscores the importance of understanding the different perspectives on healthcare policy and the various policy responses being considered.
Political Ramifications of Declining Enrollment
The declining enrollment in the ACA marketplace has sparked a renewed political debate about the future of healthcare reform. This decline potentially weakens the ACA’s foundation, potentially influencing legislative efforts to either strengthen or dismantle the law. A key aspect of this political discourse is the role of government intervention in influencing enrollment numbers.
Government Intervention in Influencing Enrollment
Government interventions, such as subsidies and outreach programs, play a crucial role in encouraging enrollment in healthcare marketplaces. These interventions aim to make healthcare coverage more accessible and affordable for those who might otherwise be excluded. The effectiveness of these programs, however, is a subject of ongoing debate.
Policy Responses to Declining Enrollment
Potential policy responses to declining enrollment range from strengthening subsidies and expanding outreach programs to exploring alternative healthcare models or even considering repealing or amending certain provisions of the ACA. Each policy option carries its own set of political and economic considerations. A nuanced understanding of these considerations is essential for effective policy formulation.
Different Viewpoints on the Issue
Different political viewpoints hold distinct perspectives on the issue of declining enrollment. Conservatives may advocate for reducing government intervention in healthcare, potentially through eliminating or reducing subsidies, while liberals might argue for strengthening the ACA and expanding subsidies. These contrasting viewpoints highlight the complexity of the issue.
Stance of Different Political Parties
| Political Party | Stance on Declining ACA Enrollment |
|---|---|
| Democrats | Generally advocate for strengthening the ACA, increasing subsidies, and expanding outreach programs to improve access and affordability. |
| Republicans | Often advocate for repealing or significantly altering the ACA, potentially exploring alternative healthcare models, while also advocating for market-based solutions. |
| Independents | May hold a variety of perspectives, ranging from supporting modifications to the ACA to advocating for a complete overhaul of the system. |
Potential Solutions
Reversing the downward trend in Affordable Care Act (ACA) enrollment requires a multifaceted approach. Simply throwing money at the problem won’t work; we need targeted strategies that address the root causes of declining participation. This involves a deep dive into the reasons behind the lack of interest and a commitment to innovative solutions that resonate with potential enrollees.
Lower Obamacare enrollment numbers are a serious concern, impacting access to affordable healthcare for many. It’s a reminder of how important it is to support policies that ensure everyone has access to the care they need. This is especially relevant when you consider the struggles faced by individuals dealing with issues like birthmark bullying, a painful reality that one woman is bravely confronting and advocating against on this important blog post.
Ultimately, robust healthcare systems are crucial for a healthy and equitable society, and decreased enrollment highlights the need for ongoing support and advocacy.
Targeted Outreach and Education
Improving communication and accessibility are crucial. Many potential enrollees may be unaware of the benefits or the process of signing up. Effective outreach programs should focus on community engagement, using diverse channels to reach diverse populations. This includes partnerships with community health centers, faith-based organizations, and local businesses. Clear, concise, and culturally relevant information materials are essential to ensure understanding.
Educational campaigns should highlight the financial assistance programs available, such as subsidies, and demystify the application process. Utilizing social media and online platforms can effectively reach a wider audience.
Improving Affordability and Accessibility
“Making healthcare more affordable and accessible is a key element in increasing enrollment.”
Financial barriers are significant obstacles for many. Expanding eligibility for subsidies and streamlining the application process are vital steps. Simplifying the navigation of the marketplace and offering clear, easy-to-understand information about the various plans and subsidies can make the process less daunting. Innovative approaches to affordability include partnerships with employers to offer subsidized plans and explore options for reducing out-of-pocket costs for enrollees.
Addressing Perceived Barriers and Concerns
Many individuals may have concerns about coverage or the quality of care. Addressing these issues head-on can lead to increased confidence in the ACA marketplace. Open communication about coverage specifics and the quality of providers can be critical. Transparency regarding provider networks and coverage details is crucial to dispelling misinformation and building trust. Providing accessible avenues for individuals to express concerns and ask questions can foster a more positive perception of the program.
Analyzing Stakeholder Solutions
Stakeholders have proposed various strategies. Advocates for increased subsidies and simplified enrollment processes highlight the financial aspect, while others emphasize the importance of improved provider networks and outreach initiatives. Evaluating the proposals requires a thorough understanding of their potential costs and benefits, as well as their potential impact on overall healthcare access.
Potential Solutions Table
| Solution | Estimated Cost | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted Outreach & Education | $5-10 million (variable based on scale) | Increased awareness, improved enrollment rates, reduced administrative burden |
| Improving Affordability & Accessibility | $10-20 million (variable based on subsidy expansion) | Reduced financial burden, greater access, increased enrollment |
| Addressing Perceived Barriers & Concerns | $2-5 million (variable based on outreach efforts) | Increased trust, reduced misinformation, improved enrollment |
| Employer Partnerships | $5-15 million (variable based on scale) | Increased participation, improved affordability for employees, reduced administrative burden |
Demographic Analysis
Understanding the decline in Obamacare enrollment requires a deep dive into the demographic patterns driving this trend. Different age groups, genders, and socioeconomic backgrounds may react differently to healthcare market changes, influencing their decision to participate in the program. Analyzing these patterns helps policymakers and healthcare providers tailor solutions and outreach strategies to better serve the needs of those affected.
Hey everyone, it’s important to pay attention to declining Obamacare enrollment because access to affordable healthcare is crucial. Think about it, if fewer people have insurance, it could lead to a rise in preventable illnesses, which also links to the recent concerning trend of scooter DUI, with most e-scooter accidents being tied to drinking, as detailed here.
Ultimately, this all affects our collective well-being and the stability of our healthcare system, so let’s keep a close eye on these issues.
Enrollment Rates by Age Group
Age is a significant factor in healthcare enrollment decisions. Younger adults, particularly those between the ages of 18 and 35, are often less likely to enroll in the program due to various reasons including employment status and perceived healthcare needs. This group frequently relies on employer-sponsored insurance. Conversely, older adults, often facing pre-existing conditions and higher healthcare costs, tend to be more inclined to enroll in coverage.
The shift in enrollment patterns within different age groups necessitates tailored strategies to engage these groups. This includes targeted outreach and education initiatives that address specific concerns and needs.
Enrollment Rates by Gender
Gender differences in enrollment patterns also play a role. For instance, women may experience higher healthcare costs related to pregnancy and other conditions, potentially leading to higher enrollment rates compared to men. However, this is not a universal trend, and further investigation into the specific circumstances and experiences of various gender groups is crucial. The complex interplay of economic factors, cultural influences, and access to healthcare resources within each gender group needs to be considered.
Enrollment Disparities by Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status strongly correlates with healthcare enrollment decisions. Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may face greater barriers to accessing and affording coverage, potentially resulting in lower enrollment rates. Factors such as lack of employment, limited income, and lack of financial resources all contribute to this disparity. Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing financial assistance programs, simplified enrollment processes, and outreach to vulnerable populations.
Enrollment Rates by Race and Ethnicity
Race and ethnicity also influence enrollment decisions. Disparities in access to healthcare, cultural factors, and language barriers can contribute to differences in enrollment rates across racial and ethnic groups. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective outreach and the development of culturally sensitive solutions. Targeted campaigns tailored to specific racial and ethnic communities can increase participation and address the underlying causes of enrollment disparities.
Visualizing Enrollment Rates
| Age Group | Female Enrollment Rate (%) | Male Enrollment Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 18-25 | 45 | 38 |
| 26-35 | 52 | 45 |
| 36-45 | 68 | 62 |
| 46-55 | 78 | 73 |
| 56+ | 85 | 80 |
Note: The data in this table is illustrative and not based on actual enrollment data.
Alternatives to Obamacare
The declining enrollment in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has sparked renewed interest in alternative healthcare models. These models aim to address the ACA’s perceived shortcomings while maintaining access to care for those who need it. The current system, while expanding coverage, faces challenges related to affordability and access, prompting exploration of different approaches.The potential alternatives to Obamacare reflect the diverse opinions and needs within the healthcare landscape.
Some proposals prioritize market-based solutions, while others focus on greater government regulation and control. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each model is crucial to evaluating their potential impact on healthcare access and the overall economy.
Potential Alternative Healthcare Models
Several alternative models are being discussed as potential replacements or supplements to the ACA. These include, but are not limited to, various forms of public option plans, tax credits for private insurance, and a shift towards more robust and comprehensive single-payer systems. Each model presents a unique approach to healthcare delivery and financing.
Comparison of Alternative Models
The comparison of alternative healthcare models reveals a spectrum of approaches, each with distinct characteristics. For instance, a public option, akin to a government-run insurance program, could offer a more affordable alternative for many, potentially reducing premiums and increasing coverage. On the other hand, tax credits for private insurance aim to incentivize private market participation, but their effectiveness in broadening access and controlling costs is a matter of ongoing debate.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Alternative Models
Each alternative healthcare model presents its own set of strengths and weaknesses. A public option plan, for example, could offer greater affordability and control over costs, but may face challenges in efficiently managing a large-scale healthcare system. Conversely, private insurance, with its flexibility and market competition, might be more responsive to consumer needs, but could struggle to provide comprehensive coverage to those with pre-existing conditions or low incomes.
Impact on Healthcare Access
The potential impact on healthcare access varies significantly across the different alternative models. A robust public option could expand access by providing an affordable alternative to private insurance. However, the expansion of access might be limited if the alternative model relies heavily on consumer choice in a private insurance market. The success of any model hinges on factors like administrative efficiency, consumer awareness, and the ability to maintain a balance between affordability and quality of care.
Summary Table of Alternative Healthcare Systems
| Alternative Model | Funding Mechanism | Coverage Expansion Potential | Potential Cost Control Measures | Potential for Market Competition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Option | Government subsidies and premiums | High | Negotiated rates, price controls | Limited, but potential for competition with private plans |
| Tax Credits for Private Insurance | Government subsidies | Moderate | Competition among private insurers | High, market-driven |
| Single-Payer System | Government funding | Universal | Negotiated rates, centralized administration | None, except in competitive private markets |
Future Outlook
The declining enrollment in Obamacare exchanges paints a complex picture for the future of healthcare in the United States. While the short-term effects are readily apparent, understanding the long-term consequences requires careful consideration of various interconnected factors. This includes the potential impact on affordability, access, and the overall health of the healthcare system. Examining potential scenarios and monitoring enrollment trends is crucial for navigating this evolving landscape.
Long-Term Consequences of Declining Enrollment
Declining enrollment in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) exchanges could lead to a number of long-term consequences for the healthcare landscape. Reduced competition among insurers could result in higher premiums and limited choices for consumers, potentially impacting access to care. This reduction in competition could also lead to a decline in the quality of care offered. Furthermore, a smaller pool of insured individuals could lead to a higher risk of adverse selection, where insurers are forced to charge higher premiums to offset the risk of sicker individuals joining the plan.
Impact on Future Healthcare Affordability and Access
The long-term impact on affordability and access is deeply intertwined with the decline in enrollment. Without sufficient enrollment, the risk pools in the exchanges may become less stable, leading to higher premiums and reduced access to care. This instability could disproportionately affect low-income individuals and those with pre-existing conditions, potentially pushing them further into the uninsured ranks. Ultimately, this could lead to a two-tiered healthcare system, where access to affordable care is limited to a select group.
Importance of Monitoring Enrollment Trends
Monitoring enrollment trends is vital to understanding the health of the healthcare system. Consistent data collection allows for proactive measures to address potential issues. Early identification of problematic trends can facilitate the implementation of targeted interventions to maintain access and affordability. Understanding the factors driving enrollment fluctuations, such as economic conditions, public perception, and policy changes, can inform the development of effective strategies for the future.
Potential Scenarios for the Future of Healthcare
Several scenarios are possible, depending on the course of future events and policy decisions. One scenario involves a further erosion of the ACA exchanges, leading to a significant increase in the uninsured population and greater disparities in access to care. Conversely, proactive measures by policymakers and insurers, combined with increased consumer engagement, could stabilize the exchanges and ensure continued access to affordable coverage.
A more optimistic scenario envisions the evolution of a hybrid system, combining elements of the ACA exchanges with other coverage options. This scenario assumes that policy changes address the root causes of declining enrollment and that consumers embrace new options.
Projected Future Enrollment Rates
| Year | Scenario 1: Continued Decline | Scenario 2: Stabilization | Scenario 3: Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 10,000,000 | 12,000,000 | 14,000,000 |
| 2025 | 9,500,000 | 12,500,000 | 15,500,000 |
| 2026 | 9,000,000 | 13,000,000 | 17,000,000 |
| 2027 | 8,500,000 | 13,500,000 | 18,500,000 |
Note: These figures are projections based on various factors, including economic conditions, policy changes, and consumer behavior. They are illustrative examples and should not be considered definitive predictions.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the decline in Obamacare enrollment presents a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. From impacting healthcare access to influencing economic and political landscapes, understanding the various factors at play is critical. This analysis highlights the importance of addressing the underlying causes and exploring innovative solutions to ensure affordable and accessible healthcare for all Americans. The future of healthcare affordability and access hinges on our collective understanding and action regarding this critical trend.